Pneumococcus infektion af primære humane endotelceller i konstant flow
Summary
Denne undersøgelse beskriver den mikroskopiske monitorering af pneumokokker-tilslutningen til von Willebrand-faktor strenge, der produceres på overfladen af differentierede humane primære endotelceller under forskydnings stress i definerede strømningsforhold. Denne protokol kan udvides til detaljeret visualisering af specifikke cellestrukturer og kvantificering af bakterier ved anvendelse af differentiale immunofarvnings procedurer.
Abstract
Interaktion af Streptococcus pneumoniae med overfladen af endotelceller er medieret i blodgennemstrømning via mekanisk følsomme proteiner såsom von Willebrand Factor (VWF). Dette glykoprotein ændrer sin molekylære konstellation som reaktion på forskydnings stress og udsætter derved bindingssteder for et bredt spektrum af Host-ligand-interaktioner. Generelt er dyrkning af primære endotelceller under en defineret forskydnings strøm kendt for at fremme den specifikke cellulære differentiering og dannelsen af et stabilt og tæt forbundet endotellag, der ligner fysiologien i den indvendige foring af et blodkar . Således kræver den funktionelle analyse af interaktioner mellem bakterielle patogener og værts Vaskulaturen, der involverer mekaniske følsomme proteiner, etablering af pumpesystemer, som kan simulere de fysiologiske strømnings kræfter, som vides at påvirke overfladen af vaskulære celler.
Den mikrofluidiske anordning, der anvendes i dette studie, muliggør kontinuerlig og Pulseless recirkulation af væsker med en defineret strømningshastighed. Det computerstyrede Lufttryks pumpesystem anvender en defineret forskydningsbelastning på endotelcellernes overflader ved at generere et kontinuerligt, envejs og kontrolleret medium flow. Morfologiske ændringer af cellerne og bakteriel fastgørelse kan mikroskopisk overvåges og kvantificeres i flowet ved hjælp af specielle kanal slides, der er designet til mikroskopisk visualisering. I modsætning til statisk cellekultur infektion, som generelt kræver en prøve fiksering forud for immun mærkning og mikroskopiske analyser, de mikrofluidisk dias muliggør både fluorescens-baserede påvisning af proteiner, bakterier, og cellulære komponenter efterprøve fiksering; seriel immunofluorescens farvning; og direkte fluorescens baseret detektion i realtid. I kombination med fluorescerende bakterier og specifikke fluorescens-mærkede antistoffer, denne infektion procedure giver en effektiv flere komponent visualisering system til et stort spektrum af videnskabelige applikationer relateret til vaskulære processer.
Introduction
Patogenesen af pneumokokker infektioner er karakteriseret ved en mangesidet interaktion med en mangfoldighed af ekstracellulære matrix forbindelser og komponenter i den menneskelige hæmostase, såsom plasminogen og vWF1,2, 3,4,5,6,7,8. Multi Domain glykoprotein vWF fungerer som nøgle regulator af en balanceret hæmostase ved at mægle trombocyt rekruttering og fibrin inkorporering på stedet for vaskulær trombusdannelse9. Betydningen af funktionel, aktiv VWF til blødningskontrol og sårheling påvises ved von Willebrands sygdom, en almindelig arvelig blødningsforstyrrelse10.
Den globulære vWF cirkulerer i det menneskelige blod system i en koncentration på op til 14,0 μg/ml11,10. Som reaktion på vaskulær skade, den lokale frigivelse af vWF af endotel Weibel Palade organer (WBP) er markant forøget11,12. Tidligere undersøgelser viser, at pneumokokker overholdelse af humane endotelceller og dets produktion af pore dannende toksin pneumolysin i betydelig grad stimulerer luminale vWF sekretionen13. De hydrodynamiske kræfter i blodgennemstrømningen inducerer en strukturel åbning af mekanismens esponsive VWF domæner. Ved strømningshastigheder på 10 dyn/cm2 vWF multimerizes til lange protein strenge på op til flere hundrede mikrometer i længden, der forbliver fastgjort til subendothelium10,12.
