시간 해결 전자 전도도를 통해 박막 태양 광 재료의 재조합 역학
Summary
A Time Resolved Microwave Conductivity technique for investigating direct and trap-mediated recombination dynamics and determining carrier mobilities of thin film semiconductors is presented here.
Abstract
구체적 유기 납 할라이드로서 티탄 석 광전지 재료 박막 반도체의 포토 – 유도 전하 캐리어의 재결합의 동력학을 조사하는 방법이 제공된다. 페 로브 스카이 트 막 두께 및 흡수 계수를 처음 프로필 로메 및 UV-VIS 흡수 스펙트럼을 특징으로한다. 레이저 파워와 공동 모두 감도 교정을 상세히 설명한다. 플래시 광분해 시분 전자 전도도 (부 (Trmc)) 실험을 수행하기위한 프로토콜은, 물질의 전도도를 결정하는 비접촉 방법은 제시된다. 마이크로파의 주파수의 함수로서 부 (Trmc)를 수행하여 복소 전도도의 실수 및 허수 성분을 식별하는 처리를 설명한다. 전하 캐리어 역학 (전력 및 파장을 모두 포함) 다른 여자 정권에서 결정된다. 직접 트랩 매개 붕괴 과정을 구분하는 기술을 제시하고 논의한다.결과는 모델과 반도체의 광유도 전하 캐리어의 일반적인 운동 모델을 참조하여 해석됩니다. 설명 된 기술은 유기 및 무기 광전지 재료를 포함하는 나노 입자의 광전자 재료의 넓은 범위에 적용 가능하고, 반도체 박막 / 전도성.
Introduction
플래시 광분해 시간 해결 전자 전도도 (FP-부 (Trmc))는 그 전하 캐리어 재결합 과정을 조사하기위한 이상적인 도구 만드는 NS-μs의 시간 척도에 광 여기 전하 캐리어의 역학을 모니터링합니다. 박막 반도체의 포토 – 유도 전하 캐리어의 붕괴 메커니즘을 이해하는 광기 전력 장치의 최적화를 포함한 애플리케이션의 범위 키 중요하다. 유도 캐리어 수명은 종종 유도 캐리어 밀도, 여기 파장, 이동성, 트랩 밀도와 트래핑 속도의 함수입니다. 이 논문은 캐리어 동적 종속성 (강도, 파장, 전자 레인지 주파수)와 그 해석의 넓은 범위를 조사하기위한 시간 해결 전자 전도도 (부 (Trmc)) 기술의 다양성을 보여줍니다.
Photogenerated 전하들은 이동성 degre에 따라 실수 및 재료의 유전율의 허수 부 모두를 수정할 수 감금 / 현지화 1의 전자. 물질의 도전율 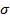 그 복소 유전율에 비례
그 복소 유전율에 비례
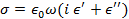
어디에 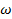 마이크로파 전계의 주파수는,
마이크로파 전계의 주파수는, 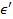 과
과 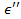 비유 전율의 실수 부이다. 따라서, 도전성의 실수 부분은 비유 전율의 허수 부에 관련되고, 도전율 (이후에, 편광이라고도 함)의 허수 부분이 공진 주파수의 변화와 관련되어있는 동안, 마이크로 웨이브 흡수에 매핑 될 수있다 전자 레인지 필드 1.
비유 전율의 실수 부이다. 따라서, 도전성의 실수 부분은 비유 전율의 허수 부에 관련되고, 도전율 (이후에, 편광이라고도 함)의 허수 부분이 공진 주파수의 변화와 관련되어있는 동안, 마이크로 웨이브 흡수에 매핑 될 수있다 전자 레인지 필드 1.
캐리어 동역학 프로브로서 마이크로파 전력을 사용하는 중요한 장점은 또한 전하 캐리어 감쇠기구의 감쇠 수명을 모니터로 / 경로는 또한 조사 할 수 있다는 점이다.
부 (Trmc)는 총 이동 3 및 수명을 결정하는데 사용될 수있다유도 전하 캐리어의 시간 4. 이러한 매개 변수는 다음에 직접 트랩 매개 재결합 메카니즘 3,5- 구별하는데 사용될 수있다. 이들 두 개의 경로 감쇠의 의존성 정량적 캐리어 밀도 3, 5, 여기 에너지 / 파장 (5)의 함수로서 분석 될 수있다. 유도 된 캐리어의 위치 파악 / 한정은 (유전율의 실수 부 허수 VS) 분극 5 대 도전성의 붕괴를 비교하여 조사 할 수있다.
