Summary
This protocol utilizes a pull down assay to determine the levels of active RhoC GTPase within cells.
Abstract
RhoC GTPase has 91% homology to RhoA GTPase. Because of its prevalence in cells, many reagents and techniques for RhoA GTPase have been developed. However, RhoC GTPase is expressed in metastatic cancer cells at relatively low levels. Therefore, few RhoC-specific reagents have been developed. We have adapted a Rho activation assay to detect RhoC GTPase. This technique utilizes a GST-Rho binding domain fusion protein to pull out active RhoC GTPase. In addition, we can harvest total protein at the beginning of the assay to determine levels of total (GTP and GDP bound) RhoC GTPase. This allows for the determination of active versus total RhoC GTPase in the cell. Several commercial versions of this procedure have been developed however, the commercial kits are optimized for RhoA GTPase and typically do not work well for RhoC GTPase. Parts of the assay have been modified as well as development of a RhoC-specific antibody.
Protocol
1. Prepare GST-fusion Protein
- Glycerol stocks of JM109 competent bacteria containing the first N-terminal 90 amino acids of the rhotekin Rho binding domain (RBD) subcloned into the BamH1/EcoR1 pGEX3x vector are made.
To ensure High efficiency the following steps MUST be performed for each experiment. In our experience, freshly prepared GST-RBD is key to a robust and accurate GTPase activation assay. - Add 50 μL (approximate, do not thaw) of glycerol stock to 50 mL of LB amp and grow 37°C overnight with shaking.
- Dilute 1:10 in 500 mL LB-amp and grow for 1 h.
- Induce GST-protein production with 0.1 mM IPTG for 2 hrs.
- Distribute evenly into centrifuge bottles and centrifuge, Sorval GSA3 rotor at 5000 RPM 4°C for 20 min.
- Resuspend pellet in centrifuge bottles, 10 mL of lysis buffer*.
*Bacterial Lysis Buffer: 20% Sucrose, 10% glycerol, 50 mM Tris pH 8.0, 0.2 mM Na2S2O5, 2 mM MgCl2, 2 mM DTT, Add fresh PMSF, benzamide, aprotinin and leupeptin. - Sonicate 2-3 min (this depends on the type of sonicator. We use a Fischer Sonic Dismembranator Model 500 set at mark 6, 50% cycle).
- Centrifuge, Sorvall SS34, 20 min 10,000 rpm at 4°C. At this point a small aliquot can be taken out and run by SDS-PAGE. The gel can be coomassie stained and a band should be apparent at 46 kDa.
- Remove supernatant and add 1 mL of 50% glutatione-Sepharose 4B slurry.
- Incubate for 30 min at 4°C with rotation. Wash 3 times with lysis buffer.
- Resuspend GST-RBD/glutatione-Sepharose beads to a 50% slurry (approximately 1 mL) with GST-fish buffer**. **GST-Fish Buffer: 10% Glycerol, 50 mM Tris pH 7.4, 100 mM NaCl, 1% NP-4, 2 mM MgCl2, Add fresh PMSF, benzamide, aprotinin and leupeptin
2. GST-fusion pull down assay
- Use 5-10 x 106 cells/assay
- Wash cells once in ice cold PBS, keep plates on ice (we use a flat glass dish filled with ice) and lyse with 0.5 mL GST-fish buffer.
- Incubate 5 min on ice, harvest cells using a rubber policeman or flat scrapper, transfer to microfuge tube and centrifuge 20,000 r.p.m. 5 min at 4°C.
- Transfer supernatant to a fresh microfuge tube. Take 50 μL to determine total Rho (i.e. GDP + GTP bound).
- Add 0.5 mL GST-RBD/glutatione-Sepharose beads and incubate at 4°C, overnight with rotation.
- Wash 6x with GST-fish buffer.
- Resuspend beads in 40 μL 2x-Laemelli sample buffer
At this point the concentration of the total Rho protein aliquot taken in 2.4 should be determined and 30 μg prepared to be run on the gel with the corresponding activation sample. - Boil samples at 90°C for 5 min, centrifuge briefly and take supernatant (i.e. avoid the beads) load and run on a 12-well 4-20% gradient SDS-PAGE gel.
- Run gel at no higher than 150 volt, transfer to membrane using Towbin buffer and constant current of 100 W.
- Block membrane with 5% milk/TBST solution and probe with RhoC-specfic antibody.
