15.8:
Zwakke Basen
15.8:
Zwakke Basen
Some compounds produce hydroxide ions when dissolved by chemically reacting with water molecules. In all cases, these compounds react only partially and so are classified as weak bases. These types of compounds are also abundant in nature and important commodities in various technologies. For example, global production of the weak base ammonia is typically well over 100 metric tons annually, being widely used as an agricultural fertilizer, a raw material for chemical synthesis of other compounds, and an active ingredient in household cleaners. When dissolved in water, ammonia reacts partially to yield hydroxide ions, as shown here:
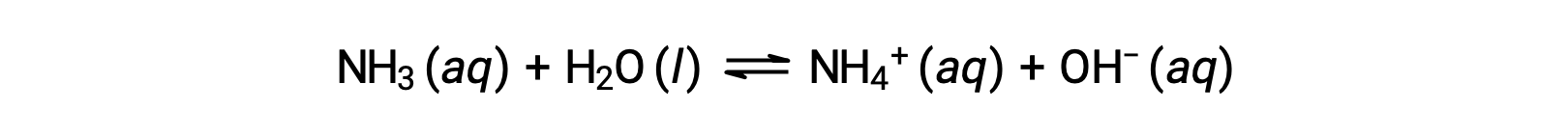
This is, by definition, an acid-base reaction, in this case involving the transfer of H+ ions from water molecules to ammonia molecules. Under typical conditions, only about 1% of the dissolved ammonia is present as NH4+ ions.
Calculating Hydroxide Ion Concentrations and pOH in a Weak Base Solution
Find the concentration of hydroxide ion, the pOH, and the pH of a 0.25 M solution of trimethylamine, a weak base:
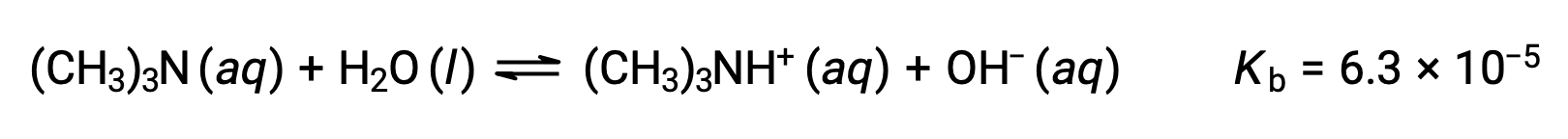
The ICE table for this system is
| (CH3)3N (aq) | (CH3)3NH+ (aq) | OH− (aq) | |
| Initial Concentration (M) | 0.25 | 0 | ~0 |
| Change (M) | −x | +x | +x |
| Equilibrium Concentration (M) | 0.25 − x | 0 + x | ~0 + x |
Substituting the equilibrium concentration terms into the Kb expression gives
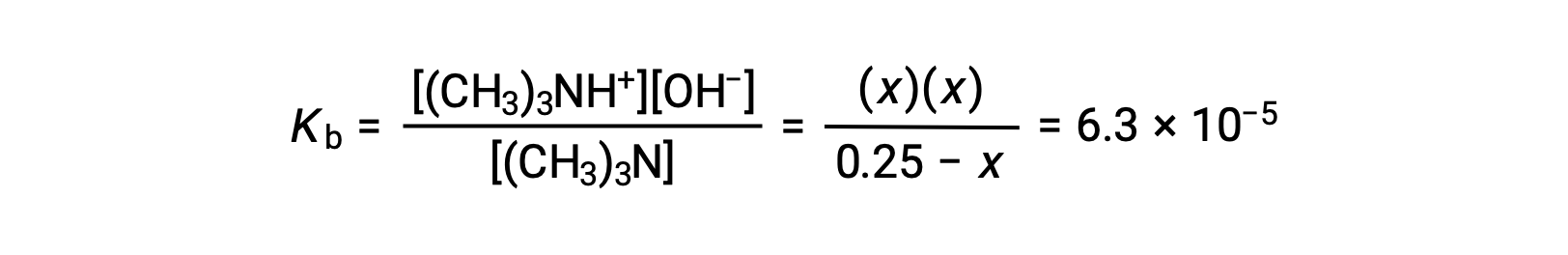
Assuming x << 0.25 and solving for x yields
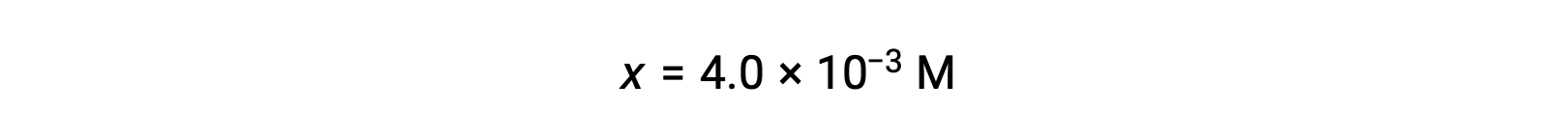
This value is less than 5% of the initial concentration (0.25), so the assumption is justified.
