הסינתזה של RGD פונקציונלית הידרוג ככלי יישומים טיפוליים
Summary
We present a protocol for the synthesis of RGD-functionalized hydrogels as devices for cell and drug delivery. The procedure involves copper catalyzed alkyne-azide cycloaddition (CuAAC) between alkyne-modified polyacrylic acid (PAA) and a RGD-azide derivative. The hydrogels are formed using microwave-assisted polycondensation and their physicochemical properties are investigated.
Abstract
The use of polymers as biomaterials has provided significant advantages in therapeutic applications. In particular, the possibility to modify and functionalize polymer chains with compounds that are able to improve biocompatibility, mechanical properties, or cell viability allows the design of novel materials to meet new challenges in the biomedical field. With the polymer functionalization strategies, click chemistry is a powerful tool to improve cell-compatibility and drug delivery properties of polymeric devices. Similarly, the fundamental need of biomedicine to use sterile tools to avoid potential adverse-side effects, such as toxicity or contamination of the biological environment, gives rise to increasing interest in the microwave-assisted strategy.
The combination of click chemistry and the microwave-assisted method is suitable to produce biocompatible hydrogels with desired functionalities and improved performances in biomedical applications. This work aims to synthesize RGD-functionalized hydrogels. RGD (arginylglycylaspartic acid) is a tripeptide that can mimic cell adhesion proteins and bind to cell-surface receptors, creating a hospitable microenvironment for cells within the 3D polymeric network of the hydrogels. RGD functionalization occurs through Huisgen 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition. Some PAA carboxyl groups are modified with an alkyne moiety, whereas RGD is functionalized with azido acid as the terminal residue of the peptide sequence. Finally, both products are used in a copper catalyzed click reaction to permanently link the peptide to PAA. This modified polymer is used with carbomer, agarose and polyethylene glycol (PEG) to synthesize a hydrogel matrix. The 3D structure is formed due to an esterification reaction involving carboxyl groups from PAA and carbomer and hydroxyl groups from agarose and PEG through microwave-assisted polycondensation. The efficiency of the gelation mechanism ensures a high degree of RGD functionalization. In addition, the procedure to load therapeutic compounds or biological tools within this functionalized network is very simple and reproducible.
Introduction
הידרוג הן רשתות תלת מימדי נוצר על ידי פולימרים צולבים הידרופילי, אשר הם טבעיים או סינתטיים, ואת המאופיינת במבנה תלת מימדי ייחודי. מכשירים אלו אטרקטיביים יותר ויותר בתחומי הביו-הרפואיים של אספקת סמים, הנדסת רקמות, נושאות גנים 1,2 חיישנים חכמים. אכן, תכולת המים הגבוהה שלהם, כמו גם המאפיינים rheological המכאניים שלהם להפוך אותם מועמדים מתאימים לחקות microenvironments רקמות רך ולגרום להם כלים יעילים ציטוקינים מסיסים במים או מסירת גורם גדילה. אחד לשימוש המבטיח ביותר הוא בתור ביולוגי בזריקות נושאת תאי תרכובות ביו. הידרוג עשוי לשפר הישרדות תא ואת גורלו תאי גזע מלא על ידי החזקה ודווקא מתן אותות רגולטוריות תאי גזע באופן רלוונטי פיסיולוגי, כפי שנצפה במבחנה בניסויי vivo 3,4. היתרון המוביל של זה הוא האפשרותכדי לשמור על תאים מוזרקים בתוך האזור של חיסון (in situ), הפחתת כמות התאים שמשאירה את שטח extravasates לתוך מבול הדם, נודד בכל רחבי הגוף ואיבוד יעד המטרה 5. היציבות של רשתות הידרוג'ל תלת ממדי נובעת מאתרי cross-linking שלה, שהוקמו על ידי קשרים קוולנטיים או כוחות משיכה בין שרשרות הפולימר 6.
