Rask og spesifikk Immunomagnetic isolasjon av musen primære Oligodendrocytes
Summary
Vi beskriver immunomagnetic isolasjon av hovedknappen på musen oligodendrocytes, som gir rask og spesifikk isolering av celler for i vitro kultur.
Abstract
Effektiv og robust isolasjon og kultur av primære oligodendrocytes (OLs) er et verdifullt verktøy for i vitro studier av utviklingen av oligodendroglia i tillegg til biologi av demyeliniserende sykdommer som multippel sklerose og Pelizaeus-Merzbacher-lignende sykdom (PMLD). Her presenterer vi en enkel og effektiv utvalg metode for immunomagnetic isolasjon av fase tre O4+ preoligodendrocytes celler fra neonatal mus pups. Siden umodne OL utgjør mer enn 80% av gnager-hjerne hvit saken i postnatal dag 7 (P7) denne isolasjon metoden ikke bare sikrer høy mobil ytelse, men også spesifikke isolasjon OLS allerede forpliktet til oligodendroglial slektslinje, redusere den muligheten for å isolere forurensende cellene som astrocyttene og andre fra musen hjernen. Denne metoden er en modifikasjon av teknikkene rapportert tidligere, og gir oligodendrocyte forberedelse renhet over 80% på omtrent 4 h.
Introduction
Oligodendrocytes (OLs) er de myelinating cellene i sentralnervesystemet (CNS)1. Isolasjon og kultur av primære oligodendrocytes i et strengt regulert miljø er et verdifullt verktøy for i vitro studier av utviklingen av oligodendroglia i tillegg til biologi av demyeliniserende sykdommer som multippel sklerose2 . Dette krever en effektiv og robust oligodendrocyte isolasjon og kultur metode3. I denne studien tok vi fordel av uttrykk for en særegen oligodendrocyte celle overflaten markør å implementere en modifisert isolasjon teknikk som er rask og spesifikk.
Fire forskjellige stadier av oligodendrocyte modning har blitt identifisert, hver preget av uttrykk for karakteristiske celle overflate markører for hver utviklingsstadiet (figur 1). Stikkordmerker cellen overflaten kan bli gjenkjent av spesifikke antistoffer4,5, og kan brukes til å isolere OLs på bestemte stadier. I den første fasen har oligodendrocyte forløper celler (OPCs) kapasitet til å spre, overføre og spesielt Ekspress blodplater-avledet vekst faktor reseptor (PDGF-Rα)6, ganglioside A2B5, proteoglycan NG27,8 , polysialic syre-nevrale celle vedheft molekyl9 og fatty-acid-bindende protein 7 (FABP7)10. OPCs har bipolar morfologi med noen korte prosesser kommer fra de motsatte polakkene av celle som er karakteristisk for neural forløper celler11.
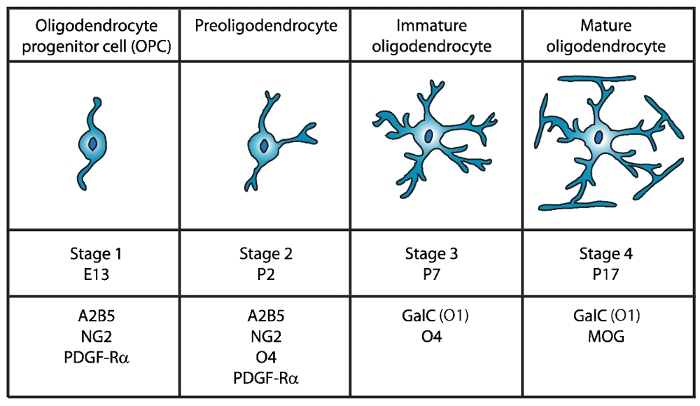
Figur 1: uttrykk for cellen overflate markører under musen oligodendrocyte utviklingen. OLs celle overflate markører som A2B5, GalC (O1), NG2, O4 og PDGF-Rα kan brukes til å isolere spesielt oligodendrocytes på bestemte utviklingsstadiet ved hjelp av spesifikke antistoffer. Klikk her for å se en større versjon av dette tallet.