As defined in the ICE table, x is equal to the equilibrium concentration of hydroxide ion:
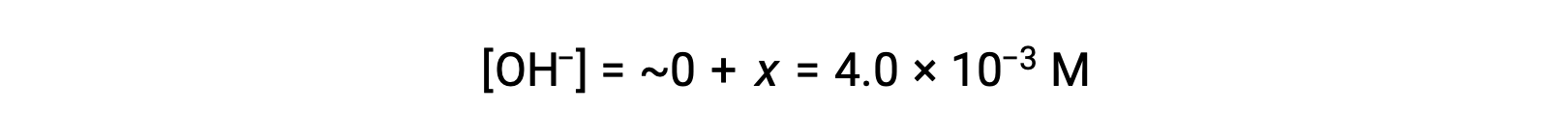
The pOH is calculated to be
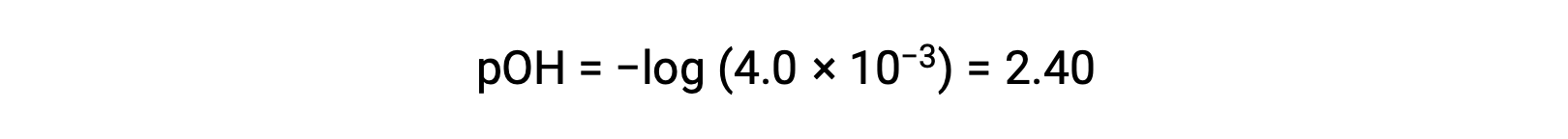
Using the relation;
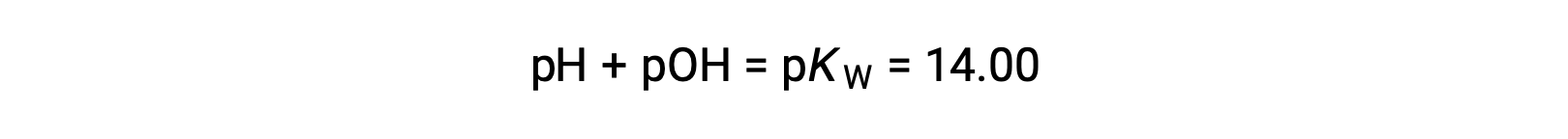
permits the computation of pH:
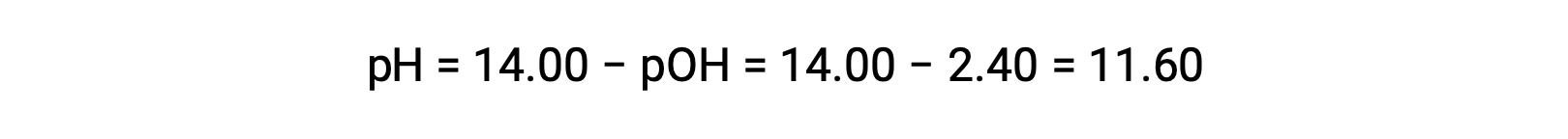
Determination of Kb from pH
If the pH of 0.28 M solution of ethylamine (C2H5NH2) is 12.10, what is its Kb?