3. Representative Results
Good results should produce a single band at approximately 22 kDa. Bad results produce multiple bands or high background. This is indicative of protein degradation, incomplete washing of samples or the use of old GST-RBD.
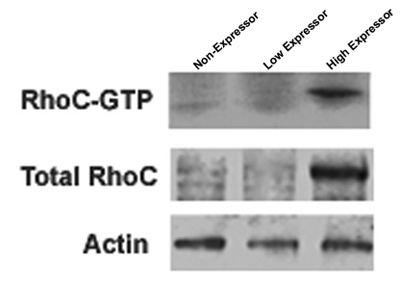
Figure 1. Three separate cell lines expressing different levels of RhoC GTPase are shown to demonstrate low levels of active and total RhoC, high levels of active and total RhoC or no RhoC. The blot was then stripped and reprobed with an antibody to the house keeping gene actin to serve as a loading control for the total RhoC protein.
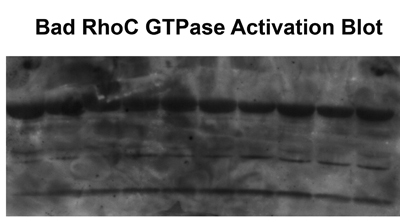
Figure 2. Multiple bands or high background results from protein degradation, incomplete washing of the samples or the use of old GST-RBD.
Discussion
The most critical step of the procedure is the generation of fresh GST-RBD. Failure to pay close attention to this step is main reason for failure. All the steps, from generation of the GST-RBD (1.2) to the overnight incubation with the cell lysate (2.5), should be done in a single day. Another crucial step is to make certain that there are enough cells to produce the cell lysates. This is of particular importance when looking at RhoC GTPase, which tends to be present in low levels in the cell.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
Dept. of Defense W81XWH-05-1-0005, W81XWH-06-1-0495, W81XWH-08-1-0029 and W81XWH-08-1-0356
Materials
| Material Name | Type | Company | Catalogue Number | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gluthione-sepharose 4B beads | GE Healthcare | 17-0756-01 | ||
| Criterion 4-20% Tris-HCl gels | BioRad | 345-0032 |
References
- van Golen, K. L., Wu, Z. F., Qiao, X. T., Bao, L. W., Merajver, S. D. RhoC GTPase, a novel transforming oncogene for human mammary epithelial cells that partially recapitulates the inflammatory breast cancer phenotype. Cancer Res. 60 (20), 5832-5838 (2000).
- van Golen, K. L., Wu, Z. F., Qiao, X. T., Bao, L., Merajver, S. D. RhoC GTPase overexpression modulates induction of angiogenic factors in breast cells. Neoplasia. 2 (5), 418-425 (2000).
- Golen, K. L. v. a. n. Reversion of RhoC GTPase-induced inflammatory breast cancer phenotype by treatment with a farnesyl transferase inhibitor. Mol Cancer Ther. 1 (8), 575-583 (2002).
- Golen, K. L. v. a. n. Mitogen activated protein kinase pathway is involved in RhoC GTPase induced motility, invasion and angiogenesis in inflammatory breast cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis. 19 (4), 301-311 (2002).
- Yao, H., Dashner, E. J., van Golen, C. M., van Golen, K. L. RhoC GTPase is required for PC-3 prostate cancer cell invasion but not motility. Oncogene. 25 (16), 2285-2296 (2006).
- Hall, C. L. Type I Collagen receptor (alpha2beta1) signaling promotes prostate cancer cell invasion through RhoC GTPase. Neoplasia. 10 (8), 797-803 (2008).
- Sequeira, L., Dubyk, C. W., Riesenberger, T. A., Cooper, C. R., van Golen, K. L. Rho GTPases in PC-3 prostate cancer cell morphology, invasion and tumor cell diapadesis. Clin Exp Metastasis. 25, 569-579 (2008).
- van Golen, K. L. CCL2 Induces Prostate Cancer Transendothelial Cell Migration via Activation of the Small GTPase Rac. J Cell Biochem. 104, 1587-1597 (2008).
- Chatterjee, M., van Golen, K. L. . Int J Cancer. , (2010).
- Sander, E. E., ten Klooster, J. P., van Delft, S., van der Kammen, R. A., Collard, J. G. Rac downregulates Rho activity: reciprocal balance between both GTPases determines cellular morphology and migratory behavior. J Cell Biol. 147 (5), 1009-1022 (1999).