I den andre fasen, OPCs gi opphav til preoligodendrocytes og express på cellemembranen ikke bare OPC markører, men også sulfatide (en sulfated galactolipid) anerkjent av O4 antistoff12,13, og i GPR17 protein14, som vedvarer til umodne oligodendrocyte (OL) scenen. På dette stadiet utvide preoligodendrocytes multipolar kort prosesser. Preoligodendrocytes er den store OL-scenen postnatal dag 2 (P2) i cerebral hvit saken rotte og mus med en liten befolkning umodne OLs15.
I den tredje fasen fortsatt umodne OLs å uttrykke O4, mister uttrykk for A2B5 og NG2 og begynne å uttrykke galactocerebroside C16. På dette stadiet, OLs er forpliktet til oligodendroglial slektslinje og bli etter mitotisk celler med lang ramified grener17,18. Umodne OL utgjør mer enn 80% av gnager hvit saken på P7 og nå første MBP+ cellene er observert15,19,20,21. Derfor kunne isolasjon OLS på P7 sikre høy mobil ytelse.
I den siste og fjerde fasen av OL utvikling uttrykke modne OLs myelinating proteiner (myelin basic protein (MBP), proteolipid protein (PLP), myelin forbundet glykoprotein (MAG) og myelin oligodendrocyte glykoprotein (MOG)22,23 ,24,25,26. På dette stadiet, modne OLs utvide membraner som skjemaet kompakt enwrapping hylser rundt axons og kan myelinate. Dette sammenfaller med observasjon at i rotte og mus hjernen, MBP+ celler blir stadig rike på P1419,20,21.
Siden første isolering av oligodendrocyte av Fewster og kolleger i 196727, har flere metoder for isolering av OLs fra gnagere CNS implementert inkludert immunopanning28,29,30, fluorescens-aktivert celle sortering (FACS) utnytte cellen overflaten-spesifikke antigener28,31, differensial gradient sentrifugering32,33,34,35 og risting metode basert på differensial etterlevelse av ulike CNS glia36,37. Eksisterende kultur metoder har imidlertid begrensninger, særlig i forhold til renhet, avkastning og tiden det tar å utføre prosedyrer38. Mer effektiv isolasjon metoder for oligodendrocytes er derfor nødvendig.
I dette papiret, presenterer vi en enkel og effektiv utvalg metode for immunomagnetic isolasjon av scene tre O4+ preoligodendrocytes celler fra neonatal mus pups. Denne metoden er en modifikasjon av teknikkene rapportert av Emery et al. 39 og Dincman et al. 40 og gir en oligodendrocyte forberedelse renhet over 80% på omtrent 4 h.
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
I dette innlegget presenterer vi en metode for effektiv isolasjon av høyrenset umodne musen oligodendrocyte kulturer. I forhold til tidligere publiserte protokoller39,40, gitt denne metoden en høyere renhet med et mye lavere nivå av GFAP-positive astrocyttene og en svært lav prosentandel av andre ikke-preget celler. Det er viktig å påpeke at disse er umodne OLs allerede forpliktet seg til den oligodendroglial avstamning. Dermed ville disse cellene ikke vær…
Declarações
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
Denne studien ble støttet av tilskudd fra det nasjonal multippel sklerose samfunnet (RG4591A1/2) og National Institutes of Health (R03NS06740402). Forfatterne takker Dr. Ivan Hernandez og hans lab medlemmer for å gi laboratoriet plass, utstyr og råd.
