- 00:00Visão Geral
- 01:28Principles of Measuring Turbidity and Total Solids
- 04:22Measuring Turbidity
- 05:56Measuring Total Solids
- 07:15Representative Results: Interpreting Impact on Water Quality
- 08:06Applications
- 09:19Summary
浊度和地表水中的总固体
English
COMPARTILHAR
Visão Geral
资料来源: 玛格丽特工人和金伯利弗莱-Depaul 大学实验室
浊度和总固形物是相关的测量处理地表水的清晰度。浊度是光的间接测量确定的可以通过水量的水清晰度。总固形物是直接测定重量测定水中悬浮的固体颗粒。
高水平的浊度和总固形物是由土壤侵蚀、 排废、 径流或生态社区包括藻类生长或可以入水了扰乱沉积物的底栖生物数量的变化引起的。高水平的浊度和悬浮的固体可以通过吸收热量增加导致水温度和氧含量 (温水持有较少的氧气) 跌幅降低水质量。这些条件也可能会导致降低光合作用,更少的阳光穿透水,使水不能支持一些水生生物。悬浮的物也可以堵塞鱼鳃、 扼杀鸡蛋、 降低经济增长率,和扰乱许多水生生物生境。
一种测量浊度的方法包括使用塞齐盘。塞齐盘是一个金属盘与备用黑色和白色处所 (图 1)。它被连接到具有单脚标记沿着它的绳子。磁盘被放入水,直到它再也不能看到 (图 2)。这种方法的缺点是必须在该字段中,理想的协议需要晴朗的条件和测试区是阴影。此外,如果有大河岸和水位之间的距离,它很难使用塞齐盘。通过使用浊度管,一个可以收集水,然后再回来在实验室中执行浊度测量。
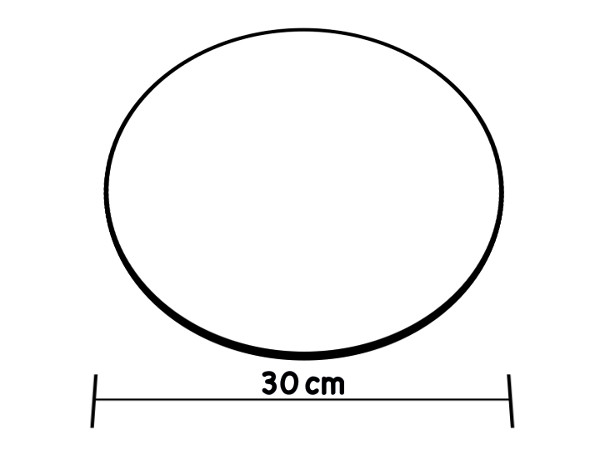
图 1.修改后的沙奇磁盘设计使用在淡水中。
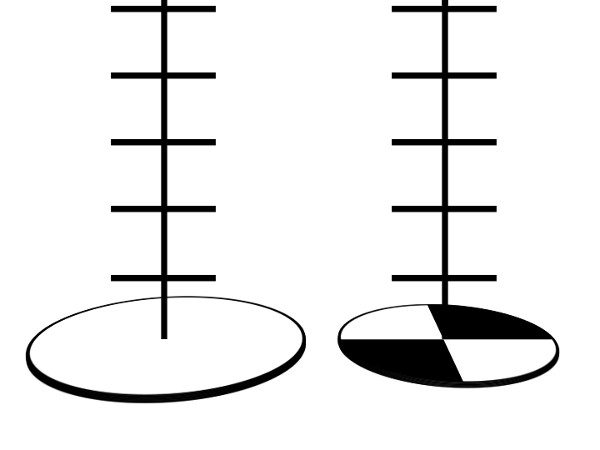
图 2.不同种类的塞齐盘。海洋的风格之一,在左边和右边的淡水版本
Princípios
Procedimento
Resultados
The table below is used to convert amount of reagents into the turbidity units (JTU). (Table 1)
TURBIDITY
Excellent < 10 JTUs
Good 11 – 20 JTUs
Fair 21 – 90 JTUs
Poor > 90 JTUs
Total solids can be assessed using the Water Quality Monitoring Quantitative Analysis categories for total solids measurements.
