파일럿 검사
English
소셜에 공유하기
개요
출처: 게리 레반도프스키,데이브 스트로메츠, 나탈리 시아로코-몬머스 대학교 의 연구소
어떤 실험에서 연구원은 일관된 참가자를 위한 경험을 만드는 도전이 있습니다(즉,신뢰할 수 있는) 및 정통(즉,유효). 그러나 하나의 변수를 조작하는 방법은 여러 가지가 있습니다. 예를 들어 참가자가 슬퍼하기를 원한다면 자신의 슬픈 기억을 생각하거나 슬픈 비디오를 보거나 슬픈 이야기를 읽을 수 있습니다.
연구원은 가능한 가장 효과적인 조작을 생산하기 위해 심리적 구조를 운영하는 가장 좋은 방법을 찾아야합니다. 종종, 주요 연구를 실행 하기 전에, 연구원은 파일럿 테스트(즉,시도) 그들의 효과 확인 하기 위해 그들의 조작.
이 비디오는 동일한 독립적인 변수(급성 응력)를 세 가지 방법으로 작동하는 방법을 보여 줍니다. 특히,이 연구는 최적의 스트레스를 조작하기 위해 어려운 작업 (복잡한 수학 문제 해결)에서 재생하는 최고의 소리 (정적, 똑딱 시계, 또는 우는 아기)를 식별하고자합니다.
심리학 연구는 종종 다른 과학연구보다 더 높은 표본 크기를 사용합니다. 많은 수의 참가자가 연구 중인 인구가 더 잘 표현되고 인간의 행동을 연구하는 것과 함께 오차 범위가 충분히 고려되도록 하는 데 도움이 됩니다. 이 비디오에서는 각 조건에 대해 하나씩 3명의 참가자만 사용하여 이 실험을 시연합니다. 그러나 결과에 나타난 바와 같이, 우리는 결과 섹션에 반영된 실험의 결론에 도달하기 위하여 각 조건에 대해 총 120 (40) 참가자를 이용했습니다.
Procedure
Results
The researcher used 40 participants per condition, and as a result, collected data from 120 participants overall. Numbers above reflect the mean reported stress levels that participants indicated on the 1-7 scale for the stressed item in each condition. This multi-group experiment showed how researchers can operationalize the same construct in multiple ways.
A large number of participants is necessary to ensure that the results are reliable. If this research were conducted using just a few participants, it is likely that the results would have been much different and not reflective of the greater population.
After collecting data from 120 people, an analysis of variance (ANOVA) comparing the static, ticking clock, and crying baby conditions was performed to see how they influenced stress level. As shown in Figure 3, the crying baby condition reported the most stress as hypothesized.
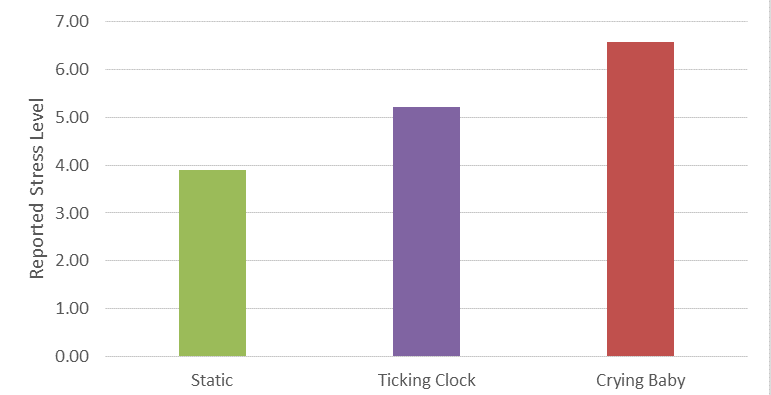
Figure 3: The effects of different noises on stress levels. Shown are the average stress levels reported by condition.
Applications and Summary
The use of a pilot test helps researchers determine the most effective way to manipulate stress. With this knowledge, researchers can use the best manipulation in their future study.
For example, researchers manipulated stress by having participants do easy or difficult math problems to determine how stress influenced relationship behaviors.1 The results indicated that those under stress were more likely to pay attention to alternate partners and were less likely to give their own partner compliments.
Another study of stress used an entirely different method for manipulating stress.2 In this study, researchers induced stress by having participants immerse their arm in cold water to see how stress influenced long-term memory. Results indicated that exposure to stress led to worse performance on long-term memory tasks.
References
- Lewandowski, G. W., Jr., Mattingly, B. A., & Pedreiro, A. Under pressure: The effects of stress on positive and negative relationship behaviors. Journal of Social Psychology. 154, 463-473. doi: 10.1080/00224545.2014.933162 (2014).