במסגרת זו, כימיה סלקטיבית מאונכת להחיל שרשרות פולימר הוא כלי תכליתי מסוגל לשפר את הביצועים הידרוג'ל 7. ואכן, השינוי של פולימרים עם קבוצות כימיות מתאימות יכול לעזור לספק כימי מתאים, פיזי תכונות מכאניות לשפר כדאיויות תא והשימוש בם היווצרות רקמה. באותו אופן, בין הטכניקות לטעון תאים או גורמי גדילה בתוך מטריצת ג'ל, השימוש של פפטיד RGD מאפשר שיפורי הידבקות תא והישרדות. RGD הוא tripeptide מורכבשל ארגינין, גליצין וחומצה אספרטית, שהוא בלי ספק היעיל ביותר, ולעתים קרובות מועסקי tripeptide בשל יכולתה לטפל יותר קולטן הידבקות תא אחד וההשפעה הביולוגית שלה על עיגון תא, התנהגות והישרדות 8,9. בעבודה זו, הסינתזה של הידרוג הפונקציונלית RGD נלמדת במטרה בעיצוב הרשתות מאופיינות תכונות הביוכימיות מספיק עבור microenvironment תא מסבירי פנים.
שימוש קרינת מיקרוגל בסינתזה הידרוג'ל מציע הליך פשוט כדי למזער תגובות לוואי ולקבל שיעורי תגובה גבוהים ותשואות בתוך פרק זמן קצר יותר לעומת התהליכים התרמיים הקונבנציונליים 10. שיטה זו אינה דורשת צעדים טיהור והתשואות הידרוג'ל סטרילית בשל אינטראקציות של פולימרים והיעדר ממיס אורגני במערכת התגובה 11. לכן, היא מבטיחה באחוזים גבוהים של RGD צמוד רשת הפולימרים כי אף modifications נדרש הקבוצות הכימיות פולימר המעורבים ביצירת ג'ל. קבוצות carboxyl, מן PAA ו carbomer, וקבוצות הידרוקסיל, מ PEG ו agarose, להצמיח את המבנה התלת-ממדי הידרוג'ל באמצעות תגובה polycondensation. הפולימרים ציינו משמשים לסינתזה של הידרוג בטיפולים תיקון פגיעה בחוט השדרה 12. התקנים אלה, כפי שדווח קודם עובד 13,14, להראות התאמה ביולוגית גבוהה, כמו גם תכונות מכניות physicochemical הדומים לאלו של רקמות חיות רבות בטבע thixotropic. יתר על כן, הם נשארים מקומי באתרו, על אזור ההזרקה.
בעבודה זו, קבוצות carboxyl PAA הם שונים עם מחצית אלקין (איור 1), וכן תרכובת RGD-יזיד הוא מסונתזת ניצול תגובתיות של קבוצת מסוף tripeptide -NH 2 עם תרכובת כימית מוכנה עם מבנה (CH 2) n – N 3 (<strong> איור 2). כתוצאה מכך, PAA השונה מגיב עם נגזר RGD-יזיד הקלקה CuAAC התגובה 15-17 (איור 3). שימוש זרז נחושת (I) מוביל לשיפורים משמעותיים בשני קצב התגובה ואת רגיוסלקטיביות. התגובה CuAAC נעשה שימוש נרחב סינתזה אורגנית ב מדע הפולימרים. הוא משלב יעילות גבוהה וסובלנות גבוהה הקבוצות הפונקציונליות, וזה מושפע שימוש בממסים אורגניים. סלקטיביות גבוהה, זמן תגובה מהיר הליך טיהור פשוט לאפשר הקניית פולימרי כוכב, קופולימרים לחסום או שרשרות השתלת moieties רצוי 18. האסטרטגיה לחץ זה מאפשר לשנות פולימרים לאחר פילמור להתאים אישית את מאפייני physicochemical בהתאם ליישום ביוכימיים הסופי. תנאי ניסוי CuAAC הם לשחזור בקלות (התגובה היא לא רגישה למים, ואילו חמצון נחושת עלול להתרחש מינימאלי), והמהותtriazole נוצר מבטיח יציבות של המוצר. השימוש מתכת נחושת יכול להיחשב נקודה קריטית, עקב השפעה רעילה הפוטנציאל שלה נגד תאים והן במיקרו-סביבה ביולוגית, אבל דיאליזה משמש כשיטה טיהור כדי לאפשר פינוי מוחלט של שאריות קטליטי. לבסוף, PAA שונה RGD משמש סינתזה הידרוג'ל (איור 4) ואת מאפייני physicochemical של רשתות וכתוצאה נחקרות, על מנת לבדוק את הפונקציונליות הפוטנציאל של מערכות אלה כנשאים תאים או סמים.
