通过选择性核糖体分析对共翻译相互作用网络进行全局鉴定
Summary
共转化相互作用在新生链修饰,靶向,折叠和组装途径中起着至关重要的作用。在这里,我们描述了选择性核糖体分析,这是一种 体内直接分析真核生物酿酒 酵母模型中这些相互作用的方法。
Abstract
近年来,很明显,核糖体不仅可以解码我们的mRNA,还可以引导多肽链进入拥挤的细胞环境。核糖体为膜靶向因子、修饰酶和折叠伴侣的空间和动力学控制结合提供了平台。最近,甚至将组装成高阶低聚物复合物以及蛋白质 – 蛋白质网络形成步骤也被发现与合成相协调。
在这里,我们描述了选择性核糖体分析,这是一种为捕获 体内共翻译相互作用而开发的方法。我们将详细介绍捕获核糖体 – 新生链复合物以及共翻译相互作用物所需的各种亲和纯化步骤,以及以近密码子分辨率破译共翻译相互作用所需的mRNA提取,大小排阻,逆转录,深度测序和大数据分析步骤。
Introduction
Selective Ribosome Profiling(SeRP)是迄今为止唯一一种在体内以直接方式捕获和表征体内共翻译相互作用的方法1,2,3,4,5,6。SeRP能够以近密码子分辨率2,7对任何因子与翻译核糖体的相互作用进行全局分析。
该方法依赖于生长细胞的快速冷冻和保留活性翻译。然后用RNase I处理细胞裂解物以消化细胞中的所有mRNA,除了被称为“核糖体足迹”的核糖体保护的mRNA片段。然后将样品分成两部分;一部分直接用于分离所有细胞核糖体足迹,代表细胞中所有正在进行的翻译。第二部分用于与感兴趣因子相关的核糖体特定子集的亲和纯化,例如:修饰酶,易位因子,折叠伴侣和复合物组装相互作用。亲和纯化的核糖体足迹统称为相互作用组。然后,提取受核糖体保护的mRNA并用于cDNA文库的生成,然后进行深度测序。
对总翻译组和相互作用组样本的比较分析可以识别与目标因子相关的所有 orfs ,以及表征每个 orf 相互作用曲线。该图谱报告了精确的参与开始和终止序列,从中可以推断出解码的密码子和新兴多肽链的各自残基,以及相互作用过程中的核糖体速度变化7,8。 图1 将协议描述为原理图。
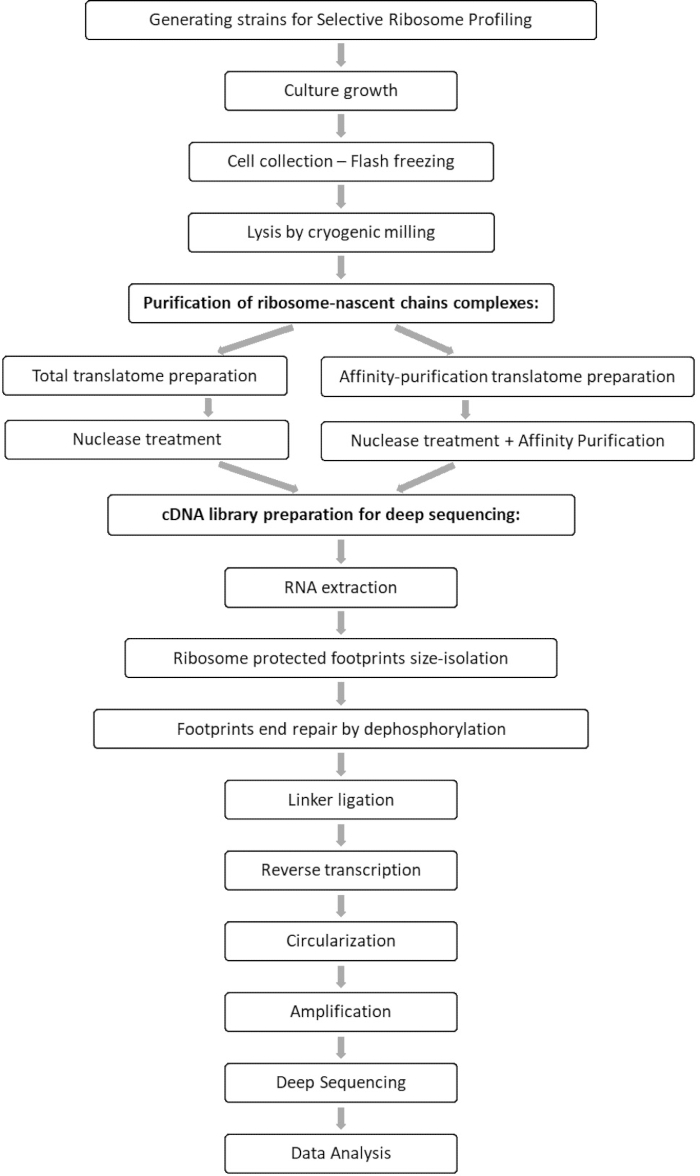
图 1:SeRP 协议概述。 该协议可以在7-10天内完整执行。 请点击此处查看此图的大图。
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
在这里,方案详细介绍了选择性核糖体分析方法,用于捕获近密码子分辨率中的共翻译相互作用。随着核糖体上升为协调新生链出现在拥挤的细胞质中的中心,这是鉴定和表征确保功能性蛋白质组所需的各种共翻译相互作用以及研究各种疾病的关键方法。迄今为止,SeRP是唯一能够以直接方式在体内捕获和表征这些相互作用的方法14,15,<…
Divulgazioni
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
我们要感谢所有实验室成员的富有成效的讨论,并感谢穆罕默德·马赫祖米(Muhammad Makhzumy)对手稿的批判性阅读。这项工作由ISF(以色列科学基金会)2106/20赠款资助。
Materials
| 3'-Phosphorylated 28 nt RNA control oligonucleotide | IDT | custom order | RNase free HPLC purification; 5'-AUGUAGUCGGAGUCGAGGCGC GACGCGA/3Phos/-3' |
| Absolute ethanol | VWR | 20821 | |
| Acid phenol–chloroform | Ambion | AM9722 | |
| Antibody: mouse monclonal anti-HA | Merck | 11583816001 | 12CA5 |
| Aprotinin | Roth | A162.3 | |
| ATP* | NEB | P0756S | 10 mM |
| Bacto agar | BD | 214030 | |
| Bacto peptone | BD | 211820 | |
| Bacto tryptone | BD | 211699 | |
| Bacto yeast extract | BD | 212720 | |
| Bestatin hydrochloride | Roth | 2937.2 | |
| Chloroform | Merck | 102445 | |
| CircLigase II ssDNA Ligase* | Epicentre | CL9025K | 100 U/μL |
| Colloidal Coomassie staining solution | Roth | 4829 | |
| cOmplete, EDTA-free protease inhibitor cocktail tablets | Roche Diagnostics | 29384100 | |
| Cycloheximide | Biological Industries | A0879 | |
| DEPC treated and sterile filtered water* | Sigma | 95284 | |
| D-Glucose anhydrous | Merck | G5767-500G | |
| Diethylpyrocarbonate | Roth | K028 | |
| Dimethylsulfoxide* | Sigma-Aldrich | 276855 | |
| DNA ladder, 10 bp O'RangeRuler* | Thermo Fisher Scientific | SM1313 | |
| DNA loading dye* | Thermo Fisher Scientific | R0631 | 6× |
