細胞外小胞の定量とサイズ決定のためのナノ粒子追跡解析
Summary
我々は、新しいナノ粒子追跡解析装置を用いて、マウスの骨膜脂肪組織およびヒト血漿から分離された細胞外小胞のサイズ分布および総粒子濃度を推定する方法を示す。
Abstract
細胞外小胞(EV)の生理学的および病的な役割はますます認識され、EV分野は急速に進化する研究分野となっています。EVの分離には多くの異なる方法があり、それぞれ、EVの下流の収率と純度に影響を与える明確な長所と短所があります。したがって、選択した方法によって所定のソースから分離されたEV準備を特徴付けることは、下流の結果の解釈および実験室間での結果の比較にとって重要である。病気の状態や外部の状態に応じて変化させることができるEVのサイズと量を決定するための様々な方法が存在します。ナノ粒子追跡解析(NTA)は、個々のEVのハイスループット分析に使用される顕著な技術の1つです。ここでは、この分野における大きな進歩を代表するNTAの画期的な技術を用いて、マウスの脂肪組織およびヒト血漿から分離されたEVの定量とサイズ決定のための詳細なプロトコルを提示する。この方法は、透過電子顕微鏡で確認された異なる方法で異なるソースから分離されたEVに対して、再現可能で有効な総粒子濃度およびサイズ分布データを提供できることを実証した。このNTA機器の適応は、EV研究における厳格化と再現性を高めるためのNTA手法における標準化の必要性に対応する。
Introduction
細胞外小胞(EV)は、ほぼ全ての細胞タイプ1によって分泌される小さな(0.03〜2 μm)膜結合小胞である。放出のメカニズムとサイズ2に応じて、「エキソソーム」、「微小胞」、「アポトーシス体」と呼ばれることがよくあります。当初は、EVは単に細胞から廃棄物を除去して恒常性3を維持する手段であると考えられていたが、DNA、RNA(mRNA、マイクロRNA)、脂質、タンパク質4、5を含む分子物質の伝達を介した細胞間コミュニケーションにも参加することができ、正常な生理学の重要な調節因子であり、病理学的プロセス1である。 5、6、7、8.
EV を分離および定量化する方法は多数ありますが、これは他の場所で説明されている 9 、 10、11、12です。EVの供給源と同様に使用される絶縁プロトコルは、EVの歩留まりと純度に大きな影響を与える可能性があります。微分遠心分離でさえ、長い間エキソソーム単離のための「ゴールドスタンダード」アプローチと考えられ、その後得られたEV集団および下流分析13に影響を与える大きな変動を受けうる。したがって、EVの分離および定量化のための様々な異なる方法論は、文献14で報告された実験の結果を比較、再現、および解釈することを困難にする。さらに、EV放出は、細胞状態または種々の外的要因によって調節することができる。細胞内ストレス15から細胞を保護することによって細胞恒常性を維持する役割を果たすEVが示唆されている。例えば、低酸素、小胞体ストレス、酸化ストレス、機械的ストレス、タバコの煙抽出物、および粒子状物質の大気汚染16、17、18、19、20、21、22への細胞暴露後にEV放出の増加が報告されている。EV放出はまた、生体内で変更することが示されている;高脂肪食や断食を16時間受けたマウスは、より多くの脂肪細胞EV23を放出した。特定の治療や状態がEV放出を変えるかどうかを調べるには、EVの数を正確に特定する必要があります。EVサイズ分布の評価はまた、EVの主要な細胞内起源(例えば、後期子宮体/多面体と原形質膜の芽出との融合)24を示す。したがって、研究されているEV準備の総濃度とサイズ分布を正確に測定するための堅牢な方法が必要です。
ソリューションにおけるEVの可視化と特性評価のための迅速かつ高感度な方法は、ナノ粒子追跡解析(NTA)です。この方法の原理の詳細な説明とEVサイズと濃度の評価のための代替方法との比較は、前に説明された25、26、27、28。簡単に言えば、NTA測定中に、EVはレーザー光を照射したときに散乱する光によって視覚化されます。散乱光は、粒子の動きを記録するカメラに顕微鏡で焦点を当てます。NTA ソフトウェアは、各パーティクルのランダムな熱運動を追跡し、ストークス-アインシュタイン方程式を使用して各粒子のサイズを計算するために使用される拡散係数を決定します。NTAは201125年に初めて生体試料中のEV測定に適用された。最近まで、商用NTA機器29を提供する主流企業は、他のNTA技術の大幅な制限を克服するために新しいハードウェアとソフトウェアソリューションの組み合わせを使用するViewSizer 3000(以下、粒子追跡機器と呼ばれる)の導入までしかありませんでした。
粒子追跡装置はブラウン運動を分析することによって液体サンプル中のナノ粒子を特徴付け、重力沈降を分析することによってより大きいミクロンサイズの粒子を特徴付ける。この装置独自の光学系は、3つのレーザー光源(450 nm、520 nm、635 nm)を備えたマルチスペクトル照明を含み、研究者は幅広い粒子サイズ(例えば、エキソソーム、マイクロベシクル)を同時に分析することを可能にします。機器のセットアップの概略を図 1に示します。
ここでは、新しいNTA機器を用いて、単離したマウスやヒトEVの粒子径分布と濃度測定を行う方法を示す。
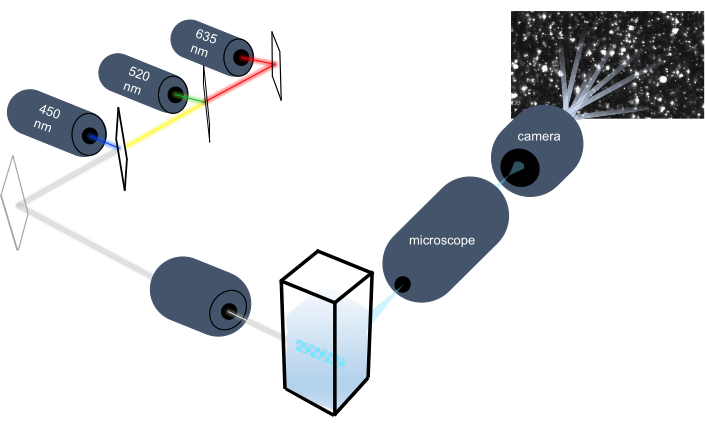
図1:粒子追跡計光学系 NTAの器械は次の波長の3つのレーザーを使用して粒子を照らす:450 nm、520 nm、635 nm。個々の粒子からの散乱光のビデオ録画は、キュベットから90°指向のデジタルビデオカメラによって検出され、追跡されます。 この図の大きなバージョンを表示するには、ここをクリックしてください。
