29.16:
Magnetostatic Boundary Conditions
Inside a homogenous magnetic medium, the magnetic field is continuous. However, on crossing a boundary, it becomes discontinuous.
Consider a Gaussian pillbox across the boundary. The zero divergence of the magnetic field ensures that the total magnetic flux enclosed within the pillbox is zero. So, the normal components of the field are equal across the boundary.
Now, consider an Amperian loop perpendicular to the surface current and apply Ampere's Law to each loop section.
The line integral of the magnetic field exists only for the loop's top and bottom sections since the loop width tends to zero. So, the field's tangential component is discontinuous.
The discontinuity of the tangential components can be expressed in vectorial form.
Now, consider an interface between two media. The divergence of magnetic field intensity equals the negative divergence of the magnetization. So, the normal component of magnetic field intensity is discontinuous.
Consider an Amperian loop perpendicular to the surface current. Applying Ampere's law, the tangential component of magnetic field intensity is discontinuous. This discontinuity can be expressed in vector form.
29.16:
Magnetostatic Boundary Conditions
An electric field suffers a discontinuity at a surface charge. Similarly, a magnetic field is discontinuous at a surface current. The perpendicular component of a magnetic field is continuous across the interface of two magnetic mediums. In contrast, its parallel component, perpendicular to the current, is discontinuous by the amount equal to the product of the vacuum permeability and the surface current. Like the scalar potential in electrostatics, the vector potential is also continuous across any boundary; hence the derivative of the vector potential is discontinuous across the boundary.
Consider two linear magnetic media with permeability μ1 and μ2, separated by an interface. The magnetic field intensity in medium 1 at a point P1 has a magnitude H1, and makes an angle α1 with the normal. Similarly, the magnetic field intensity in medium 2 at a point P2 has a magnitude H2, and makes an angle α2 with the normal.
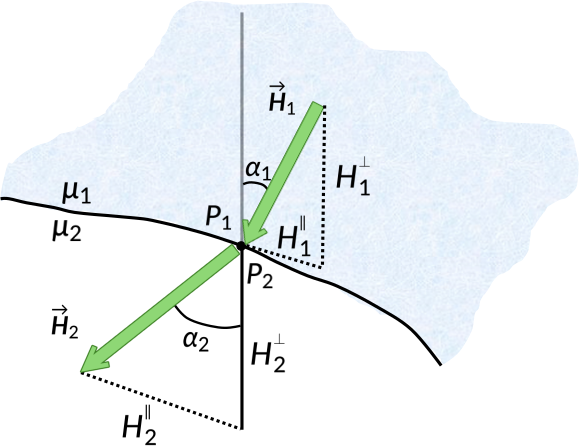
The zero divergence of the magnetic field ensures that the normal component of the magnetic field is continuous across the boundary. The magnetic field is proportional to the magnetic field intensity for linear magnetic media. Thus, the boundary conditions for the normal component of the magnetic field intensity are obtained.
Rewriting the normal components of the magnetic field in terms of the angles α1 and α2,
Since both media possess finite conductivities, free surface currents do not exist at the interface. Thus, the tangential component of the magnetic field intensity is continuous across the boundary. Again, the tangential components can be rewritten in terms of the angles α1 and α2:
Taking the ratio of normal and tangential components, a new expression is derived:
This expression is similar to the expression obtained for boundary conditions for two dielectric interfaces, except that the permittivity replaces the permeability.
If the first medium is a non-magnetic medium, like air, and the second one is a magnetic medium, the permeability of the second medium is greater than the permeability of the first medium. Thus, the angle α2 approaches ninety degrees. This implies that, for any arbitrary angle α1 that is not close to zero, the magnetic field in a ferromagnetic medium runs parallel to the interface. If the first medium is ferromagnetic and the second is non-magnetic, α2 approaches zero. This implies that if a magnetic field originates in a ferromagnetic medium, the magnetic flux lines emerge into the air medium in a direction almost normal to the interface.
Suggested Reading
- Ida, Nathan, Engineering Electromagnetics, 3rd Edition, Springer. Pp. 451
- Cheng, David K., Field and Wave Electromagnetics, Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Pp. 183