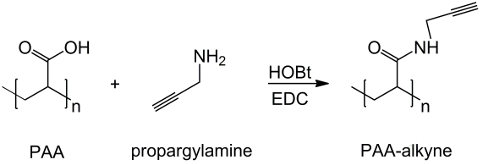
איור 1: PAA שונה סינתזה אלקין סכימה של functionalization PAA עם קבוצת אלקין;. "n" מציין את מונומרים עם קבוצת carboxyl מגיבים עם propargylamine. אנא לחץ כאן לצפייהגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.
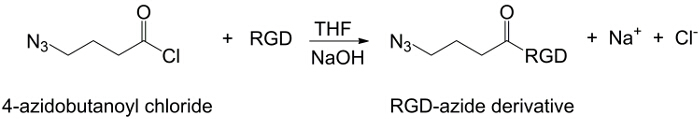
איור 2:.. סינתזה-יזיד RGD הסינתזה של נגזרי RGD-יזידו אנא לחץ כאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.
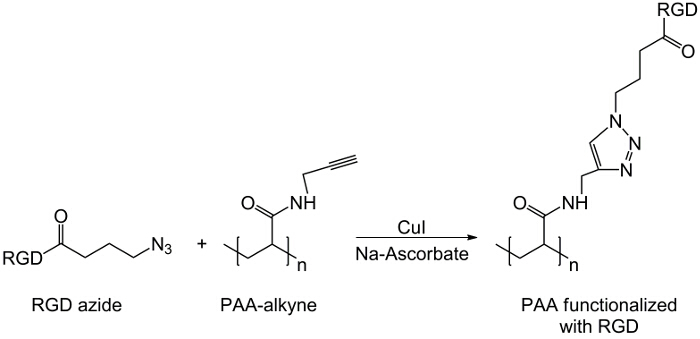
איור 3: לחץ תגובת תכנית תגובה קליק בין נגזרת RGD-יזיד ו-PAA אלקין.. אנא לחץ כאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.
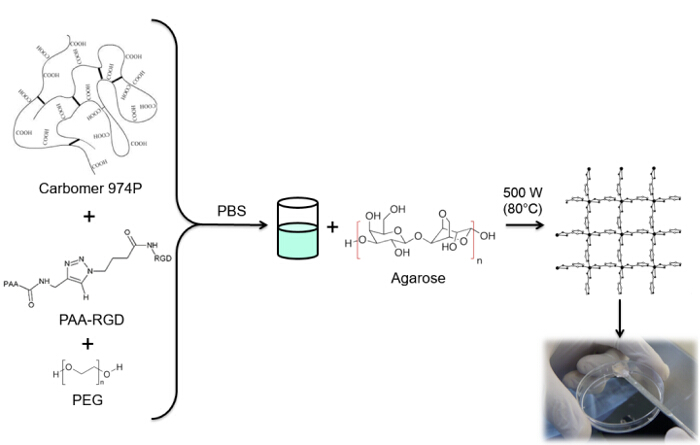
איור 4: הידרוג'ל synthesis. הליך סינתזת הידרוג'ל פונקציונלי RGD. אנא לחץ כאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
The PAA post-polymerization modification with alkyne moieties and the RGD functionalization with the azide group guarantee the formation of a stable bond between the polymer and the peptide. Indeed, triazole serves as a rigid linking unit among the carbon atoms, attached to the 1,4 positions of the 1,2,3-triazole ring and it cannot be cleaved hydrolytically or otherwise. In addition, triazole is extremely difficult to oxidize and reduce, unlike other cyclic structures such as benzenoids and related aromatic heterocycles<…
Divulgazioni
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
המחברים מבקשים להודות פרופ 'מאוריציו Masi לדיון פורה מיס קיארה Allegretti לעריכה השפה. מחקר 'מחברים נתמך על ידי Bando Giovani Ricercatori 2010 (Ministero דלה הצדעה GR-2010- 2,312,573).