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
ここでは、幅広い粒子サイズのサイズ分布を同時に測定し、多分散サンプル中の全EV濃度を測定するためのプロトコルを示す。本研究では、マウスのペリゴナリ脂肪組織およびヒト血漿をEVの供給源として使用した。しかし、血清、尿、唾液、母乳、羊水、細胞培養上清などの他の組織または生物学的液体から隔離されたEVもNTAに使用され得る。ポリスチレンビーズ規格の測定により、装置が?…
Divulgations
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
この研究は、国立衛生研究所(ES030973-01A1、R01ES025225、R01DK066525、P30DK026687、P30DK063608)によってサポートされました。私たちは、HORIBAインスツルメンツ株式会社のジェフリー・ボディコム博士が楽器の校正を支援した場合に認めます。
Materials
| 1X dPBS | VWR | 02-0119-1000 | To dilute samples |
| 100 nm bead standard | Thermo Scientific | 3100A | To test ViewSizer 3000 calibration |
| 400 nm bead standard | Thermo Scientific | 3400A | To test ViewSizer 3000 calibration |
| Centrifugal Filter Unit | Amicon | UFC901024 | To filter PBS diluent |
| Collection tubes, 2 mL | Qiagen | 19201 | For isolation of human plasma extracellular vesicles |
| Compressed air duster | DustOff | DPSJB-12 | To clean cuvettes |
| Cuvette insert | HORIBA Scientific | – | Provided with purchase of ViewSizer 3000 |
| Cuvette jig | HORIBA Scientific | – | To align magnetic stir bar while placing inserts inside cuvette; Provided with purchase of ViewSizer 3000 |
| De-ionized water | VWR | 02-0201-1000 | To clean cuvettes |
| Desktop computer with monitor, keyboard, mouse, and all necessary cables | Dell | – | Provided with purchase of ViewSizer 3000 |
| Ethanol (70-100%) | Millipore Sigma | – | To clean cuvettes |
| ExoQuick ULTRA | System Biosciences | EQULTRA-20A-1 | For isolation of human plasma extracellular vesicles |
| Glass scintillation vials with lids | Thermo Scientific | B780020 | To clean cuvettes |
| "Hook" tool | Excelta | – | Provided with purchase of ViewSizer 3000 |
| Lint-free microfiber cloth | Texwipe | TX629 | To clean cuvettes and cover work surface |
| Microcentrifuge tubes, 2 mL | Eppendorf | 22363344 | For isolation of human plasma extracellular vesicles |
| Stir bar | Sp Scienceware | F37119-0005 | |
| Suprasil Quartz cuvette with cap | Agilent Technologies | AG1000-0544 | Initially provided with purchase of ViewSizer 3000 |
| ViewSizer 3000 | HORIBA Scientific | – | Nanoparticle tracking instrument |
References
- Colombo, M., Raposo, G., Théry, C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology. 30, 255-289 (2014).
- Hessvik, N. P., Llorente, A. Current knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cellular and molecular life sciences: CMLS. 75, 193-208 (2018).