For at forstå funktionen af multimeriserede vWF-strenge genereret under forskydnings stress i interaktionen af pneumokokker med endoteloverfladen blev der etableret en mikrofluidic-baseret cellekultur infektion tilgang. Der blev anvendt en mikrofluidic-enhed med et software kontrolleret lufttryk pumpesystem. Dette gav mulighed for en kontinuerlig, ensrettet recirkulation af cellekulturmedium med en defineret strømningshastighed. Derved anvendte systemet en defineret forskydningsbelastning på overfladen af endotelceller, som forblev fastgjort inde i specialiserede kanalrutschebaner. Denne fremgangsmåde gjorde det muligt at simuleringen af forskydnings kraften i blodstrømmen i det menneskelige vaskulære system, hvor VWF-strengene genereres på differentierede endotelceller under definerede konstante strømningsforhold. Til dette formål blev endotelcellerne dyrket i specifikke kanalrutschebaner (Se tabel over materialer), som blev tilpasset til mikroskopiske analyser under gennemstrømningen. Det mikrofluidisk pumpesystem leverede den meget definerede og kontrollerede forskydnings stresssituation, der kræves for dannelsen af udvidede vWF strenge på flydende endotheliale cellelag. Efter stimulering af VWF-sekretion af confluently dyrket humane navle formede vene endotelceller (HUVEC) af histamin tilskud, strengen dannelse blev induceret ved at anvende en shear stress (ԏ) af 10 dyn/cm2. Forskydnings belastningen defineres som den kraft, der handler på cellelaget. Det beregnes omtrent efter Cornish et. al.14 med ligning 1:
Hvor ԏ = forskydningsbelastning i dyn/cm2, η = viskositet i (dyn ∙ s)/cm2, h = halvdelen af kanal højden, w = halvdelen af kanalbredden og Φ = flow hastigheds i ml/min.
Resultatet af ligning 1 afhænger af de forskellige højder og bredder på de forskellige anvendte slides (Se tabel over materialer). I dette studie blev der anvendt et luer-kanal udtræk på 0,4 μm, som resulterede i en kammer slide faktor på 131,6 (Se formel 2).
Viskositeten af mediet ved 37 °C er 0,0072 dyn ∙ s/cm ², og der blev anvendt en forskydningsbelastning på 10 dyn/cm ². Dette resulterede i en strømningshastighed på 10,5 mL/min (Se formel 3).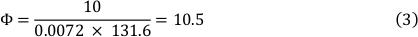
Her er tilpasningen og fremskridt af en mikrofluidisk celledyrkning procedure ved hjælp af et ensrettet laminar flow system til undersøgelse og visualisering af bakterielle infektions mekanismer i værts vasculaturen beskrevet i detaljer. Generering af VWF strenge på endotellag kan også stimuleres ved hjælp af andre pumpesystemer, der er i stand til at anvende en kontinuerlig og stabil shear stress15.
Efter dyrkning af primære endotelceller til sammenløbet i flow og stimulering af VWF-streng dannelse blev pneumokokker, der udtrykker rødt fluorescens protein (RFP)16 , føjet til endotelcellelag under konstant mikroskopisk kontrol. Tilknytningen af bakterier til VWF strenge på overfladen af endotelceller blev mikroskopisk visualiseret og overvåges i op til tre timer i realtid ved hjælp af VWF-specifikke fluorescerende-mærkede antistoffer. Med denne tilgang, rolle vWF som en vedhæftning cofaktor fremme bakteriel tilknytning til den vaskulære endotelum blev bestemt8.
Ud over den mikroskopiske visualisering af protein sekretion og konformationsmæssige ændringer, denne metode kan bruges til at overvåge enkelte trin af bakteriel infektion processer i realtid og at kvantificere mængden af vedhæftede bakterier på forskellige tidspunkter af Infektion. Det specifikke softwarestyrede pumpesystem giver også mulighed for at kultur de endotelceller i definerede konstante strømningsforhold i op til flere dage og muliggør en defineret pulseret medium flow inkubation. Desuden kan denne metode anvendes ved hjælp af forskellige celletyper. Tilpasning af farvnings protokollen giver også mulighed for påvisning og visualisering af bakterier internaliseret i eukaryote celler.
