Kidney Flat Mount Preparation: A Procedure to Dissect and Prepare a Flat Mount for Microscopic Analysis of Adult Zebrafish Kidney
Abstract
Source: McCampbell, K. K. et al. Analysis of Nephron Composition and Function in the Adult Zebrafish Kidney. J. Vis. Exp. (2014)
This video demonstrates the dissection and preparation of a flat mount of the adult zebrafish kidney. The prepared flat mount can be visualized under the microscope for specimen analysis.
Protocol
All procedures involving animal models have been reviewed by the local institutional animal care committee and the JoVE veterinary review board.
1. Dissection and Flat Mount Preparation of the Adult Zebrafish Kidney from an Unfixed Animal Sample to Visualize Fluorescent Dextran Labeling of the Proximal Tubule
- Euthanize the dextran-injected adult zebrafish by placing it into a dish with 0.2% Tricaine pH 7.0 for 4–5 min.
NOTE: Ensure that the fish has been euthanized before proceeding, by monitoring carefully whether the gills have ceased movement and the heart has stopped beating. - Using a plastic spoon, lift the fish from the Tricaine solution, decant the solution and place the animal on a tissue or paper towel.
- Use a sharp pair of dissection scissors to make a cut behind the gill operculum and remove the head.
- Immediately open the body of the fish with the dissection scissors by making a long ventral incision from the head to the base of the caudal fin.
- Remove the internal organs of the fish using a pair of fine forceps.
- Use super-fine dissection needles to pin open the body walls to allow visualization of the kidney organ, which is adherent to the dorsal wall of the animal.
- Use fine forceps to detach the kidney from the dorsal wall.
- Gently place the kidney into a 5 mL glass vial containing 1X PBS and wash 3 times with 3–5 mL of fresh 1X PBS for 5 min each.
NOTE: The use of a glass vial for handling of adult kidney samples facilitates visualization of the tissue and allows for washes with large volumes (relative to the tissue mass) of approximately 3–5 mL. Alternatively, a 12-well cell culture dish can be used. While a plastic microcentrifuge tube could be used, the standard sized tubes (1.5 mL) could restrict the washing. - Remove the kidney with a transfer pipette and place onto a clean glass slide with 1–2 drops of 1X PBS.
- Use fine forceps, flattened the kidney on the slide, making sure no tissue has curled or otherwise overturned on itself.
NOTE: Alternatively, a tungsten wire tool can be used to make small incisions in the connective tissue to facilitate flattened positioning of the kidney. - Place small pieces of modeling clay on each corner of an 18 x 18 mm glass coverslip and slowly set the coverslip onto the kidney.
NOTE: Slightly angle the coverslip during placement to minimize trapping air bubbles in the solution. The modeling clay divots are approximately 2 mm in diameter (Figure 1A). Alternatively, divots of vacuum grease can be substituted in lieu of modeling clay. Add an additional drop of 1X PBS to fill the space between the coverslip and glass slide if necessary. - Observe and/or image the kidney by placing the glass slide into the field of view on a stereomicroscope or compound microscope with the appropriate filter.