Materials
| Poly(acrylic acid) solution average Mw ~ 100,000, 35 wt % in H2O | Sigma Aldrich | 523925 | CAS 9003-01-4 |
| Poly(ethylene glycol) 2,000 | Sigma Aldrich | 84797 | CAS 25322-68-3 |
| Carbomeer 974P | Fagron | 1387083 | |
| Agarose | Invitrogen Corp. | 16500-500 | UltraPure Agarose |
| RGD peptide | abcam | ab142698 | |
| 4-azidobutanoic acid | Aurum Pharmatech | Z-2421 | CAS 54447-68-6 |
| Oxalyl chloride | Sigma Aldrich | O8801 | CAS 79-37-8 |
| Propargylamine hydrochloride 95% | Sigma Aldrich | P50919 | CAS 15430-52-1 |
| Copper(I) iodide | Sigma Aldrich | 3140 | CAS 7681-65-4 |
| Sodium ascorbate | Sigma Aldrich | Y0000039 | CAS 134-03-2 |
| Phosphate buffered saline | Sigma Aldrich | P4417 | |
| Dialysis Membrane | Spectrum Laboratories, Inc. | 132725 | Spectra/Por 3 Dialysis Membrane Standard RC Tubing MWCO: 3,5 kD |
Riferimenti
- Slaughter, B. V., Khurshid, S. S., Fisher, O. Z., Khademhosseini, A., Peppas, N. A. Hydrogels in Regenerative Medicine. Adv. Mater. 21 (32-33), 3307-3329 (2009).
- Rossi, F., Perale, G., Papa, S., Forloni, G., Veglianese, P. Current options for drug delivery to the spinal cord. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 10 (3), 385-396 (2013).
- Huebsch, N., et al. Harnessing traction-mediated manipulation of the cell/matrix interface to control stem-cell fate. Nat. Mater. 9 (6), 518-526 (2010).
- Mothe, A. J., Tam, R. Y., Zahir, T., Tator, C. H., Shoichet, M. S. Repair of the injured spinal cord by transplantation of neural stem cells in a hyaluronan-based hydrogel. Biomaterials. 34 (15), 3775-3783 (2013).
- Khetan, S., et al. Degradation-mediated cellular traction directs stem cell fate in covalently crosslinked three-dimensional hydrogels. Nat. Mater. 12 (5), 458-465 (2013).
- Ashley, G. W., Henise, J., Reid, R., Santi, D. V. Hydrogel drug delivery system with predictable and tunable drug release and degradation rates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 110 (6), 2318-2323 (2013).
- Rossi, F., van Griensven, M. Polymer Functionalization as a Powerful Tool to Improve Scaffold Performances. Tissue Eng. Part A. 20 (15-16), 2043-2051 (2014).
- Gould, S. T., Darling, N. J., Anseth, K. S. Small peptide functionalized thiol-ene hydrogels as culture substrates for understanding valvular interstitial cell activation and de novo tissue deposition. Acta Biomater. 8 (9), 3201-3209 (2012).
- Azagarsamy, M. A., Anseth, K. S. Wavelength-Controlled Photocleavage for the Orthogonal and Sequential Release of Multiple Proteins. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 52 (51), 13803-13807 (2013).
- Larrañeta, E., et al. Microwave-Assisted Preparation of Hydrogel-Forming Microneedle Arrays for Transdermal Drug Delivery Applications. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 300 (6), 586-595 (2015).
