Confocal Imaging of Double-Stranded RNA and Pattern Recognition Receptors in Negative-Sense RNA Virus Infection
Instructor Prep
concepts
Student Protocol
1. Preparation of A549 cells and JUNV infection
- Seed 2 x 105 human lung epithelial A549 cells onto poly-D-lysine (PDL) coated glass coverslips in 12-well plates at 24 hours prior to infection.
- Prepare aliquots of 150 μL of JUNV13 at a multiplication of infection (MOI) of 1.0 plaque forming unit per cell diluted in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM) media supplemented with 2% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% penicillin and streptomycin (P/S).
- Remove media from cell culture. Add virus inoculum on each well containing coverslip and incubate for 1.5 h at 37 °C. Shake the plates every 15 min.
- Remove the virus inoculum, add 1 mL of DMEM supplemented with 5% FBS and 1% P/S. Incubate the plate at 37 °C for desired time point.
2. Fixation and immunostaining
- Aspirate the media. Rinse the cells by adding 1 mL of phosphate buffered saline (PBS) supplemented with calcium and magnesium to each well.
- Remove PBS. Add 1 mL of methanol (MeOH) pre-chilled at -20 °C and incubate at -20 °C or on dry ice for 15 min.
- Remove MeOH.
- Add 1 mL of PBS to each well, and wash samples at 4 °C with gentle rocking for 5 min. Repeat the wash for total of 4 times.
- Wash the fixed cells on coverslips in 1 mL of 0.2% t-octylphenoxypolyethoxyethanol for 5 min at 4 °C, with gentle rocking.
- Add 1 mL of PBS to each well. Wash samples at 4 °C for 5 min with gentle rocking. Repeat the washing step for total of 4 times.
- To detect dsRNA and MDA5, incubate samples in 200 μL of primary antibodies diluted in 3% bovine serum albumin (BSA). Dilute the anti-dsRNA 9D5 antibody at a 1:2 dilution and dilute the anti-MDA-5 antibody at 1:250. Incubate with gentle rocking at 4 °C overnight.
- Remove primary antibodies and wash each well with 1 mL of PBS for 5 min with gentle rocking at RT. Repeat this wash four more times.
- Add 200 μL of secondary antibodies (1:2,000 dilution) diluted in 3% BSA and incubate at RT for 1 h.
- Remove secondary antibodies and wash each well with 1 mL of PBS for 5 min with gentle rocking at RT. Repeat this wash four more times.
- To detect JUNV nucleoprotein (NP) and RIG-I, add 200 μL of conjugated antibodies diluted in 3% BSA. Dilute the conjugated anti-JUNV NP (AG-12) at 1:1,000 and incubate samples for 2 h at RT with gentle rocking. Dilute the conjugated anti-RIG-I antibody at 1:500 and incubate at 4 °C overnight with gentle rocking.
- Remove conjugated antibodies and wash each well with 1 mL of PBS for 5 min with gentle rocking at RT. Repeat this wash four more times.
- Counterstain the coverslips with DAPI (1:1,000) for 3 min with gentle rocking at RT.
- Wash the coverslips 3 times, each time for 5 min in 1 mL of 0.5% t-octylphenoxypolyethoxyethanol with gentle rocking at RT.
- Wash twice in 1 mL of PBS for 5 min each time with gentle rocking at RT.
- Wash once in 1 mL of ddH2O for 1 min at RT, rocking gently.
- Mount coverslips onto glass slides using mounting media. Let cure overnight.
- Seal the slides with nail polish and air dry for 1 h.
- Image on confocal microscope with the 60x/1.42 numerical aperture oil immersion lens using the same laser emissions for each sample.
- When analyzing the data, if necessary, make adjustments for brightness and contrast using the same linear adjustment for all samples.
Confocal Imaging of Double-Stranded RNA and Pattern Recognition Receptors in Negative-Sense RNA Virus Infection
Learning Objectives
This protocol was applied to study the distribution and colocalization between the RLRs (RIG-I and MDA-5) and dsRNA in JUNV-infected cells. As shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2, the accumulation of dsRNA increases over time as viral infection progresses. Concentrated MDA-5 (Figure 1) and RIG-I (Figure 2) signals were found colocalized with the punctate structures of the NP and dsRNA.
