Controlled Infusion of Aβ Peptide-Specific Antibodies and Aβ Oligomers into the Rat Hippocampus
Abstract
Source: Sajadi, A., et al. Neurodegeneration in an Animal Model of Chronic Amyloid-beta Oligomer Infusion Is Counteracted by Antibody Treatment Infused with Osmotic Pumps. J. Vis. Exp. (2016).
This video demonstrates a technique for the continuous infusion of amyloid-beta (Aβ) peptide-specific antibodies into the hippocampus of a rat. The study employs implanting a bilateral cannula system for a controlled infusion of Aβ peptide-specific antibodies coupled with the infusion of soluble Aβ oligomers (Aβo) into the rat hippocampus to study the interactions between the oligomers and the antibodies.
Protocol
All procedures involving animal models have been reviewed by the local institutional animal care committee and the JoVE veterinary review board.
1. Catheter Preparation before Stereotaxic Surgery
- Cut PE50 catheters (6 cm in length) that will be used to connect the cannula with osmotic pumps (see Figure 1). Fill PE50 catheters with artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF) and seal both ends of the catheters. Keep the catheter at 4 °C until used.
2. Cannula Implantation by Stereotaxy
- Perform the surgery in sterile conditions. Sterilize all the surgical instruments and materials by autoclaving. Clean the stereotaxic apparatus and the working area thoroughly and disinfect with a 70% ethanol solution. Wear a surgical mask, hair bonnet, and sterile gloves.
- Anesthetize rats by injecting intraperitoneally (i.p.) a solution of ketamine and xylazine (100 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg, respectively). Confirm anesthesia by checking movement after a gentle toe pinch.
- Inject a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (Meloxicam; 1 mg/kg) subcutaneously (s.c.) to the anesthetized animal at least 30 min before surgery.
- Shave the head of the animal using clippers and disinfect the skin three times with a solution of chlorhexidine gluconate 2% and isopropyl alcohol 2%. Apply veterinary ophthalmic ointment on the eyes to prevent dryness while under anesthesia.
- Place the animal on a stereotaxic frame with the ear bars. Fix one cannula on the holder arm of the stereotaxic frame. Inject (s.c.) a local anesthetic agent (bupivacaine (1.5 mg/kg) and lidocaine (1.5 mg/kg) on the top of the head. Anesthesia is maintained during the whole procedure by placing a nose cone delivering 3% isoflurane. The entire surgical field should be draped off, but it was not done here to demonstrate the technique better.
- Make an incision of 3 cm on the top of the head with a scalpel. Install 4 clamps around the incision to leave the skull clear. Using a round-tip scissor, make a pocket (2 x 2 cm2) under the skin between the shoulder blades of the animal.
- Scrape the periosteum of the skull with a blade. Apply a gauze pad on the skull if it is bleeding.
- Verify that the skull is flat and well aligned on the stereotaxic frame. To ensure the skull is flat, check the height coordinates at the bregma and lambda. Take the bregma coordinates that will be used as the reference point.
- Starting from the bregma, calculate the coordinates of the two guide cannula that will be implanted bilaterally in the hippocampus (anteroposterior: – 0.42 cm; mediolateral: ± 0.30 cm; dorsoventral: – 0.28 cm according to the Paxinos and Watson rat brain atlas). Indicate the position of the cannula with a marker.
- Drill a hole (0.5 mm) in the skull at the implantation point of both cannulas. Drill two other holes approximately 5 mm above and below those points to insert screws that will solidify the cannula when applying dental cement.
- Cut one end of the catheter previously filled with aCSF with a scalpel and insert it in the angle arm of the cannula. Fix the first cannula with dental cement. Avoid putting dental cement around the position on the second cannula.
- Let the dental cement dry for 2 – 3 min, then remove the holder arm from the first cannula, and fix the second cannula in it. Repeat steps 2.11 and 2.12. Put a dummy cannula on both guide cannulas. Ensure that the dummy and guide cannula are the same length to prevent tissue infiltration and blocking of the cannula.