- Trammell, J. P., & Clore, G. L. Does stress enhance or impair memory consolidation? Cognition and Emotion. 28 (2), 361-374. doi:10.1080/02699931.2013.822346 (2014).
내레이션 대본
Before administering any experiment it is beneficial to perform a smaller preliminary analysis, or a pilot study, to test and refine the experimental procedure. Pilot testing is the assessment of one aspect of a pilot study.
In psychological experiments, researchers have the challenge of creating experiences for participants that are consistent and authentic; however, there are many ways to manipulate any one variable. For example, if you want participants to feel sad you can have them think of their own sad memory, watch a sad video, or read a sad story.
Researchers must find the best way to modify a psychological construct in order to produce the most effective manipulation. Often, before running the main study, researchers will “pilot test” their manipulations to check their effectiveness.
This video demonstrates how to design and execute a pilot test with an example that seeks to identify the best sound to play during a difficult task to maximally manipulate acute stress.
Before performing a pilot test, proper experimental design is essential. This process includes creation of operational definitions, or clear descriptions of specific concepts.
In this experiment, several stressful sounds are being piloted as acute stress inducers for the participant while they complete a difficult task.
For the purposes of this experiment, the operational definition of a stressful sound is any noise that creates a feeling of tension, immediacy, or anxiety within participants.
This will be manipulated through three different sounds—static, ticking clock, and crying baby—which are subjected to three experimental groups.
Next an operational definition is created for acute stress. For the purposes of this experiment, acute stress is defined as the stress or feeling of tension and strain resulting from recent demands or pressures.
Here, pressure is applied through administration of complex math problems.
In order to measure acute stress accurately, participants will be asked about their own stress levels using a straightforward question on a survey.
The item “stressed” appears embedded within several other distractor items and is rated on a 1 to 7 scale.
Distractor items are not related to the present study but are included to make the true purpose of the study less obvious.
From this scale, the experimenter will evaluate the different sounds to find which one most consistently results in the highest level of acute stress in the participant.
To conduct the study, first meet the participant at the lab. Provide the participant with informed consent. This is a brief description of the research, a sense of the procedure, an indication of potential risks and benefits, the freedom of withdrawal at any time, and a manner to get help if they experience discomfort.
To run the condition, tell the participant that they will receive a series of math problems that should be easy to solve, and they are to complete as many as possible in the 2 min time limit. Tell the participant to try to concentrate and ignore any sounds they may hear.
Next, give the participant the math problem sheet. Start the timer and immediately play the sound being tested. Now, indicate to the participant that they may start.
Following the math task, measure the dependent variable of acute stress by giving the participant a form that asks them to indicate how they currently feel.
After the experiment, debrief the participant by telling them the nature of the study. Specifically, explain that to determine what type of sound led to the most stress, three different groups worked on the same math problems for 2 min while listening to one of three sounds.
Further debrief the participant by explaining that deception was used in this experiment by indicating that the study was about concentration and that the math problems were easy.
Explain that in both cases, deception was necessary to capture the participants’ natural reaction. Divulging that the study was actually about inducing stress and that difficult math problems would be used would likely increase initial stress levels.
In a large-scale pilot study, 40 participants were tested for each sound used. This number of participants was necessary to ensure that the results are reliable and reflective of the greater population.
After collecting data from 120 people, an analysis of variance comparing the static, ticking clock, and crying baby conditions was performed to see how they influenced stress level. The numbers presented here reflect the mean reported stress levels that participants indicated on the 1 to 7 scale for the “stressed” item in each condition.
As seen in the figure, the crying baby condition reported the most stress as hypothesized.
Now that you are familiar with how researchers conduct pilot experiments, let’s take a look at how these data are incorporated into future studies.
For example, based on the results of this pilot study, researchers expanded upon the type of math problems given—easy or difficult—to induce different levels of stress and then examined the effects on relationship behaviors.
The results indicated that those under more stress were more likely to pay attention to alternate partners and were less likely to give their own partner compliments.
In another study, pilot data were collected to test the feasibility of using a multimedia mobile phone program for youth smoking cessation intervention.
As the program’s content was found to be appropriate and technically easy to distribute to the target audience, the study was designed for a larger population of youth and revealed its benefits to help youth quit smoking.
You’ve just watched JoVE’s introduction to pilot testing. Now you should have a good understanding of how to modify a variable to determine the best manipulation for an experiment. The video demonstrated how to conduct a pilot test, as well as how to evaluate the results, and concluded with examples of larger studies informed by pilot tests.