또한, 아마도 가장 중요한 부 (Trmc)는 전하 캐리어 감쇠 통로 역할 트랩 상태를 특성화하기 위해 사용될 수있다. 표면 트랩, 예를 들면, 패시베이션 샘플 6 대 패시베이션 비교하여 벌크 트랩 구별 될 수있다. 서브 – 밴드 갭 상태 수직접 서브 밴드 갭 여기 에너지 (5)를 사용하여 조사한다. 트랩 밀도가 부 (Trmc) 용 데이터 (7)를 끼워 맞춤으로써 도출 될 수있다.
나노 튜브 (1), 유기 반도체 (12) 재료를 혼합, 실리콘 (6), (8) 및 이산화 티탄 9, 10과 같은 기존의 박막 반도체 11 나노 입자 : 때문에이 기술의 다양성에 부 (Trmc)를 포함한 다양한 재료를 연구에 적용된 13, 14, 및 하이브리드 광전지 재료 3, 4, 5.
부 (Trmc)를 이용하여 정량적 인 정보를 획득하기 위해, 정확하게 수를 결정할 수 있도록 중요주어진 광 여진 용 광자 흡수. 박막, 나노 입자, 솔루션 및 불투명 한 샘플의 흡수를 정량화하는 방법이 다르기 때문에, 여기에 제시된 샘플 준비 및 교정 기술은 박막 샘플을 위해 특별히 설계되었습니다. 그러나, 제시된 측정 부 (Trmc) 프로토콜은 매우 일반적이다.
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
부 (Trmc) 기법 광유 전하 캐리어 역학에 대한 풍부한 정보를 제공 할 수 있지만,이 도전성의 간접 측정이므로, 결과를 해석 할 때주의 할 필요가 관심. 부 (Trmc) 기술은 전체 이동도를 측정하고, 전자와 정공 이동도를 구별하는 데 사용할 수 없다. 변화가 작은 (<5 %) 16 때만 도전성 반사 전력의 변화에 비례한다는 기본 가정은 보유하고있다. 붕괴시의 공진 주파수의 변화가 큰 경?…
Declarações
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
Acknowledgment is made to the Australian Research Council (LE130100146, DP160103008). JAG is supported via an Australian Postgraduate Award, and DRM by an ARC Future Fellowship (FT130100214). We thank Nikos Kopidakis for helpful discussions.
Materials
| Hellmanex III detergent | Sigma Aldrich www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/sial/z805939?lang=en®ion=AU |
Z805939 | Corrosive and toxic. See SDS. |
| Lead (II) iodide (99%) | Sigma Aldrich www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/aldrich/211168?lang=en®ion=AU |
211168 | Toxic. See SDS |
| Anhydrous dimethylformamide (99.8%) | Sigma Aldrich www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/sial/227056?lang=en®ion=AU |
227056 | Toxic. See SDS |
| Anhydrous dimethylsulfoxide (99.9%) | Sigma Aldrich www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/sial/276855?lang=en®ion=AU |
276855 | Toxic. See SDS |
| Anhydrous 2-Propanol (99.5%) | Sigma Aldrich www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/sial/278475?lang=en®ion=AU&gclid= COnlgPaw780CFQZvvAod17EA4Q |
278475 | |
| Methylammonium iodide | Dyesol www.dyesol.com/products/dsc-materials/perovskite-precursors/methylammonium-iodide.html |
MS101000 | Also sold by Sigma Aldrich |
| Poly(methyl methacrylate) | Sigma Aldrich | 445746 | |
| Anhydrous chlorobenzene (99.8%) | Sigma Aldrich www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/aldrich/445746?lang=en®ion=AU |
284513 | Toxic. See SDS |
| Equipment | Company | Model | Comments/Description |
| UV-VIS-NIR spectrophotometer | Perkin-Elmer | Lambda 900 | |
| Profilometer | Veeco | Dektak 150 | |
| Vector Network Analyzer | Keysight www.keysight.com/en/pdx-x201927-pn-N9918A/fieldfox-handheld-microwave-analyzer-265-ghz?cc=US&lc=eng |
Fieldfox N9918A | |
| Tunable wavelength laser | Opotek www.opotek.com/product/opolette-355 |
Opolette 355 | |
| Neutral density filters | Thorlabs www.thorlabs.hk/newgrouppage9.cfm?objectgroup_id=3193 |
NUK01 | |
| Power meter | Thorlabs www.thorlabs.com/thorproduct.cfm?partnumber=PM100D |
PM100D | |
| Power sensor | Thorlabs www.thorlabs.com/thorproduct.cfm?partnumber=S401C |
S401C | |
| Cavity | Custom built | The cavity used in for this experiment was designed and built in-house. |
Referências
- Park, J., Reid, O. G., Blackburn, J. L., Rumbles, G. Photoinduced spontaneous free-carrier generation in semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotubes. Nat. Comm. 6 (8809), (2015).