Dette manuskript beskriver denne avancerede eksperimentelle protokol, der kan bruges som en defineret, pålidelig og reproducerbar tilgang til en effektiv og alsidig karakterisering af patofysiologiske processer.
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
Simuleringen af bakteriel interaktion med mekanisnofølsomme værts proteiner som VWF kræver et perfbrugbart cellekultursystem, der muliggør generering af en defineret, ensrettet og kontinuerlig strøm af væsker, hvilket skaber pålidelig forskydningsbelastning . Flere mikrofluidisk pumpesystemer er allerede blevet beskrevet. En omfattende anmeldelse fra Bergmann et al. opsummerer de vigtigste aspekter af forskellige to-og tre-dimensionelle cellekultur modeller17.
De…
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
Projektet blev finansieret af DFG (BE 4570/4-1) til S.B.
Materials
| 1 mL Luer-syringe | Fisher Scientific | 10303002 | with 1 mL volume for gelatin injection using the luer-connection of the slides |
| 2 mL Luer-syringe | Sarstedt | 9077136 | For pieptting/injecting fluids into the luer connections of the channel chamber slides |
| Accutase | eBioscience now thermo fisher | 00-4555-56 | protease mix used for gentle detachment of endothelial cells |
| AlexaFluor350-conjugated Phalloidin | Abcam | ab176751 | no concentration available from the manufacturer, stock solution is sufficient for 300 tets, company recommends to use 100 µl of a 1:1000 dilution, blue fluorescence (DAPI-filter settings) |
| AlexaFluor488-conjugated goat-derived anti-mouse antibody | Thermo Fisher Sientific | A11001 | stock concentration: 2 mg/mL for immunostaining of human VWF in microfluidic slide after PFA fixation, green fluorescence |
| AlexaFluor568-conjugated goat-derived anti-rabbit-antibody | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A-11011 | stock concentration: 2 mg/mL for immunostaining of pneumococci in microfluidic slide after pFA fixation, red fluorescence |
| Bacto Todd-Hewitt-Broth | Becton Dickinson GmbH | BD 249210 | complex bacterial culture medium |
| Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) | Sigma Aldrich | A2153-25G | solubilized, for preparation of blocking buffer |
| Cell culture flasks with filter | TPP | 90026 | subcultivation of HUVEC in non-coated cell culture flasks of 25 cm2 surface |
| Centrifuge Allegra X-12R | Beckman Coulter Life Sciences | 392304 | spinning down of bacteria (volumes of > 2mL) |
| Centrifuge Allegra X-30 | Beckman Coulter Life Sciences | B06314 | spinning down of eukaryotic cells |
| Centrifuge Z 216 MK | Hermle | 305.00 V05 – Z 216 M | spinning down of bacteria (volumes of less than 2 mL) |
| Chloramphenicol | Carl Roth GmbH + Co. KG, Karlsruhe | 3886.2 | used in a concentration of 0.2 /mL for cultivation of pneumococci transformed with genetic construct carrying red fluorescent protein and chloramphenicol resistance cassette |
| Clamp for perfusion tubing | ibidi | 10821 | for holding the liquid in the tube bevor connecting the slide to the pump system |
| CO2-Incubator | Fisher Scientific | MIDI 40 | incubator size is perfectly adapted to teh size of the fluidic unit with connected channel slide and was used for flow cultivation at 37°C and 5% CO2 |
| CO2-Incubator | Sanyo | MCO-18 AIC | for incubation of bacteria and cells in a defined atmosphere at 5% CO2 and 37°C |
| Colombia blood agar plates | Becton Dickinson GmbH | PA-254005.06 | agar-based complex culture medium for S. pneumoniae supplemented with 7% sheep blood |
| Computer | Dell | Latitude 3440 | Comuter with pressure pump software |
| Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope (CLSM) | Leica | DMi8 | An inverse microscope with a stage covered by a heatable chamber and with a fluorescence unit equipped with fluorescence filter, Xenon-light source (SP8, DMi8) and DFC 365 FX Kamera (1392 x 1040, 1.4 Megapixel) |
