White and Brown Adipose Depot Collection from Mouse Pup: A Surgical Procedure to Harvest the White Adipose Tissue and Brown Adipose Tissue from Mouse Pup
Abstract
Source: Galmozzi, A. et al. Isolation and Differentiation of Primary White and Brown Preadipocytes from Newborn Mice. J. Vis. Exp. (2021)
In this video, we demonstrate the surgical procedure to isolate the subcutaneous white adipose tissue and interscapular brown adipose tissue from a newborn mouse.
Protocol
All procedures involving animal models have been reviewed by the local institutional animal care committee and the JoVE veterinary review board.
1. Collection and digestion of adipose depots (day 1)
- Prepare two 1.5 mL tubes for each pup: one for brown adipose tissue (BAT) and one for white adipose tissue (WAT). Add 250 µL of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) + 200 µL of 2x isolation buffer (123 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 1.3 mM CaCl2, 5 mM glucose, 100 mM 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid (HEPES), penicillin-streptomycin, and 4% fatty acid-free bovine serum albumin) to each tube. Keep solutions sterile and on ice.
- Place the pups into small chambers (e.g., one well of a 6-well plate), and set them on ice until they become hypothermic. Make sure that there is no direct contact between the pups and the ice. Prick a paw with a tip to assure loss of consciousness and euthanize the pups by decapitation using sharp scissors.
NOTE: if working with different genotypes, prepare an additional tube to collect a tail biopsy (3 mm cut) for genotyping. If genotyping is performed immediately, keep the euthanized pups on ice until the dissection to collect adipose depots. - Calculate and weigh out the amount of collagenase needed to digest all the depots. Add 50 µL of 15 mg/mL collagenase type I in 2x isolation buffer to each tube. Do not resuspend the collagenase in isolation buffer until all the tissues have been collected.
- To collect subcutaneous WAT, cut the skin around the pup's abdomen (avoid peritoneal rupture), and gently pull the skin down below the legs. Without taking the skin, carefully collect the fat depot, which will appear as a clear (P1 or younger) or white (P2 and older), thin, elongated tissue attached on the inside or on top of the quadriceps (Figure 1A, B). Rinse the fat depot in PBS and place it in one of the tubes containing 250 µL of PBS + 200 µL of 2x isolation buffer. Keep on ice.
NOTE: P0 and P1 mice give the best yield. In P0-1 pups, the subcutaneous WAT depot is nearly transparent. In P2 mice and older, the depot is easier to identify because it is already turning white, indicating the presence of fully mature, lipid-loaded, white adipocytes. - To collect interscapular BAT, pull the skin from the shoulder blades over the head. Lift the BAT – the deep red tissue between the shoulder blades – and carefully make incisions all around it to detach it from the body (Figure 1A, B). Check for consistency and color; rinse with PBS; place it in the other tube containing 250 µL of PBS + 200 µL of 2x isolation buffer; and keep on ice.
NOTE: When harvesting BAT from P2 mice and older, carefully remove the white adipose tissue surrounding the BAT. It consists of a thin, soft, white sheet of adipocytes located between the skin and the BAT, which is deeper between the shoulder blades.
Representative Results
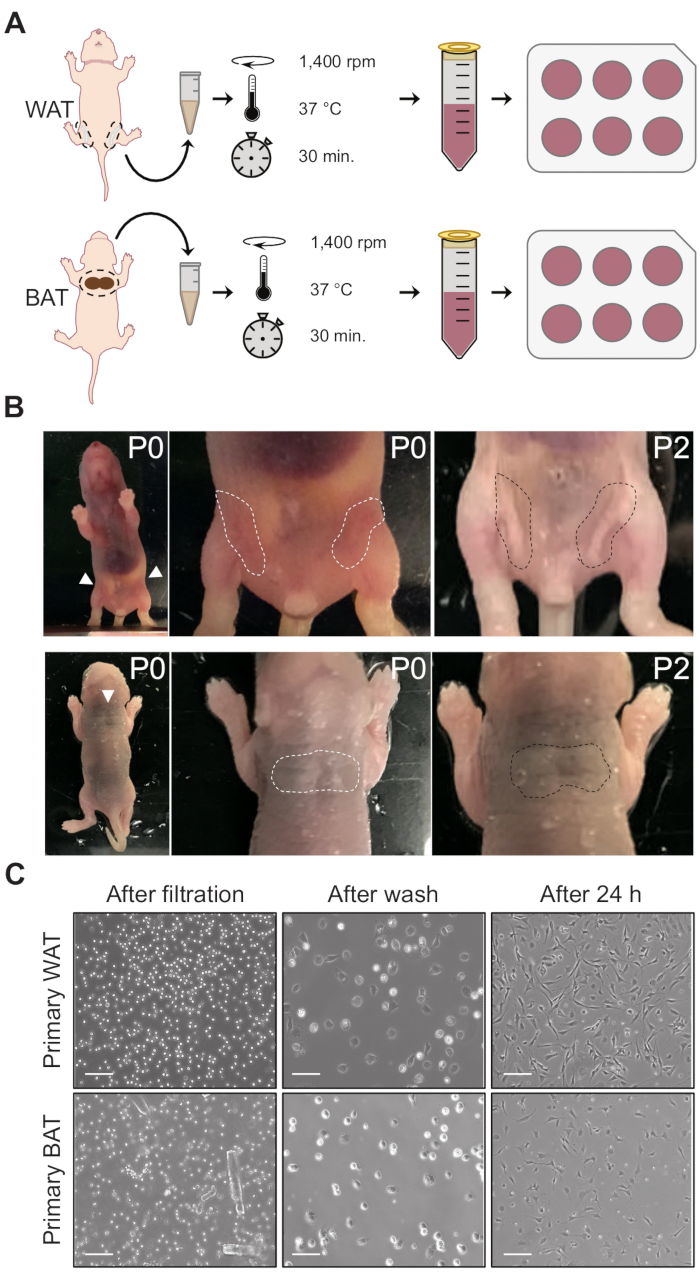
Figure 1: Collection and processing of fat pads. (A) Schematic representation of primary white (top) and brown (bottom) adipocyte isolation. (B) Subcutaneous white (top) and brown (bottom) adipose depots. In P0 mice, subcutaneous WAT is almost invisible, but becomes distinguishable on ~day 2 after birth. In contrast, BAT has a distinct dark color even at P0. In older pups, the BAT is surrounded by a thin superficial layer of WAT, which requires removal when the tissue is dissected. (C) Representative images of primary white and brown precursor cells after filtration through the 100 µm cell strainer, after the initial washes, and 24 h after isolation. Scale bars = 100 µm. Abbreviations: WAT = white adipose tissue; BAT = brown adipose tissue.
Offenlegungen
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Materials
| 6-well plates | Corning | 353046 | |
| Fatty Acid-Free BSA | Sigma-Aldrich | A8806 | |
| CaCl2 | Sigma-Aldrich | C4901 | |
| Glucose | Sigma-Aldrich | G7021 | |
| HEPES | Sigma-Aldrich | H3375 | |
| KCl | Sigma-Aldrich | P9333 | |
| NaCl | Sigma-Aldrich | S7653 | |
| Pen/Strep | Gibco | 15140122 | |
| Surgical forceps | ROBOZ Surgical Instrument Co | RS-5158 | |
| Surgical Scissors | ROBOZ Surgical Instrument Co | RS-5880 | |
| DPBS, no calcium, no magnesium | Gibco | 14190144 |