Materials
| 10ml serological pipets | Fisher Scientific | 13-676-10J | |
| 10ml syringe Luer-Loc tip | BD, Becton Dickinson | 309604 | |
| 15ml conical tubes | Falcon | 352097 | |
| 24-well tissue culture plates | Falcon | 353935 | |
| 40µm cell strainer | Fisher Scientific | 22368547 | |
| 50ml conical tubes | Falcon | 352098 | |
| 5ml serological pipets | Fisher Scientific | 13-676-10H | |
| 60mm tissue culture plates | Falcon | 353002 | |
| 70µm cell strainer | Fisher Scientific | 22363548 | |
| Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) secondary antibody | Invitrogen | A11001 | |
| Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-rabbit IgM (H+L) secondary antibody | Invitrogen | A21042 | |
| Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-rabbit IgM (H+L) secondary antibody | Invitrogen | A11008 | |
| Alexa Fluor 594 goat anti-chicken IgG (H+L) secondary antibody | Invitrogen | A11042 | |
| Anti-O4 beads- Anti-O4MicroBeads | Miltenyi Biotec | 130-094-543 | |
| Apo-Transferrin human | Sigma | T1147 | |
| Autofil complete bottle top filter assembly, 0.22um filter, 250ml | USA Scientific | 6032-1101 | |
| Autofil complete bottle top filter assembly, 0.22um filter, 250ml | USA Scientific | 6032-1102 | |
| B27 Supplement | Invitrogen | 17504-044 | |
| Boric acid | Sigma | B7660 | |
| Bovine Growth Serum (BGS) | GE Healthcare Life Sciences | SH30541.03 | |
| BSA | Fisher Scientific | BP-1600-100 | |
| CNTF | Peprotech | 450-50 | |
| d-Biotin | Sigma | B4639 | |
| Desoxyribonuclease I (DNAse I) | Worthington | LS002007 | |
| EDTA | Fisher Scientific | S311 | |
| Epifluorescence microscope with an Olympus DP70 camera | Olympus | Bx51 | |
| Feather disposable scalpels | Andwin Scientific | EF7281C | |
| Forskolin | Sigma | F6886 | |
| German glass coverslips, #1 thickness, 12mm diameter round | NeuVitro | GG-12-oz | |
| GFAP antibody | Aves | GFAP | |
| Glucose | Fisher Scientific | D16-1 | |
| GlutaMAX | Invitrogen | 35050-61 | |
| Insulin | Invitrogen | 12585-014 | |
| Magnetic separator stand – MACS multistand | Miltenyi Biotec | 130-042-303 | |
| Magnetic separator-MiniMACS separator | Miltenyi Biotec | 130-042-302 | |
| Millex PES 0.22µm filter unit | Millipore | SLG033RS | |
| Mounting media- Prolong Gold with DAPI | Thermo Fisher | P36930 | |
| N-acetyl-cysteine (NAC) | Sigma | A8199 | |
| Natural mouse laminin | Invitrogen | 23017-015 | |
| Neurobasal Medium A | Invitrogen | 10888-022 | |
| Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) | Peprotech | 450-03 | |
| NG2 antibody | Millipore | AB5320 | |
| Papain | Worthington | LS003126 | |
| PBS without Ca2+ and Mg2+ | Sigma | D5652 | |
| PDGF | Peprotech | 100-13A | |
| Petri dishes | Falcon | 351029 | |
| Poly-D-Lysine | Sigma | P6407 | |
| Primocin | Invivogen | ant-pm-2 | |
| Progesterone | Sigma | P8783 | |
| Putrescine | Sigma | P5780 | |
| Selection column-LS columns | Miltenyi Biotec | 130-042-401 | |
| Sodium Selenite | Sigma | S5261 | |
| Trace elements B | Corning | 25-000-CI | |
| Triiodothyronine (T3) | Sigma | T6397 | |
| Triton-X | Sigma | T8787 | |
| Trypan Blue Solution | Corning | 25-900-CI | |
| Tween 20 | Sigma | P1379 | |
| B27NBMA | 487.75 mL Neurobasal Medium A; 10 mL B27 Supplement; 1 mL Primocin; 1.25 mL Glutamax; Filter sterilize and store at 4 °C until use. | ||
| B27NBMA + 10% BGS | 27 mL B27NBMA; 3 mL Bovine growth serum | ||
| CNTF solution stock (10 µg/ml; 1000X) | Order from Peprotech (450-50). Make up at 0.1 to 1 mg/ml according to Manufacturer’s instruction (may vary from lot to lot) in buffer (e.g. DPBS + 0.2% BSA). Store at -80 °C. Working solution (10 µg/ml, 1000X) 1. Make on 0.2% BSA (Fisher scientific BP-1600-100) in DPBS solution and filter sterilize. 2. Dilute master stock aliquot to 10µg/ml in sterile, chilled 0.2% BSA/DPBS. 3. Aliquot (20µl/tube) and snap freeze in liquid nitrogen. 4. Store aliquots at -80 °C. |