TOTAL SOLIDS (mg/L)
Excellent <100
Good 101 – 250
Fair 251 – 400
Poor > 400
| Number of Measured Additions | Amount in mL | Turbidity (JTUs) |
| 1 | 0.5 | 5 |
| 2 | 1.0 | 10 |
| 3 | 1.5 | 15 |
| 4 | 2.0 | 20 |
| 5 | 2.5 | 25 |
| 6 | 3.0 | 30 |
| 7 | 3.5 | 35 |
| 8 | 4.0 | 40 |
| 9 | 4.5 | 45 |
| 10 | 5.0 | 50 |
| 15 | 7.5 | 75 |
| 20 | 10.0 | 100 |
Table 1. Turbidity Test Results Table to convert number of drops (turbidity reagent) to turbidity units (JTU) and the Water Quality Monitoring Quantitative Analysis categories for turbidity.
Applications and Summary
Turbidity and total solids are important measurements of water quality because they are the most visible indicators of how “clean” a water-source is. High turbidity levels and total solids can indicate the presence of water pollutants that have an adverse effect on human, animal and plant life including bacteria, protozoa, nutrients (e.g. nitrates and phosphorus), pesticides, mercury, lead and other metals. Increased turbidity and total solids in surface water make water unpalatable for human use aesthetically and can also provide surfaces in the water for disease-causing microorganisms to grow harboring water-borne pathogens such as cryptosporidiosis, cholera and giardiasis. High amounts of suspended solids can also become be a problem to other species living in the water if particles become lodged into gills of oxygen-breathing animals in the water. Suspended particles can also disrupt light cycles and photosynthesis, altering the concentration of oxygen in the water and disturbing the aquatic system food web. Turbidity and total solids both increase at times when algal growth is high or when sediment is lifted up into the water during a storm. Both can also increase in response to human activity such as water pollution including industrial, agricultural, and residential runoff. Wastewater from sewage systems, urban runoff, and soil erosion from development can also contribute to high levels of turbidity and total solids. Easy to conduct at the site of water collection, these two simple measurements are broad indicators for a wide range of threats to water quality, all of which render surface water less useful for human purposes and also less able to support itself as an aquatic ecosystem.
Total solids are important to as use as a monitoring test for discharges from sewage treatment plants, industrial plants, or extensive crop irrigation. Areas where freshwater levels are low tend to have higher rates of evaporation and more vulnerable to higher concentrations of solids. Turbidity and total solids concentrations also tend to increase during rainfall events, especially in more highly developed areas with increased amounts of impervious surfaces and urban runoff.
Transcrição
Turbidity and total solids are related measurements used to quantify the clarity of surface waters.
Turbidity is an indirect measure of water clarity that determines the amount of light that can pass through the water. Total solids is a direct measurement, which records the total mass of solid particles suspended in water.
High levels of turbidity or total solids in water can be caused by many environmental factors. These include soil erosion, waste discharge, runoff, or changes in ecological communities including algal growth or abundance of benthic organisms that can disrupt sediments into the water column.
Higher turbidity and suspended solids can lower water quality by absorbing heat, causing increased water temperature and a corresponding decrease in oxygen levels, as warm water holds less oxygen. Photosynthesis may decline, as less sunlight is able to penetrate the water, making it unable to support some aquatic life. Additionally, suspended solids can clog gills, smother eggs, reduce growth rates, and disrupt the microhabitats of many aquatic organisms.
This video will illustrate how to quantify turbidity in a laboratory setting, and how to calculate the total solids in water samples.
Turbidity is caused by solid particles suspended in the water that scatter light rather than allowing it to be transmitted. The degree of the turbidity is determined by the concentration, size, and color of the particles. Larger particles scatter and concentrate light into a forward direction compared to smaller particles. Particle size can also affect light quality, with larger particles scattering longer wavelengths of light more than shorter wavelengths. Conversely, smaller particles scatter short wavelengths more intensely, whilst having relatively little effect on the longer wavelengths.
If particles are densely clustered in a sample, light will come into contact with an increased number of particles, and travel a shorter distance between them, resulting in multiple scattering events. Less dense solutions have a longer mean free path. Darker particles absorb more light, and lighter particles increase scattering, with both resulting in overall increased turbidity. Overall, darker particulates result in higher turbidity than lighter particulates due to the increased amount of light energy absorbed.
One method of measuring turbidity is with a Secchi disk. For freshwater, this is a metal disk 20 cm in diameter with alternating black and white quarters. For marine use a plain white disk of approximately 30 cm in diameter is standard. In both cases the disk is attached to a rope marked at known intervals, and dropped into the water until it can no longer be seen. The length of the rope at the point of disappearance is recorded as the Secchi depth, which is related to the turbidity of the water.