| DNase I, recombinant | Roche | 4716728001 | RNAse free |
| dNTP solution set* | NEB | N0446S | |
| EDTA* | Roth | 8043 | |
| Glycerol | VWR | 24388.260. | |
| Glycine solution | Sigma-Aldrich | 67419-1ML-F | 1 M |
| GlycoBlue | Ambion | AM9516 | 15 mg/mL |
| HEPES | Roth | HN78.3 | |
| HF Phusion polymerase* | NEB | M0530L | |
| HK from S. cerevisiae | Sigma-Aldrich | H6380-1.5KU | |
| Hydrochloric acid | AppliChem | A1305 | |
| Isopropanol | Sigma-Aldrich | 33539 | |
| Isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside | Roth | CN08 | |
| Kanamycin | Roth | T832.4 | |
| KCl | Roth | 6781.1 | |
| KH2PO4 | Roth | 3904.1 | |
| Leupeptin | Roth | CN33.4 | |
| Linker L(rt) | IDT | custom order | |
| Liquid nitrogen | |||
| MgCl2 | Roth | KK36.3 | |
| Na2HPO4 | Roth | P030.2 | |
| Na2HPO4·2H2O | Roth | T879.3 | |
| NaCl* | Invitrogen | AM97606 | 5 M |
| NaH2PO4·H2O | Roth | K300.2 | |
| NHS-activated Sepharose 4 fast-flow beads | GE Life Sciences | 17090601 | |
| Nonidet P 40 substitute | Sigma | 74385 | |
| Pepstatin A | Roth | 2936.2 | |
| Phenylmethyl sulfonyl fluoride | Roth | 6367 | |
| Precast gels | Bio-Rad | 5671034 | 10% and 12% |
| RNase I | Ambion | AM2294 | |
| SDS, 20% | Ambion | AM9820 | RNase free |
| Sodium acetate* | Ambion | AM9740 | 3 M, pH 5.5 |
| Sodium azide | Merck | S8032-100G | |
| Sodium chloride | Roth | 9265 | |
| Sodium hydroxide* | Sigma | S2770 | 1 N |
| Sucrose | Sigma-Aldrich | 16104 | |
| SUPERase-In RNase Inhibitor | Ambion | AM2694 | |
| Superscript III Reverse Transciptase* | Invitrogen | 18080-044 | |
| SYBR Gold* | Invitrogen | S11494 | |
| T4 polynucleotide kinase* | NEB | M0201L | |
| T4 RNA ligase 2* | NEB | M0242L | |
| TBE polyacrylamide gel* | Novex | EC6215BOX | 8% |
| TBE–urea polyacrylamide gel* | Novex | EC68752BOX | 10% |
| TBE–urea polyacrylamide gel* | Novex | EC6885BOX | 15% |
| TBE–urea sample buffer* | Novex | LC6876 | 2× |
| Tris | Roth | 4855 | |
| Tris* | Ambion | AM9851 | 1 M, pH 7.0 |
| Tris* | Ambion | AM9856 | 1 M, pH 8.0 |
| UltraPure 10× TBE buffer* | Invitrogen | 15581-044 | |
| * – for library preparation | |||
| gasket and spring clamp , 90 mm, | Millipore | XX1009020 | |
| ground joint flask 1 L , | Millipore | XX1504705 |
Riferimenti
- Oh, E., et al. Selective ribosome profiling reveals the cotranslational chaperone action of trigger factor in vivo. Cell. 147 (6), 1295-1308 (2011).
- Shiber, A., et al. Cotranslational assembly of protein complexes in eukaryotes revealed by ribosome profiling. Nature. 561 (7722), 268-272 (2018).