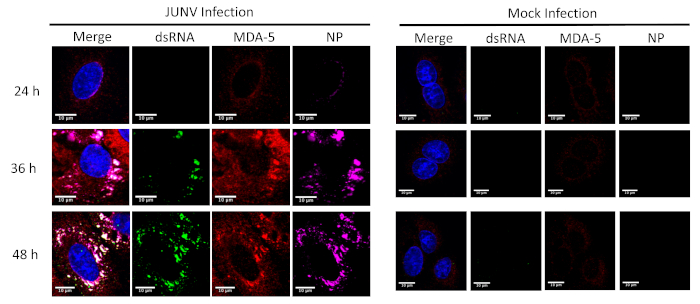
Figure 1: Time course of dsRNA and JUNV NP formation and the distribution of MDA-5. JUNV-infected and mock-infected A549 cells were fixed, stained and imaged according to the protocol at 24, 36, and 48 hours post infection (HPI). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
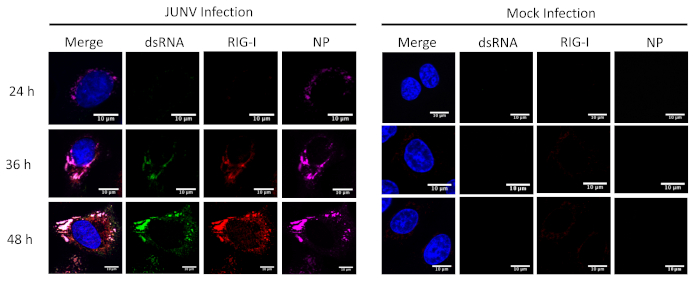
Figure 2: Time course of dsRNA and JUNV NP formation and the distribution of RIG-I. JUNV-infected and mock-infected A549 cells were fixed, stained and imaged according to the protocol at 24, 36, and 48 HPI. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
List of Materials
| APEX Alexa Fluor 647 antibody labeling kit | Invitrogen | A10475 | |
| BSA | Sigma Aldrich | A4503 | |
| DAPI | Cell Signaling | 4083 | 1:1,000 dilution |
| Donkey-anti rabbit Alexa Fluor 594 | Invitrogen | A-11058 | 1:2,000 dilution; Lot #: 1454437 |
| Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium | Corning | 10-013-CV | |
| Fetal Bovine Serum | Atlanta Bio | S11150 | |
| Glass microscope slides | Fisher | 12-550-15 | |
| Goat-anti mouse Alexa Fluor 488 | Invitrogen | A-11029 | 1:2000 dilution; Lot #: 1874804 |
| Human lung epithelial A549 cells | ATCC | CCL-185 | |
| Methanol | Fisher | A412 | Stored at -20 °C |
| Mouse MAb anti-JUNV NP | BEI | NA05-AG12 | Conjugated to Alexa-647 at 1:1,000 dilution |
| Mouse MAb pan-Enterovirus 9D5 Reagent | Millipore Sigma | 3361 | ready for use; diluted to 1:2; Lot #: 3067445 |
| PBS supplemented with Ca and Mg | Corning | 21-030-CV | |
| PDL Coated coverslips | Neuvitro | H-12-1.5-pdl | |
| ProLong Gold antifade | Invitrogen | P10144 | |
| Rabbit MAb MDA-5 | Abcam | ab126630 | 1:250 dilution; Lot #: GR97758-7 |
| recombiant Candid#1 strain of JUNV | Lab generated | Lab generated | As previously described in reference 13. |
| RIG-I mouse MAb conjugated to Alexa-594 | Santa Cruz | sc-376845 | 1:1000 dilution; Lot #: AO218 |
| Triton X-100 | Sigma Aldrich | T8787 |
Lab Prep
Double-stranded (ds) RNA is produced as a replicative intermediate during RNA virus infection. Recognition of dsRNA by host pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) such as the retinoic acid (RIG-I) like receptors (RLRs) RIG-I and melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5 (MDA-5) leads to the induction of the innate immune response. The formation and intracellular distribution of dsRNA in positive-sense RNA virus infection has been well characterized by microscopy. Many negative-sense RNA viruses, including some arenaviruses, trigger the innate immune response during infection. However, negative-sense RNA viruses were thought to produce low levels of dsRNA, which hinders the imaging study of PRR recognition of viral dsRNA. Additionally, infection experiments with highly pathogenic arenaviruses must be performed in high containment biosafety level facilities (BSL-4). The interaction between viral RNA and PRRs for highly pathogenic RNA virus is largely unknown due to the additional technical challenges that researchers need to face in the BSL-4 facilities. Recently, a monoclonal antibody (Mab) (clone 9D5) originally used for pan-enterovirus detection has been found to specifically detect dsRNA with a higher sensitivity than the traditional J2 or K1 anti-dsRNA antibodies. Herein, by utilizing the 9D5 antibody, we describe a confocal microscopy protocol that has been used successfully to visualize dsRNA, viral protein and PRR simultaneously in individual cells infected by arenavirus. The protocol is also suitable for imaging studies of dsRNA and PRR distribution in pathogenic arenavirus infected cells in BSL4 facilities.