- Dicker, G., de Haas, M. P., Siebbeles, L. D., Warman, J. M. Electrodeless time-resolved microwave conductivity study of charge-carrier photogeneration in regioregular poly (3-hexylthiophene) thin films. Phys. Rev. B. 70 (4), 045203 (2004).
- Oga, H., Saeki, A., Ogomi, Y., Hayase, S., Seki, S. Improved understanding of the electronic and energetic landscapes of perovskite solar cells: high local charge carrier mobility, reduced recombination, and extremely shallow traps. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136 (39), 13818-13825 (2014).
- Ponseca, C. S., et al. Organometal halide perovskite solar cell materials rationalized: ultrafast charge generation, high and microsecond-long balanced mobilities, and slow recombination. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136 (14), 5189-5192 (2014).
- Guse, J. A., et al. Spectral dependence of direct and trap-mediated recombination processes in lead halide perovskites using time resolved microwave conductivity. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18, 12043-12049 (2016).
- Kunst, M., Abdallah, O., Wünsch, F. Passivation of silicon by silicon nitride films. Solar energy materials and solar cells. 72 (1-4), 335-341 (2002).
- Hutter, E. M., Eperon, G. E., Stranks, S. D., Savenije, T. J. Charge Carriers in Planar and Meso-Structured Organic-Inorganic Perovskites: Mobilities, Lifetimes and Concentrations of Trap States. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 6 (15), 3082-3090 (2015).
- Cosme, I., et al. Lifetime assessment in crystalline silicon: From nanopatterned wafer to ultra-thin crystalline films for solar cells. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells. 135, 93-98 (2015).
- Katoh, R., Furube, A., Yamanaka, K. I., Morikawa, T. Charge separation and trapping in N-doped TiO2 photocatalysts: A time-resolved microwave conductivity study. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 1 (22), 3261-3265 (2010).
- Colbeau-Justin, C., Valenzuela, M. A. Time-resolved microwave conductivity (TRMC) a useful characterization tool for charge carrier transfer in photocatalysis: a short review. Revista mexicana de física. 59 (3), 191-200 (2013).
- Luna, A. L., et al. Synergetic effect of Ni and Au nanoparticles synthesized on titania particles for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen production. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental. 191, 18-28 (2016).
- Ferguson, A. J., Kopidakis, N., Shaheen, S. E., Rumbles, G. Quenching of excitons by holes in poly (3-hexylthiophene) films. J. Phys. Chem. C. 112 (26), 9865-9871 (2008).
- Ferguson, A. J., Kopidakis, N., Shaheen, S. E., Rumbles, G. Dark carriers, trapping, and activation control of carrier recombination in neat P3HT and P3HT: PCBM blends. J. Phys. Chem. C. 115 (46), 23134-23148 (2011).
- Savenije, T. J., Ferguson, A. J., Kopidakis, N., Rumbles, G. Revealing the Dynamics of Charge Carriers in Polymer:fullerene Blends Using Photoinduced Time-Resolved Microwave Conductivity. J. Phys. Chem. C. 117 (46), 24085-24103 (2013).
- Xiao, Z., et al. Efficient, high yield perovskite photovoltaic devices grown by interdiffusion of solution-processed precursor stacking layers. Energy Environ. Sci. 7 (8), 2619-2623 (2014).
- Infelta, P. P., De Haas, M. P., Warman, J. M. The study of the transient conductivity of pulse irradiated dielectric liquids on a nanosecond timescale using microwaves. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 10 (5-6), 353-365 (1977).
- Saeki, A., Seki, S., Sunagawa, T., Ushida, K., Tagawa, S. Charge-carrier dynamics in polythiophene films studied by in-situ measurement of flash-photolysis time-resolved microwave conductivity (FP-TRMC) and transient optical spectroscopy (TOS). Philosophical Magazine. 86 (9), 1261-1276 (2006).
- Choi, W., Miyakai, T., Sakurai, T., Saeki, A., Yokoyama, M., Seki, S. Non-contact, non-destructive, quantitative probing of interfacial trap sites for charge carrier transport at semiconductor-insulator boundary. Appl. Phys. Lett. 105 (3), 033302 (2014).