| Di Potassium hydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4) | Carl Roth GmbH + Co. KG, Karlsruhe | 3904.1 | used for PBS buffer |
| Drying material | Merck | 101969 | orange silica beads for drying used in a glass bottle with a tubing adaptor |
| ECGM supplement Mix | Promocell | C-39215 | supplement mix for ECGM -medium, required for precultivation of endothelial cells: 0.02 mL/mL Fetal calf serum, 0.004 mL/ mL endothelial cell growth supplement, 0.1 ng / mL epidermal growth factor, 1 ng / mL basic fibroblast growth factor, 90 µg / mL heparin, 1 µg / mL Hydrocortisone |
| ECGMS | Promocell | C-22010 | ECGM supplemented with 5 % [w/w] FCS and 1 mM MgSO4 to increase cell adhesion |
| Endothelial Cell growth medium (ECGM, ready to use) | Promocell | C-22010 | culture medium of HUVECs, already supplemented with all components of the supplement mix |
| Fetal Calf Serum (FCS) | biochrome now Merck | S 0415 | supplement for cell culture, used for infection analyses |
| FITC-conjugated goat anti-human VWF antibody | Abcam | ab8822 | stock concentration: 10 mg/mL, for immunodetection of globular and multimerized VWF in flow |
| Fluidic Unit | ibidi | 10903 | fluidic unit for flow cultivation |
| Gelatin (porcine) | Sigma Aldrich | G-1890-100g | for precoating of microslide channel surface |
| histamine dihydrochloride | Sigma Aldrich | H-7250-10MG | for induction of VWF secretion from endothelial Weibel Palade Bodies |
| Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cell (HUVEC) | Promocell | C-12203 Lot-Nr. 396Z042 | primary endothelial cells from pooled donor, stored crypcoserved in liquid nitrogen |
| Human VWF-specific antibody derived from mouse (monoclonal) | Santa Cruz | sc73268 | stock concentration: 200 µg/mL for immunostaining of VWF in microfluidic slide after PFA fixation |
| Injection Port | ibidi | 10820 | for injection of histamin or bacteria into the reservoir tubing during the flow circulation |
| Light microscope | Zeiss | Axiovert 35M | inverse light microscope for control of eukaryotic cell detachement and cell counting using a 40 x water objective allowing 400 x magnification |
| Luer-slides I0.4 (ibiTreat472microslides) | ibidi | 80176 | physically modified slides for fludic cultivation (μ–Slide I0.4Luer with a channel hight of 0.4 mm, a channel volume of 100 μl, a growth area of 2.5 cm and a coating area of 25.4 cm2) suitable for all kinds of flow assay, the physical treatment generates a hydrophilic and adhesive surface. |
| Magnesium sulfate (MgSO4, unhydrated) | Sigma Aldrich | M7506-500G | For preparation of ECGMS medium |
| Microfluidic Pump | ibidi | 10905 | air pressure pump |
| Neubauer cell counting chamber | Karl Hecht GmbH&Co KG | 40442002 | microscopic counting chamber for HUVECs |
| Paraformaldehyde 16% (PFA) | Electron Microscopy Sciences | 15710-S | for cross linking of samples |
| Perfusion Set | ibidi | 10964 | Perfusion Set Yellow/Green has a tubing diameter of 1.6 mm, a tube length of 50 cm, a total working volume of 13.6 mL, a dead tube volume of 2.8 mL and a reservoir size of 10 mL. combined with the µ-slide L0.4Luer, at 37°C and a viscosity of 0.0072 dyn x s/cm2 a flow rate range of 3.8mL/min up to 33.9 mL/min and shear stress between 3.5 dyn/cm2 and 31.2 dyn/cm2 can be reached. with 50 cm lenght for microfluidic |
| Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) | the solution was prepared using the following chemicals: 0.2 g/L KCl, 1.44 g/L Na2HPO4, 0.24 g/L KH2PO4 , pH 7.4 | ||
| Plastic cuvettes | Sarstedt | 67,741 | (2 x optic) for OD measurement at 600 nm |
| Pneumococcus-specific antiserum | Pineda | raised in rabbit using heat-inactivated Streptococcus pneumoniae NCTC10319 and D39, IgG-purified using proteinA-sepharose column. | |