- Insert the free end of both catheters in the pocket previously made between the shoulder blades of the animal. Remove the clamps and stitch the skin with a suture thread 4-0.
NOTE: The top guide cannula must be accessible for upcoming Aβo infusions. - Remove the animal from the stereotaxic frame and put it back in its cage. During post-surgical recovery, place the cage on a heating water blanket until the animal wakes up. The cage should be partially on the pad so the rat can escape the heat if needed. Monitor the animal constantly until it regains sufficient consciousness to maintain sternal recumbency.
- Return rats to the animal facility to recover from the surgery for 10 days under close monitoring.
NOTE: Do not return an animal that has undergone surgery to the company of other animals until fully recovered. Meloxicam (1 mg/kg) is given once per day for two days following surgery to treat pain.
3. Osmotic Pump Installation
- One day before installation, fill osmotic pumps with 6E10 antibody (1 mg/ml; 100 µl) and control IgG1 antibody (1 mg/ml; 100 µl) according to the manufacturer's instructions under sterile conditions. Keep the pumps in sterile distilled water at 37 °C overnight to activate pumps.
- Anesthetize rats with isoflurane 3% to install osmotic pumps (0.5 µl/hr for 7 days). Shave between shoulder blades and disinfect the skin with a solution of chlorhexidine gluconate 2% and isopropyl alcohol 2%. Make an incision of 2 cm with a scalpel between the shoulder blades to locate the PE50 catheters connected to the guide cannula.
- Cut the end of the PE50 catheters containing dental cement with a scalpel. Connect the osmotic pumps to the PE50 catheters and add some dental cement at the pump and catheter junction to secure the connection.
- Stitch the skin tightly with a suture thread 4-0. Put the animal back in its cage on a heating water pad. Observe the animal wake up rapidly from an isoflurane anesthesia (about 5 min).
NOTE: The surgery takes approximately 5 to 10 min.
4. Aβo Infusions in Awake and Freely Moving Rats
- Prepare the Aβo solution (0.2 µg/µl). Allow Aβo to aggregate dynamically and spontaneously for 1 hr at room temperature before infusion.
- Install two 10 µl syringes on an infusion pump. Fill the syringes with 5 µl of sterile distilled water. Cut two PE50 catheters to about 60 cm in length with a scalpel. Fill both catheters with sterile distilled water using 1 ml syringes and 21G needles.
- Keep the 1 ml syringes at one end of the catheter and connect the other end to the Hamilton syringes. Remove the 1 ml syringes and check that there are no air bubbles within the catheters.
- Insert the internal cannula at the end of the PE50 catheters. Using sterile distilled water, fill the internal cannula connected to PE50 catheters up to1 µl on Hamilton syringes. Make an air bubble by pulling back the pistons up to 2 µl.
- Mix the Aβo solution by pipetting up and down using a tip of minimum adherence. Avoid forming bubbles during mixing. Fill both internal cannulas with 1.5 µl of Aβo solution by pulling back the pistons up to 3.5 µl.
- Make lines with a marker before and after the air bubble in both catheters. This serves as a checkpoint for ongoing infusion. For infusion, bring the cage near the infusion pump and remove its cover.
- Place the rat in a snuggle and tightly scrape the arm of the snuggle around its neck to immobilize the head of the rat. Remove the dummy cannula from the two guide cannula. Insert the internal cannula previously prepared in the guide cannula. Verify that they are fully inserted and well-fixed to the base of the guide cannula.
- Release the rat from the snuggle and put it back in its cage to limit contention stress. Monitor closely to ensure the catheters do not twist together and the infusion is done correctly.
- Turn on the infusion pump. Inject 1 µl of Aβo solution at a rate of 0.1 µl/min (10 min). During infusion, check that the syringe piston moves from 3.5 µl to 2.5 µl and that the air bubble in both PE50 catheters moves continuously.