However, there are limitations to this field method. Ideal recording protocol requires sunny conditions and a shaded test area. Steep, wide, or loose riverbanks may pose difficulties or danger for disk operators, or access to a boat may be necessary. Using turbidity tubes to collect water to perform analysis back in the laboratory allows safer and more standardized measurements.
Once the water samples are back in the lab, they are compared to a reference sample. To do this, Standard Turbidity Reagent is added to deionized water in predetermined increments to increase cloudiness until the samples are matched, based on observation of a fixed point at the bottom of the two columns. The amount of reagent added to match the samples can then be recorded and converted to Jackson Turbidity Units or “JTU” using a reference table.
Total solids can be obtained by evaporating the water from the sample to isolate and weigh the solids.
Now that we are familiar with the principles behind the measurements of turbidity and total solids, let’s take at look at how these are measured in a laboratory setting.
Once the sample water has been collected in the field, bring it into the laboratory for analysis. First, select a clean turbidity column and fill to the 50-mL line with the sample water.
Next, fill a second “blank” turbidity column with deionized water to the 50-mL line.
Place the two tubes side-by-side and observe the black dot at the base of the turbidity column. If the black dot is equally clear in both tubes, turbidity is zero. If the black dot in the sample tube is less visible, it will be necessary to add Standard Turbidity Reagent to match the turbidity of the reference sample to that of the test sample.
Shake the Standard Turbidity Reagent to re-suspend the particulates. Add 0.5 mL of the reagent to the distilled water tube, and use a stirring rod to mix the contents thoroughly.
Check the turbidity again by placing the sample tube and reference tube side-by-side, and looking down through the solutions at the black dots. If the turbidity of the sample water is still greater than that of the distilled water, continue to add Standard Turbidity Reagent in 0.5 mL increments, until the turbidity of the two tubes appears matched, recording the amount of reagent used and mixing after each addition. Finally, record the total amount of Standard Turbidity Reagent added. Use this value to convert to Jackson Turbidity Units.
In addition to measuring turbidity, the total solids contained in the sample can also be determined. With gloved hands, label abeaker with a grease pencil. A grease pencil is ideal, as these beakers will later be placed into an oven. Next, turn on the balance and tare it. Using gloved hands to avoid transferring body moisture and altering the weight of the beaker, place one of the empty beakers on the balance, and record the weight.
Ensure the sample water is well mixed by swirling it gently, then take a graduated cylinder and measure 100 mL of the water sample. Pour this into the beaker. Place the sample beaker in an oven set to 100 °C for 48 h in order to evaporate the liquid and dry the resulting residue. Remove the beaker from the oven with gloved hands, let it cool to room temperature, and reweigh the beaker containing the residue. To determine the weight of the residue, subtract the initial weight of the empty beaker from the weight of the beaker with residue. Next, convert the weight of the residue into mg/L using this calculation.
Turbidity samples with a JTU of less than 10 are classed as “Excellent”; a range of 11 to 20 JTU is classed as “Good”, 21 to 90 JTU samples are “Fair”, and in samples of greater than 90 JTU turbidity is classed as “Poor”.
Total solids can be categorized using the Water Quality Monitoring Quantitative Analysis categories for total solids measurements. Here, a total solids measurement of less than 100 mg/L is classed as “Excellent”, 101 to 250 as “Good”, 251 to 400 are “Fair”, and samples with greater than 400 mg/L are rated “Poor”.
Measures of turbidity and total solids can be useful in a variety of situations, and other potential methods to collect and measure these data.
Another method to measure turbidity utilizes a sensor optimized to measure it directly. First, the sensor is calibrated using a sample of known turbidity and deionized water blank. Next, a water sample is placed in the turbidity sensor, and the handheld monitor will display a readout of turbidity. This method has benefits over the laboratory measurements in that it is faster, simpler, and can be carried out in the field, but does require the purchase of more expensive equipment.
Total dissolved solids can also be measured in the field using an automated device, which uses a conductivity probe to obtain a reading. Here, the probe is manually calibrated and set to record particulates in mg/L. The probe is submerged into the water sample and the total dissolved solids reading is displayed on the handheld monitor. Again, this method provides quicker and easier results than the laboratory method, but requires the purchase of a LabQuest meter and conductivity probe.
You’ve just watched JoVE’s introduction to Turbidity and Total Solids in Surface Water. You should now understand the theory and principles underlying these two valuable measurements of water quality, how to measure them, and how to use these measurements to determine the quality of your water samples. Thanks for watching!