| Polystyrene or Styrofoam plate | this is a precaution step to avoid cold stress on the cells seeded in the channel slides. Any type of styrofoam such as packaging box-material can be used. The plate might by 0.5 cm thick and should have a size of 20 cm2. | ||
| Potassium chloride (KCl) | Carl Roth GmbH + Co. KG, Karlsruhe | 6781.1 | used for PBS buffer |
| Pump Control Software (PumpControl v1.5.4) | ibidi | v1.5.4 | Computer software for controlling the pressure pump, setting the flow conditions and start/end the flow |
| reaction tubes 1.5/ 2.0mL | Sarstedt | 72.706/ 72.695.500 | required for antibody dilutions |
| reaction tubes with 50 mL volume | Sarstedt | 6,25,48,004 | |
| RFP-expressing pneumococci | National Collection of Type Cultures, Public Health England | 10,319 | Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 47 expressing RFP fused to ahistone-like protein integrated into the genome |
| serological pipets 5, 10 mL | Sarstedt | 86.1253.025/ 86.1254.025 | for pipeting larger volumes |
| Sodium Carbonate (Na2CO3, water free) | Sigma Aldrich | 451614-25G | for preparation of 100 mM Sodium Carbonate buffer |
| Sodium dihydrogen phosphate (NaH2PO4) | Carl Roth GmbH + Co. KG, Karlsruhe | P030.2 | used for PBS buffer |
| Spectral Photometer Libra S22 | Biochrom | 80-2115-20 | measurement of optical density (OD) of bacterial suspension at 600 nm |
| Sucrose | Sigma Aldrich | S0389-500G | for preparation of blocking buffer |
| Triton X-100 | Sigma Aldrich | T9284-500ML | Used in 0.1% end concentration diluted in dH20 for eukaryotic cell permeabilization after PFA fixation |
| Yeast extract | oxoid | LP0021 | bacteria are cultivated in THB supplement with 1% [w/w] yeast extract = complete bacterial cultivation medium THY |
References
- Weiser, J. N., Ferreira, D. M., Paton, J. C. Streptococcus pneumoniae: transmission, colonization and invasion. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 16 (6), 355-367 (2018).
- Bergmann, S., Hammerschmidt, S. Versatility of pneumococcal surface proteins. Microbiology. 152, 295-303 (2006).
- Bergmann, S., et al. Integrin-linked kinase is required for vitronectin-mediated internalization of Streptococcus pneumoniae by host cells. Journal of Cell Science. 122, 256-267 (2009).
- Bergmann, S., Schoenen, H., Hammerschmidt, S. The interaction between bacterial enolase and plasminogen promotes adherence of Streptococcus pneumoniae to epithelial and endothelial cells. International Journal of Medical Microbiology. 303, 452-462 (2013).
- Bergmann, S., Rohde, M., Chhatwal, G. S., Hammerschmidt, S. Alpha-enolase of Streptococcus pneumoniae is a plasmin(ogen)-binding protein displayed on the bacterial cell surface. Molecular Microbiology. 40, 1273-1287 (2001).
- Bergmann, S., et al. Identification of a novel plasmin(ogen)-binding motif in surface displayed alpha-enolase of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Molecular Microbiology. 49, 411-423 (2003).
- Bergmann, S., Rohde, M., Preissner, K. T., Hammerschmidt, S. The nine residue plasminogen-binding motif of the pneumococcal enolase is the major cofactor of plasmin-mediated degradation of extracellular matrix, dissolution of fibrin and transmigration. Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 94, 304-311 (2005).
- Jagau, H., et al. Von willebrand factor mediates pneumococcal aggregation and adhesion in flow. Frontiers in Microbiology. 10, 511 (2019).
- Tischer, A., et al. Enhanced local disorder in a clinically elusive von willebrand factor provokes high-affinity platelet clumping. Journal of Molecular Biology. 429, 2161-2177 (2017).
- Ruggeri, Z. M. Structure of von willebrand factor and its function in platelet adhesion and thrombus formation. Best Practice Research Clinical Haematology. 14, 257-279 (2001).
- Spiel, A. O., Gilbert, J. C., Jilma, B. Von willebrand factor in cardiovascular disease: Focus on acute coronary syndromes. Circulation. 117, 1449-1459 (2008).