- Johnstone, R. M., Adam, M., Hammond, J. R., Orr, L., Turbide, C. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 262, 9412-9420 (1987).
- Théry, C., Ostrowski, M., Segura, E. Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nature Reviews Immunology. 9, 581-593 (2009).
- Yáñez-Mó, M., et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. 4, 27066 (2015).
- Lo Cicero, A., Stahl, A., Raposo, G. Extracellular vesicles shuffling intercellular messages: for good or for bad. Current Opinion in Cell Biology. 35, 69-77 (2015).
- Raposo, G., Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. The Journal of Cell Biology. 200, 373-383 (2013).
- Mathivanan, S., Ji, H., Simpson, R. J. Exosomes: extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. Journal of Proteomics. 73, 1907-1920 (2010).
- Zhang, M., et al. Methods and technologies for exosome isolation and characterization. Small Methods. 2, 1800021 (2018).
- Szatanek, R., et al. The methods of choice for extracellular vesicles (EVs) characterization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 18, (2017).
- Erdbrügger, U., Lannigan, J. Analytical challenges of extracellular vesicle detection: A comparison of different techniques. Cytometry. Part A: The Journal of the International Society for Analytical Cytology. 89, 123-134 (2016).
- Konoshenko, M. Y., Lekchnov, E. A., Vlassov, A. V., Laktionov, P. P. Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles: General Methodologies and Latest Trends. BioMed Research International. 2018, 1-27 (2018).
- Cvjetkovic, A., Lötvall, J., Lässer, C. The influence of rotor type and centrifugation time on the yield and purity of extracellular vesicles. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. 3, (2014).
- Taylor, D. D., Shah, S. Methods of isolating extracellular vesicles impact down-stream analyses of their cargoes. Methods. 87, 3-10 (2015).
- Desdín-Micó, G., Mittelbrunn, M. Role of exosomes in the protection of cellular homeostasis. Cell Adhesion & Migration. 11, 127-134 (2017).
- Kanemoto, S., et al. Multivesicular body formation enhancement and exosome release during endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 480, 166-172 (2016).
- Benedikter, B. J., et al. Cigarette smoke extract induced exosome release is mediated by depletion of exofacial thiols and can be inhibited by thiol-antioxidants. Free Radical Biology & Medicine. 108, 334-344 (2017).
- Saeed-Zidane, M., et al. Cellular and exosome mediated molecular defense mechanism in bovine granulosa cells exposed to oxidative stress. PloS One. 12, 0187569 (2017).
- Wang, K., et al. Mechanical stress-dependent autophagy component release via extracellular nanovesicles in tumor cells. ACS Nano. 13, 4589-4602 (2019).
- King, H. W., Michael, M. Z., Gleadle, J. M. Hypoxic enhancement of exosome release by breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 12, 421 (2012).
- Bonzini, M., et al. Short-term particulate matter exposure induces extracellular vesicle release in overweight subjects. Environment Research. 155, 228-234 (2017).
- Neri, T., et al. Particulate matter induces prothrombotic microparticle shedding by human mononuclear and endothelial cells. Toxicology In Vitro. 32, 333-338 (2016).
- Flaherty, S. E., et al. A lipase-independent pathway of lipid release and immune modulation by adipocytes. Science. 363, 989-993 (2019).
- van Niel, G., D’Angelo, G., Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology. 19, 213-228 (2018).
- Dragovic, R. A., et al. Sizing and phenotyping of cellular vesicles using Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology, and Medicine. 7, 780-788 (2011).
- Saveyn, H., et al. Accurate particle size distribution determination by nanoparticle tracking analysis based on 2-D Brownian dynamics simulation. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science. 352, 593-600 (2010).
- Vander Meeren, P., Kasinos, M., Saveyn, H. Relevance of two-dimensional Brownian motion dynamics in applying nanoparticle tracking analysis. Methods in Molecular Biology. , 525-534 (2012).
- Filipe, V., Hawe, A., Jiskoot, W. Critical evaluation of Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) by NanoSight for the measurement of nanoparticles and protein aggregates. Pharmaceutical Research. 27, 796-810 (2010).
- Bachurski, D., et al. Extracellular vesicle measurements with nanoparticle tracking analysis – An accuracy and repeatability comparison between NanoSight NS300 and ZetaView. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. 8, 1596016 (2019).
- Varga, Z., et al. Hollow organosilica beads as reference particles for optical detection of extracellular vesicles. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 16, 1646-1655 (2018).
- Serrano-Pertierra, E., et al. Extracellular vesicles: Current analytical techniques for detection and quantification. Biomolecules. 10, (2020).
- Maguire, C. M., Rösslein, M., Wick, P., Prina-Mello, A. Characterisation of particles in solution – a perspective on light scattering and comparative technologies. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials. 19, 732-745 (2018).
- Bohren, C. F., Huffman, D. R. . Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles. , (1983).