||
| d-Biotin stock solution (50 µg/ml; 5000X) | Resuspend d-Biotin (Sigma-B4639) in double-distilled H2O at 50 µg/ml (e.g. 2.5 mg in 50 ml of ddH2O). Resuspension might take fair amount of agitation/vortexing, or mild warming briefly at 37°C. If the d-Biotin still will not solubilize, it is fine to make up a less concentrated (e.g. 10µg/ml), and to add a higher volume to the B27NBMA (1/1000), instead of 1/5000). Store at 4°C. | ||
| DNase I stock solution | 1. Dissolve at 12,500 U Deoxyribonuclease I / ml in HBSS chilled on ice. 2. Filter sterilize on ice 3. Aliquot at 200 µl and freeze overnight at -20°C. 4. Store aliquots at -20 to -30°C. |
||
| Dulbecco’s Phosphate Buffered Saline (w/o Ca2+ and Mg2+) | Dissolve pouch in 1 Liter of water to yield 1 liter of medium at 9.6 grams of powder per liter of medium. Store at 2-8 °C. | ||
| Forskolin stock solution (4.2 mg/ml; 1000X) | Add 1 ml of sterile DMSO to 50 mg Forskolin in bottle (Sigma-F6886) and pipette until resuspended. Transfer to a 15 ml centrifuge tube and add 11 ml of sterile DMSO to bring to 4.2 mg/ml. Aliquot (e.g. 20 µl) and store at -20°C. | ||
| Hank’s balanced salts (HBSS) (Sigma | 1. Measure 900 ml of water (temperature 15-20 °C) in a cylinder and stir gently. 2. Add the power and stir until dissolved. 3. Rinse original package with a small amount of water to remove all traces of the powder. 4. Add to the solution in step 2. 5. Add 0.35 gr of sodium bicarbonate (7.5% w/v) for each liter of final volume. 6. Keep stirring until dissolved. 7. Adjust the pH of the buffer while stirring to 0.1-0.3 units below pH= 7.4 since it may rise during filtration. The use of 1N HCl or 1N NaOH is recommended to adjust the pH. 8. Add additional water to bring the final volume to 1L. 9. Sterilize by filtration using a membrane with a porosity of 0.22 microns. 10. Store at 2-8 °C. |
||
| Insulin stock solution (4000 µg/ml) | Thaw the bottle and aliquot 25 µl per microcentrifuge tube and store at -20°C. | ||
| Laminin solution | Slowly thaw laminin in the cold (2°C to 8°C) to avoid gel formation. Then, aliquot into polypropylene tubes. Store at 5° C to -20° C in aliquots (e.g. 20 µl) and do not freeze/thaw repeatedly. Laminin may be stored at these temperatures for up to six months. | ||
| Magnetic Cell Sorting (MCS) Buffer | Prepare the solution containing phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.2, and 0.5% bovine serum albumin (BSA), 0.5 mM EDTA, 5µg/ml Insulin, 1 g/L Glucose. Sterilize and degas by filtration the buffer by passing it through a 0.22 µm Millex filter. Store the buffer at 4°C until use | ||
| N-Acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) stock solution (5mg/ml; 1000X) | Dissolve N-Acetyl-L-cysteine (Sigma-A8199) at 5 mg/ml in DMEM (e.g. 50 mg NAC in 10 ml B27NBMA). Filter sterilize and aliquot (e.g. 20 µl). Store at -20°C. | ||
| NT3 stock solution (1 µg/ml; 1000X) | Master stock: Order from Peprotech (450-03). Make up at 0.1 to 1 mg/ml according to manufacturer’s instructions (may vary from lot to lot), in buffer (e.g. DPBS + 0.2% BSA). Store at -80°C. Working stock (1µg/ml; 1000X): 1. Make on 0.2% BSA in DPBS solution and filter sterilize. 2. Dilute master stock aliquot to 1 µg/ml in sterile, chilled 0.2% BSA/DPBS. 3. Aliquot (e.g. 20µl/tube) and snap freeze in liquid nitrogen. 4. Store aliquots at -80°C. |
||