Double-stranded (ds) RNA is produced as a replicative intermediate during RNA virus infection. Recognition of dsRNA by host pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) such as the retinoic acid (RIG-I) like receptors (RLRs) RIG-I and melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5 (MDA-5) leads to the induction of the innate immune response. The formation and intracellular distribution of dsRNA in positive-sense RNA virus infection has been well characterized by microscopy. Many negative-sense RNA viruses, including some arenaviruses, trigger the innate immune response during infection. However, negative-sense RNA viruses were thought to produce low levels of dsRNA, which hinders the imaging study of PRR recognition of viral dsRNA. Additionally, infection experiments with highly pathogenic arenaviruses must be performed in high containment biosafety level facilities (BSL-4). The interaction between viral RNA and PRRs for highly pathogenic RNA virus is largely unknown due to the additional technical challenges that researchers need to face in the BSL-4 facilities. Recently, a monoclonal antibody (Mab) (clone 9D5) originally used for pan-enterovirus detection has been found to specifically detect dsRNA with a higher sensitivity than the traditional J2 or K1 anti-dsRNA antibodies. Herein, by utilizing the 9D5 antibody, we describe a confocal microscopy protocol that has been used successfully to visualize dsRNA, viral protein and PRR simultaneously in individual cells infected by arenavirus. The protocol is also suitable for imaging studies of dsRNA and PRR distribution in pathogenic arenavirus infected cells in BSL4 facilities.
Procedure
Double-stranded (ds) RNA is produced as a replicative intermediate during RNA virus infection. Recognition of dsRNA by host pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) such as the retinoic acid (RIG-I) like receptors (RLRs) RIG-I and melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5 (MDA-5) leads to the induction of the innate immune response. The formation and intracellular distribution of dsRNA in positive-sense RNA virus infection has been well characterized by microscopy. Many negative-sense RNA viruses, including some arenaviruses, trigger the innate immune response during infection. However, negative-sense RNA viruses were thought to produce low levels of dsRNA, which hinders the imaging study of PRR recognition of viral dsRNA. Additionally, infection experiments with highly pathogenic arenaviruses must be performed in high containment biosafety level facilities (BSL-4). The interaction between viral RNA and PRRs for highly pathogenic RNA virus is largely unknown due to the additional technical challenges that researchers need to face in the BSL-4 facilities. Recently, a monoclonal antibody (Mab) (clone 9D5) originally used for pan-enterovirus detection has been found to specifically detect dsRNA with a higher sensitivity than the traditional J2 or K1 anti-dsRNA antibodies. Herein, by utilizing the 9D5 antibody, we describe a confocal microscopy protocol that has been used successfully to visualize dsRNA, viral protein and PRR simultaneously in individual cells infected by arenavirus. The protocol is also suitable for imaging studies of dsRNA and PRR distribution in pathogenic arenavirus infected cells in BSL4 facilities.