- Leave the internal cannula in place for another 5 min after infusion to allow efficient diffusion of Aβo solution. Bring the rat back in the snuggle to remove the internal cannula and capped guide cannula to prevent reflux of the injected solution. Use a dummy cannula that stops just before the angle arm of the cannula. Return the animal to its cage.
- Repeat Aβo infusion once per day over 6 consecutive days. Euthanize the animal by decapitation.
Representative Results
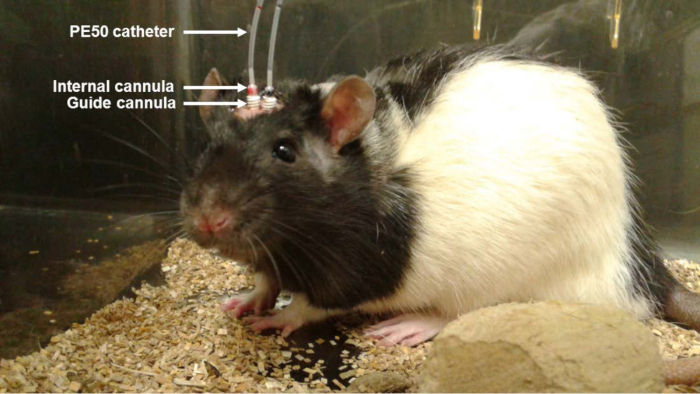
Figure 1. Photo of the Animal with Bilateral Cannula During Aβo Infusion. A solution of Aβo (0.2 µg/µl; 1 µl) was injected in awake and freely moving rats (once a day for 6 days) using PE50 catheters connected to an internal cannula inserted into a guide cannula. Treatment with control (Ctl) IgG1 or 6E10 antibody was infused directly at the site of Aβo infusion using osmotic pumps located subcutaneously between the shoulder blades of the animal.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Materials
| Artificial Cerebrospinal Fluid (aCSF) | Harvard Apparatus | 59-7316 | |
| PE50 Catheter thin wall | Plastics one | C232CT | |
| Ketamine Hydrochloride (100 mg/mL) | Bioniche | 1989529 | |
| Xylaxine Hydrochloride (100 mg/mL) | Bimeda | 8XYL004C | |
| Meloxicam (5 mg/mL) | Norbrook | 215670I01 | |
| Solution of chlorhexidine gluconate 2% and isopropyl alcohol 2% | Carefusion | 260100C | |
| Lidocaine Hydrochloride | Alveda Pharma | 0122AG01 | |
| Bupivacaine Hydrochloride | Hospira | 1559 | |
| Ophthalmic ointment | Baussh and Lomb inc. | 2125706 | |
| Stereotaxic frame | Stoelting | 51600 | |
| Stereotaxic cannula holder arm | Harvard Apparatus | 72-4837 | |
| Drill | Dremel | 8050-N/18 | |
| Guide Cannula | Plastics one | 326OPG/spc | |
| Injection Cannula | Plastics one | C315I/spc | |
| Dummy Cannula | Plastics one | C315DC/spc | |
| Suture thread coated vicryl rapide 4-0 | Ethicon | VR2297 | |
| Dental Acrylic Cement | Harvard Apparatus | 72-6906 | |
| Screws | JI Morris Company | P0090CE125 | |
| 6E10 antibody (mouse IgG1 isotype) | BioLegend | 803003 | |
| Mouse IgG1 isotype control antibody | Abcam | AB18447 | |
| Alzet osmotic pumps model 1007D | Durect corporation | 290 | |
| Isoflurane | Baxter | CA2L9100 | |
| Amyloid-beta 1-42 | rPeptide | A-1163-1 | |
| Hamilton syringe (10 µL) | Fisher Scientique | 14815279 | |
| Infusion Syringe Pump CMA 402 | Harvard Apparatus | CMA8003110 | |
| Syringe 1 mL | BD | 309659 | |
| Needle 21G | Terumo | NN-2125R | |
| Snuggle | Lomir Biomedical | RTS04 |