| PDGF stock solution (10 µg/ml; 1000X) | Master stock: Order from Peprotech (100-13A). Make up at 0.1 to 1 mg/ml according to manufacturer’s instructions (may vary from lot to lot) in buffer (e.g. DPBS) + 0.2% BSA). Store at -80°C. Working stock (1µg/ml; 1000X): 1. Make on 0.2% BSA in DPBS solution and filter sterilize. 2. Dilute master stock aliquot to 1µg/ml in sterile, chilled 0.2% BSA/DPBS. 3. Aliquot (e.g. 20µl/tube) and snap freeze in liquid nitrogen. 4. Store aliquots at -80°C. |
||
| Poly-D-lysine (1mg/ml; 100X) | Resuspend poly-D-lysine, molecular weight 70-150 kD (Sigma P6407) at 0.5mg/ml in 0.15M boric acid pH 8.4 (e.g. 50mg in 50ml borate buffer). Filter sterilize and aliquot (e.g. 100µl/tube). Store at -20°C. Prior to use, dilute the 100X stock (1mg/ml) to 50 µg/ml in sterile water. | ||
| Oligodendrocyte proliferation media | see Supplementary Table 1 | ||
| Oligodendrocyte differentiation media | see Supplementary Table 1 | ||
| Sato supplement (100X) | see Supplementary Table 1 | ||
| References: the list of reagents and recipes were adopted from the protocols previously described by Emery et. al. 2013 (Emery, B. & Dugas, J. C. Purification of oligodendrocyte lineage cells from mouse cortices by immunopanning. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2013 (9), 854-868, doi:10.1101/pdb.prot073973, (2013)) and Dincman et. al. (Dincman, T. A., Beare, J. E., Ohri, S. S. & Whittemore, S. R. Isolation of cortical mouse oligodendrocyte precursor cells. J Neurosci Methods. 209 (1), 219-226, doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2012.06.017, (2012)) |
Referências
- Emery, B. Regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation and myelination. Science. 330 (6005), 779-782 (2010).
- Yang, Z., Watanabe, M., Nishiyama, A. Optimization of oligodendrocyte progenitor cell culture method for enhanced survival. J Neurosci Methods. 149 (1), 50-56 (2005).
- Niu, J., et al. An efficient and economical culture approach for the enrichment of purified oligodendrocyte progenitor cells. J Neurosci Methods. 209 (1), 241-249 (2012).
- Zhang, S. C. Defining glial cells during CNS development. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2 (11), 840-843 (2001).
- Pfeiffer, S. E., Warrington, A. E., Bansal, R. The oligodendrocyte and its many cellular processes. Trends Cell Biol. 3 (6), 191-197 (1993).
- Hart, I. K., Richardson, W. D., Heldin, C. H., Westermark, B., Raff, M. C. PDGF receptors on cells of the oligodendrocyte-type-2 astrocyte (O-2A) cell lineage. Development. 105 (3), 595-603 (1989).
- Nishiyama, A., Lin, X. H., Giese, N., Heldin, C. H., Stallcup, W. B. Interaction between NG2 proteoglycan and PDGF alpha-receptor on O2A progenitor cells is required for optimal response to PDGF. J Neurosci Res. 43 (3), 315-330 (1996).
- Pringle, N. P., Mudhar, H. S., Collarini, E. J., Richardson, W. D. PDGF receptors in the rat CNS: during late neurogenesis, PDGF alpha-receptor expression appears to be restricted to glial cells of the oligodendrocyte lineage. Development. 115 (2), 535-551 (1992).
- Grinspan, J. B., Franceschini, B. Platelet-derived growth factor is a survival factor for PSA-NCAM+ oligodendrocyte pre-progenitor cells. J Neurosci Res. 41 (4), 540-551 (1995).
- Sharifi, K., et al. Differential expression and regulatory roles of FABP5 and FABP7 in oligodendrocyte lineage cells. Cell Tissue Res. 354 (3), 683-695 (2013).
- Chittajallu, R., Aguirre, A., Gallo, V. NG2-positive cells in the mouse white and grey matter display distinct physiological properties. J Physiol. 561 (Pt 1), 109-122 (2004).
- Bansal, R., Warrington, A. E., Gard, A. L., Ranscht, B., Pfeiffer, S. E. Multiple and novel specificities of monoclonal antibodies O1, O4, and R-mAb used in the analysis of oligodendrocyte development. J Neurosci Res. 24 (4), 548-557 (1989).