- Cook, J. P., Goodall, G. W., Khutoryanskaya, O. V., Khutoryanskiy, V. V. Microwave-Assisted Hydrogel Synthesis: A New Method for Crosslinking Polymers in Aqueous Solutions. Macromol. Rapid Comm. 33 (4), 332-336 (2012).
- Perale, G., et al. Multiple drug delivery hydrogel system for spinal cord injury repair strategies. J. Control. Release. 159 (2), 271-280 (2012).
- Rossi, F., Perale, G., Storti, G., Masi, M. A Library of Tunable Agarose Carbomer-Based Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications: The Role of Cross-Linkers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 123 (4), 2211-2221 (2012).
- Frith, J. E., et al. An injectable hydrogel incorporating mesenchymal precursor cells and pentosan polysulphate for intervertebral disc regeneration. Biomaterials. 34 (37), 9430-9440 (2013).
- Kolb, H. C., Finn, M. G., Sharpless, K. B. Click chemistry: Diverse chemical function from a few good reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 40 (11), (2001).
- Sacchetti, A., Mauri, E., Sani, M., Masi, M., Rossi, F. Microwave-assisted synthesis and click chemistry as simple and efficient strategy for RGD functionalized hydrogels. Tetrahedron Lett. 55 (50), 6817-6820 (2014).
- Ossipov, D. A., Hilborn, J. Poly(vinyl alcohol)-based hydrogels formed by "click chemistry". Macromolecules. 39 (5), 1709-1718 (2006).
- Truong, V., Blakey, I., Whittaker, A. K. Hydrophilic and Amphiphilic Polyethylene Glycol-Based Hydrogels with Tunable Degradability Prepared by "Click" Chemistry. Biomacromolecules. 13 (12), 4012-4021 (2012).
- Hou, R. Z., et al. New synthetic route for RGD tripeptide. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 36 (3), 243-252 (2006).
- Rossi, F., Chatzistavrou, X., Perale, G., Boccaccini, A. R. Synthesis and Degradation of Agar-Carbomer Based Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 123 (1), 398-408 (2012).
- Mauri, E., Rossi, F., Sacchetti, A. Tunable drug delivery using chemoselective functionalization of hydrogels. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 61, 851-857 (2016).
- Joaquin, A., Peppas, N. A., Zoldan, J. Hydrogel Polymer Library for Developing Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Derived Cardiac Patches. Tissue Eng. Part A. 20, S55-S55 (2014).
- Rossi, F., et al. Tunable hydrogel-Nanoparticles release system for sustained combination therapies in the spinal cord. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces. 108, 169-177 (2013).
- Kolb, H. C., Sharpless, K. B. The growing impact of click chemistry on drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today. 8 (24), 1128-1137 (2003).
- Ossipov, D. A., Yang, X., Varghese, O., Kootala, S., Hilborn, J. Modular approach to functional hyaluronic acid hydrogels using orthogonal chemical reactions. Chem. Commun. 46 (44), 8368-8370 (2010).
- Anderson, S. B., Lin, C. C., Kuntzler, D. V., Anseth, K. S. The performance of human mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in cell-degradable polymer-peptide hydrogels. Biomaterials. 32 (14), 3564-3574 (2011).
- Caron, I., et al. A new three dimensional biomimetic hydrogel to deliver factors secreted by human mesenchymal stem cells in spinal cord injury. Biomaterials. 75, 135-147 (2016).
- Lee, J. W., Kim, H., Lee, K. Y. Effect of spacer arm length between adhesion ligand and alginate hydrogel on stem cell differentiation. Carbohyd. Polym. 139, 82-89 (2016).
- Liu, Y., Fan, Z., Wang, Y., Yu, L. Controlled Release of Low Molecular Protein Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 through Self-Assembling Peptide Hydrogel with Biotin Sandwich Approach. J.Biomed. Eng. 32 (2), 387-392 (2015).