- Springer, T. A. Von Willebrand factor, Jedi knight of the bloodstream. Blood. 124, 1412-1425 (2014).
- Luttge, M., et al. Streptococcus pneumoniae induces exocytosis of weibel-palade bodies in pulmonary endothelial cells. Cellular Microbiology. 14, 210-225 (2012).
- Cornish, R. J. Flow in a Pipe of Rectangular Cross-Section. Proceedings of the Royal Society A. 786, 691-700 (1928).
- Michels, A., Swystun, L. L., Mewburn, J., Albánez, S., Lillicrap, D. Investigating von Willebrand Factor Pathophysiology Using a Flow Chamber Model of von Willebrand Factor-platelet String Formation. Journal of Visualized Experiments. 14 (126), (2017).
- Kjos, M., et al. fluorescent Streptococcus pneumoniae for live-cell imaging of host-pathogen interactions. Journal of Bacteriology. 197, 807-818 (2015).
- Bergmann, S., Steinert, M. From single cells to engineered and explanted tissues: New perspectives in bacterial infection biology. International Reviews of Cell and Molecular Biology. 319, 1-44 (2015).
- Harrison, D. J., et al. Micromachining a miniaturized capillary electrophoresis-based chemical analysis system on a chip. Science. 261 (5123), 895-897 (1993).
- Magnusson, M. K., Mosher, D. F. Fibronectin: Structure, assembly, and cardiovascular implications. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 18, 1363-1370 (1998).
- Zerlauth, G., Wolf, G. Plasma fibronectin as a marker for cancer and other diseases. The American Journal of Medicine. 77 (4), 685-689 (1984).
- Li, X. J., Valadez, A. V., Zuo, P., Nie, Z. 2012. Microfluidic 3D cell culture: potential application for tissue-based bioassays. Bioanalysis. 4, 1509-1525 (2019).
- Fiddes, L. K., et al. A circular cross-section PDMS microfluidics system for replication of cardiovascular flow conditions. Biomaterials. 31, 3459-3464 (2010).
- Schimek, K., et al. Integrating biological vasculature into a multi-organ-chip microsystem. Lab on a Chip. 13, 3588-3598 (2013).
- Pappelbaum, K. I., et al. Ultralarge von willebrand factor fibers mediate luminal Staphylococcus aureus adhesion to an intact endothelial cell layer under shear stress. Circulation. 128, 50-59 (2013).
- Schneider, S. W., et al. Shear-induced unfolding triggers adhesion of von willebrand factor fibers. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 104, 7899-7903 (2007).
- Reneman, R. S., Hoek, A. P. G. Wall shear stress as measured in vivo: consequences for the design of the arterial system. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing. 46 (5), 499-507 (2008).
- Valentijn, K. M., Sadler, J. E., Valentijn, J. A., Voorberg, J., Eikenboom, J. Functional architecture of Weibel- Palade bodies. Blood. 117, 5033-5043 (2011).
- Freshney, R. I. . Culture of animal cells: A manual of basic Technique, 5th edition. , (2005).
- Shaw, J. A., Shaw, A. J. . Epithelial cell culture- a practical approach. , 218 (1996).
- Elm, C., et al. Ectodomains 3 and 4 of human polymeric Immunoglobulin receptor (hpIgR) mediate invasion of Streptococcus pneumoniae into the epithelium. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 279 (8), 6296-6304 (2004).
- Nerlich, A., et al. Invasion of endothelial cells by tissue-invasive M3 type group A streptococci requires Src kinase and activation of Rac1 by a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-independent mechanism. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 284 (30), 20319-20328 (2009).
- Ho, C. T., et al. Liver-cell patterning lab chip: mimicking the morphology of liver lobule tissue. Lab on a Chip. 13, 3578-3587 (2013).
- Huh, D., et al. Reconstituting organ-level lung functions on a chip. Science. 328, 1662-1668 (2010).
- Harink, B., Le Gac, S., Truckenmuller, R., van Blitterswijk, C., Habibovic, P. Regeneration-on-a-chip? The perspectives on use of microfluidics in regenerative medicine. Lab on a Chip. 13, 3512-3528 (2013).