Representative Results
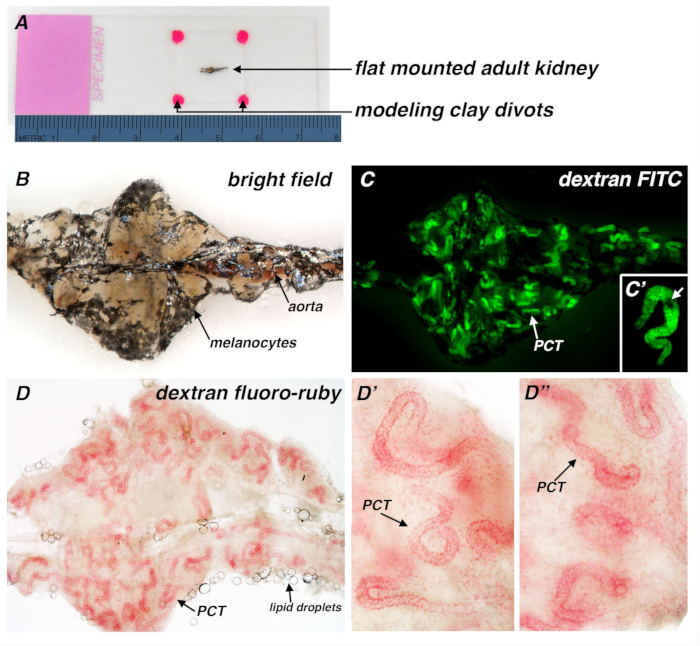
Figure 1. Adult zebrafish kidney flat mount preparation and application to visualize conjugated dextran uptake in the PCT segment of kidney nephrons. (A) Brightfield image of a kidney specimen flat mount preparation, in which the organ has been positioned flat on a glass slide, with a coverslip placed on top of the tissue that is resting on four divots of modeling clay (hot pink color). Here the renal preparation is imaged alongside a metric ruler to provide a scaled comparison. The typical adult kidney is approximately 5–7 millimeters (mm) from head to tail. (B) Brightfield image of an unbleached kidney. The black pigmentation corresponds to the scattered population of melanocytes found in association with the kidney, and the aorta runs along the midline of the kidney. (C) Visualization of nephron PCT segments 3 days following intraperitoneal injection of 40 kDa dextran-fluorescein (FITC), without bleaching of the adult kidney. PCT segments are seen throughout the kidney but are partly obscured due to the melanocytes. (C’) Digital zoom of a single nephron, with melanocytes (white arrow). (D) Image of an adult kidney 3 days following intraperitoneal injection of 10 kDa dextran fluoro-ruby, fixation of the kidney, and bleaching. The melanocyte pigmentation was removed and the PCT regions were visualized here based on their endocytic uptake of dextran under brightfield lighting. Lipid droplets (arrow) from the abdomen can sometimes be seen in association with renal tissue samples. (D’, D”) Representative images depict slight morphological variations between PCT segments. While many nephron PCTs are tightly coiled (D’), other nephrons contain PCT regions that have minimal coiling (D”).
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Materials
| 1X PBS | Made by diluting 10 X PBS in distilled water. | ||
| Fine Forceps | Roboz | RS-1050 | Dumont Tweezers Pattern #55 |
| Glass slide | Thermo-Fisher | 4445 | White Frost |
| Glass coverslip | Thermo-Fisher | 12-540A | 18 x 18 mm |
| Modeling clay | Hasbro | Playdoh | Other modeling clays can be substituted and work similarly. |
| Slide holder | Thermo-Fisher | 12-587 | Optional: cardboard tray to store slides flat. |
| Stereomicroscope | Nikon | SMZ645; SMZ1000; 83455 P-Blue GFP/DAPI; 83457 P-Endow GFP/ FITC; 83457 P-TRITC | Filter set used was as follows: Hoechst/DAPI filter was used for DAPI, propidium iodide, dextran-cascade blue and alkaline phosphatase detection. GFP/FITC filter was used for dextran-FITC, dextran lucifer yellow, and antiGFP detection. The TRITC filter was used for dextran-fluoro-ruby, PI, and DBA detection. |
| Compound microscope | Nikon | 96310 C-FL UV-2E/C DAPI; 96311 C-FL B-2E/C FITC; 96313 C-FL Y-2E/C Texas Red | Filter set used was as follows: Hoechst/DAPI filter was used for DAPI, propidium iodide, dextran-cascade blue and alkaline phosphatase detection. GFP/FITC filter was used for dextran-FITC, dextran lucifer yellow, and antiGFP detection. The Texas Red filter was used for dextran-fluoro-ruby, PI, and DBA detection. |