- Sommer, I., Schachner, M. Monoclonal antibodies (O1 to O4) to oligodendrocyte cell surfaces: an immunocytological study in the central nervous system. Dev Biol. 83 (2), 311-327 (1981).
- Boda, E., et al. The GPR17 receptor in NG2 expressing cells: focus on in vivo cell maturation and participation in acute trauma and chronic damage. Glia. 59 (12), 1958-1973 (2011).
- Dean, J. M., et al. Strain-specific differences in perinatal rodent oligodendrocyte lineage progression and its correlation with human. Dev Neurosci. 33 (3-4), 251-260 (2011).
- Yu, W. P., Collarini, E. J., Pringle, N. P., Richardson, W. D. Embryonic expression of myelin genes: evidence for a focal source of oligodendrocyte precursors in the ventricular zone of the neural tube. Neuron. 12 (6), 1353-1362 (1994).
- Armstrong, R. C., Dorn, H. H., Kufta, C. V., Friedman, E., Dubois-Dalcq, M. E. Pre-oligodendrocytes from adult human CNS. J Neurosci. 12 (4), 1538-1547 (1992).
- Gard, A. L., Pfeiffer, S. E. Oligodendrocyte progenitors isolated directly from developing telencephalon at a specific phenotypic stage: myelinogenic potential in a defined environment. Development. 106 (1), 119-132 (1989).
- Bjelke, B., Seiger, A. Morphological distribution of MBP-like immunoreactivity in the brain during development. Int J Dev Neurosci. 7 (2), 145-164 (1989).
- Hardy, R. J., Friedrich, V. L. Progressive remodeling of the oligodendrocyte process arbor during myelinogenesis. Dev Neurosci. 18 (4), 243-254 (1996).
- Hartman, B. K., Agrawal, H. C., Kalmbach, S., Shearer, W. T. A comparative study of the immunohistochemical localization of basic protein to myelin and oligodendrocytes in rat and chicken brain. J Comp Neurol. 188 (2), 273-290 (1979).
- Wei, Q., Miskimins, W. K., Miskimins, R. Stage-specific expression of myelin basic protein in oligodendrocytes involves Nkx2.2-mediated repression that is relieved by the Sp1 transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 280 (16), 16284-16294 (2005).
- Stolt, C. C., et al. Terminal differentiation of myelin-forming oligodendrocytes depends on the transcription factor Sox10. Genes Dev. 16 (2), 165-170 (2002).
- Emery, B., et al. Myelin gene regulatory factor is a critical transcriptional regulator required for CNS myelination. Cell. 138 (1), 172-185 (2009).
- Reynolds, R., Wilkin, G. P. Development of macroglial cells in rat cerebellum. II. An in situ immunohistochemical study of oligodendroglial lineage from precursor to mature myelinating cell. Development. 102 (2), 409-425 (1988).
- Scolding, N. J., et al. Myelin-oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) is a surface marker of oligodendrocyte maturation. J Neuroimmunol. 22 (3), 169-176 (1989).
- Fewster, M. E., Scheibel, A. B., Mead, J. F. The preparation of isolated glial cells from rat and bovine white matter. Brain Res. 6 (3), 401-408 (1967).
- Gard, A. L., Williams, W. C., Burrell, M. R. Oligodendroblasts distinguished from O-2A glial progenitors by surface phenotype (O4+GalC-) and response to cytokines using signal transducer LIFR beta. Dev Biol. 167 (2), 596-608 (1995).
- Gard, A. L., Pfeiffer, S. E. Glial cell mitogens bFGF and PDGF differentially regulate development of O4+GalC- oligodendrocyte progenitors. Dev Biol. 159 (2), 618-630 (1993).
- Barres, B. A., Raff, M. C. Proliferation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells depends on electrical activity in axons. Nature. 361 (6409), 258-260 (1993).
- Behar, T., McMorris, F. A., Novotny, E. A., Barker, J. L., Dubois-Dalcq, M. Growth and differentiation properties of O-2A progenitors purified from rat cerebral hemispheres. J Neurosci Res. 21 (2-4), 168-180 (1988).