- Becker, A. H., Oh, E., Weissman, J. S., Kramer, G., Bukau, B. Selective ribosome profiling as a tool for studying the interaction of chaperones and targeting factors with nascent polypeptide chains and ribosomes. Nature Protocols. 8 (11), 2212-2239 (2013).
- Galmozzi, C. V., Merker, D., Friedrich, U. A., Döring, K., Kramer, G. Selective ribosome profiling to study interactions of translating ribosomes in yeast. Nature Protocols. , (2019).
- Knorr, A. G., et al. Ribosome-NatA architecture reveals that rRNA expansion segments coordinate N-terminal acetylation. Nature Structural and Molecular Biology. 26 (1), 35-39 (2019).
- Matsuo, Y., Inada, T. The ribosome collision sensor Hel2 functions as preventive quality control in the secretory pathway. Cell Reports. 34 (12), (2021).
- Döring, K., et al. Profiling Ssb-Nascent chain interactions reveals principles of Hsp70-assisted folding. Cell. , (2017).
- Chartron, J. W., Hunt, K. C. L., Frydman, J. Cotranslational signal-independent SRP preloading during membrane targeting. Nature. 536 (7615), 224-228 (2016).
- Janke, C., et al. A versatile toolbox for PCR-based tagging of yeast genes: New fluorescent proteins, more markers and promoter substitution cassettes. Yeast. 21 (11), 947-962 (2004).
- Levi, O., Arava, Y. Expanding the CRISPR/Cas9 Toolbox for Gene Engineering in S. cerevisiae. Current Microbiology. 77 (3), 468-478 (2020).
- Giannoukos, G., et al. Efficient and robust RNA-seq process for cultured bacteria and complex community transcriptomes. Genome Biology. 13 (3), 23 (2012).
- . Illumina Index Adapters – Pooling Guide Available from: https://support.illumina.com/content/dam/illumina-support/documents/documentation/chemistry_documentation/experiment-design/index-adapters-pooling-guide-1000000041074-05.pdf (2019)
- Kanagawa, T. Bias and artifacts in multitemplate polymerase chain reactions (PCR). Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering. 96 (4), 317-323 (2003).
- Bertolini, M., et al. Interactions between nascent proteins translated by adjacent ribosomes drive homomer assembly. Science. 371 (6524), (2021).
- Kramer, G., Shiber, A., Bukau, B. Mechanisms of cotranslational maturation of newly synthesized proteins. Annual Review of Biochemistry. 88, 337-364 (2019).
- Joazeiro, C. A. P. Mechanisms and functions of ribosome-associated protein quality control. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 20 (6), 368-383 (2019).
- Beaupere, C., Chen, R. B., Pelosi, W., Labunskyy, V. M. Genome-wide quantification of translation in budding yeast by ribosome profiling. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (130), e56820 (2017).