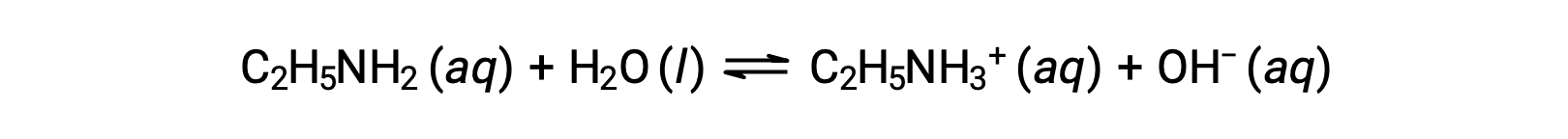
To calculate the Kb of ethylamine, first the pOH and the hydroxide ion concentration need to be determined. As the pH is 12.10, the pOH can be calculated as follows:
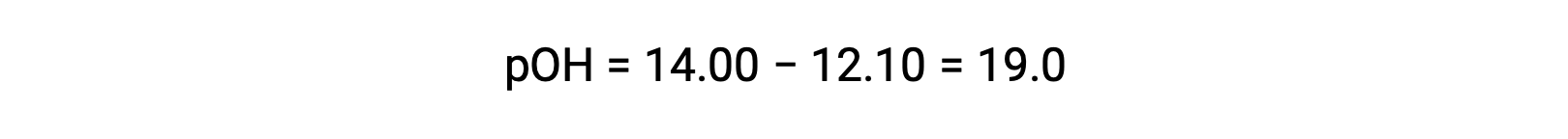
As the pOH is 1.90, the hydroxide ion concentration of the solution can be calculated using the formula
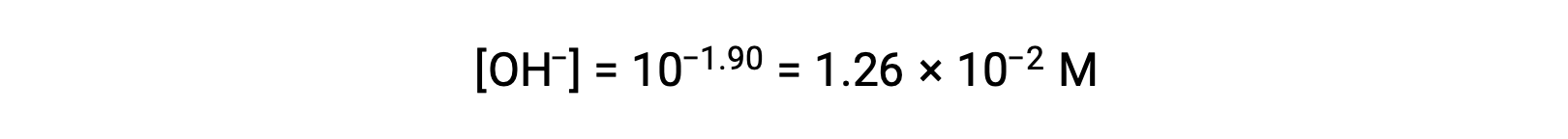
The ICE table can be constructed for this system as follows
| C2H5NH2 (aq) | C2H5NH3+ (aq) | OH− (aq) | |
| Initial Concentration (M) | 0.28 | 0 | ~0 |
| Change (M) | −0.0126 | +0.0126 | +0.0126 |
| Equilibrium Concentration (M) | 0.28 − 0.0126 | 0.0126 | 0.0126 |
As the 0.0126 M is 4.5% of 0.28 M, 0.28 − 0.0126 can be considered as almost equal to 0.28 M by the 5% rule.
After substituting the above values in the expression for the Kb of ethylamine,
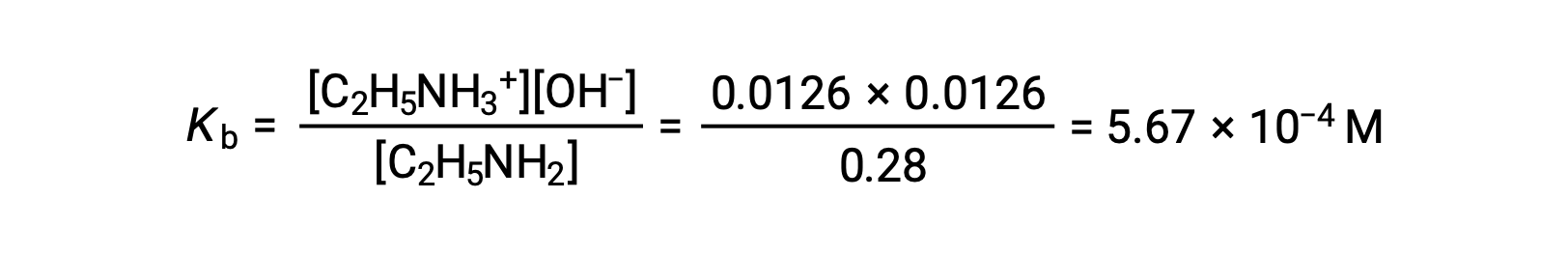
This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e Section 4.2: Classifying Chemical Reactions and 14.3 Relative Strengths of Acids and Bases.