- Vitry, S., Avellana-Adalid, V., Lachapelle, F., Baron-Van Evercooren, A. Migration and multipotentiality of PSA-NCAM+ neural precursors transplanted in the developing brain. Mol Cell Neurosci. 17 (6), 983-1000 (2001).
- Duncan, I. D., Paino, C., Archer, D. R., Wood, P. M. Functional capacities of transplanted cell-sorted adult oligodendrocytes. Dev Neurosci. 14 (2), 114-122 (1992).
- Goldman, J. E., Geier, S. S., Hirano, M. Differentiation of astrocytes and oligodendrocytes from germinal matrix cells in primary culture. J Neurosci. 6 (1), 52-60 (1986).
- Althaus, H. H., Montz, H., Neuhoff, V., Schwartz, P. Isolation and cultivation of mature oligodendroglial cells. Naturwissenschaften. 71 (6), 309-315 (1984).
- McCarthy, K. D., de Vellis, J. Preparation of separate astroglial and oligodendroglial cell cultures from rat cerebral tissue. J Cell Biol. 85 (3), 890-902 (1980).
- Szuchet, S., Yim, S. H. Characterization of a subset of oligodendrocytes separated on the basis of selective adherence properties. J Neurosci Res. 11 (2), 131-144 (1984).
- Chew, L. J., DeBoy, C. A., Senatorov, V. V. Finding degrees of separation: experimental approaches for astroglial and oligodendroglial cell isolation and genetic targeting. J Neurosci Methods. 236, 125-147 (2014).
- Emery, B., Dugas, J. C. Purification of oligodendrocyte lineage cells from mouse cortices by immunopanning. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2013 (9), 854-868 (2013).
- Dincman, T. A., Beare, J. E., Ohri, S. S., Whittemore, S. R. Isolation of cortical mouse oligodendrocyte precursor cells. J Neurosci Methods. 209 (1), 219-226 (2012).
- Buttery, P. C., ffrench-Constant, C. Laminin-2/integrin interactions enhance myelin membrane formation by oligodendrocytes. Mol Cell Neurosci. 14 (3), 199-212 (1999).
- Chun, S. J., Rasband, M. N., Sidman, R. L., Habib, A. A., Vartanian, T. Integrin-linked kinase is required for laminin-2-induced oligodendrocyte cell spreading and CNS myelination. J Cell Biol. 163 (2), 397-408 (2003).
- Colognato, H., Ramachandrappa, S., Olsen, I. M., ffrench-Constant, C. Integrins direct Src family kinases to regulate distinct phases of oligodendrocyte development. J Cell Biol. 167 (2), 365-375 (2004).
- ffrench-Constant, C., Colognato, H. Integrins: versatile integrators of extracellular signals. Trends Cell Biol. 14 (12), 678-686 (2004).
- Oh, L. Y., Yong, V. W. Astrocytes promote process outgrowth by adult human oligodendrocytes in vitro through interaction between bFGF and astrocyte extracellular matrix. Glia. 17 (3), 237-253 (1996).
- Besnard, F., Perraud, F., Sensenbrenner, M., Labourdette, G. Effects of acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors on proliferation and maturation of cultured rat oligodendrocytes. Int J Dev Neurosci. 7 (4), 401-409 (1989).
- Armstrong, R., Friedrich, V. L., Holmes, K. V., Dubois-Dalcq, M. In vitro analysis of the oligodendrocyte lineage in mice during demyelination and remyelination. J Cell Biol. 111 (3), 1183-1195 (1990).
- Grinspan, J. B., Stern, J. L., Franceschini, B., Pleasure, D. Trophic effects of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) on differentiated oligodendroglia: a mechanism for regeneration of the oligodendroglial lineage. J Neurosci Res. 36 (6), 672-680 (1993).
- Mason, J. L., Goldman, J. E. A2B5+ and O4+ Cycling progenitors in the adult forebrain white matter respond differentially to PDGF-AA, FGF-2, and IGF-1. Mol Cell Neurosci. 20 (1), 30-42 (2002).
- Schildge, S., Bohrer, C., Beck, K., Schachtrup, C. Isolation and culture of mouse cortical astrocytes. J Vis Exp. (71), (2013).

