אנטרופיה
English
分享
概述
מקור: קטרון מיטשל-ווין, PhD, אסנטה קוריי, PhD, המחלקה לפיזיקה ואסטרונומיה, בית הספר למדעי הפיזיקה, אוניברסיטת קליפורניה, אירווין, קליפורניה
החוק השני של התרמודינמיקה הוא חוק יסוד הטבע. הוא קובע כי האנטרופיה של מערכת תמיד גדלה עם הזמן או נשארת קבועה במקרים אידיאליים כאשר מערכת נמצאת במצב יציב או עוברת “תהליך הפיך”. אם המערכת עוברת תהליך בלתי הפיך, האנטרופיה של המערכת תמיד תגדל. משמעות הדבר היא שהשינוי באנטרופיה, ΔS, תמיד גדול או שווה לאפס. האנטרופיה של מערכת היא מדד למספר התצורות המיקרוסקופיות שהמערכת יכולה להשיג. לדוגמה, גז במיכל עם נפח, לחץ וטמפרטורה ידועים יכול להיות מספר עצום של תצורות אפשריות של מולקולות הגז הבודדות. אם המיכל נפתח, מולקולות הגז בורחות ומספר התצורות גדל באופן דרמטי, ובעצם מתקרב לאינסוף. כאשר המיכל נפתח, האנטרופיה אמורה לגדול. לכן, אנטרופיה יכולה להיחשב מידה של “הפרעה” של מערכת.
Principles
Procedure
Results
Representative results for 680 mL of water are shown in Table 1. The cooling constant k was found using the data points in the table and solving Equation 7. After 35 min, T(35) = 50.6. The initial temperature was 100 °C, and data collection ceased at 28.5 °C. Using these variables gives the following equation to obtain k:
50.6 = 28.5 + (100 – 28.5) e-k 35. (Equation 8)
Solving for k gives a value k = 0.034. The curve with this cooling constant is shown as a dashed gray line in Figure 1, along with the data points from the experiment. The functional form of Equation 6 matches the experimental results very closely.
As the water cools, the entropy decreases, since the number of states available to the water molecules decreases. The entropy of the ambient air in the room increases because the water beaker transfers heat to the air molecules surrounding it; the overall entropy of the water + air system increases. The number of states that the now-hotter air molecules can occupy is much higher than before the hot water was introduced to the room.
In differential form, the heat dQ added to or removed from the water can be calculated using the relationship between mass, specific heat c, and temperature change:
dQ = mc dT, (Equation 9)
where c is known to be 4.18 J/(gK) for water. The change in entropy of the water is then:
ΔSwater = 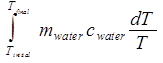
= mwater cwater ln(Tfinal / Tinitial). (Equation 10)
Using the conversion to Kelvin as K = °C + 273.15, the change in the entropy of the water is calculated as:
ΔSwater = 680 g * 4.18 J/(g K) * ln[(28.5 + 273.15)/(100 + 273.15)]
= -604 J/K.
The ambient air temperature is constant at 20.4 °C, so this is an isothermal process. The entropy change of the air is then:
ΔSair = 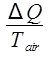 ,
,
where Q is the heat released by the water, which is given by Equation 9. The change in entropy of the air is then calculated as:
ΔSair = 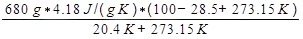
= 3337 J/K.
The total change in the entropy of the water + air system, ΔStot, is the sum of the individual changes in entropy of the water and ambient air:
ΔStot = ΔSwater +ΔSair (Equation 11)
= -604 J/k + 3337 J/K
= 2733 J/K.
Table 1. Temperatures recorded during the experiment.
| Time (min s) | Water Temperature (°C) |
| 0 0 | 99.6 |
| 1 10 | 97.1 |
| 1 50 | 94.2 |
| 2 30 | 91.8 |
| 3 22 | 89 |
| 4 05 | 87.2 |
| 5 08 | 82.7 |
| 6 05 | 82.4 |
| 8 25 | 78 |
| 9 15 | 76.5 |
| 10 15 | 74.6 |
| 11 38 | 72.7 |
| 12 58 | 70.7 |
| 13 58 | 69.2 |
| 15 15 | 67.7 |
| 16 55 | 65.8 |
| 18 38 | 64 |
| 20 25 | 62.3 |
| 24 02 | 58.8 |
| 25 45 | 57.3 |
| 34 45 | 50.6 |
| 40 50 | 47.4 |
| 44 30 | 45.9 |
| 49 59 | 43.6 |
| 53 42 | 42.4 |
| 60 01 | 40.2 |
| 64 20 | 39.5 |
| 76 37 | 37 |
| 103 50 | 32.1 |
| 116 41 | 30.3 |
| 122 46 | 29.6 |
| 134 11 | 28.5 |
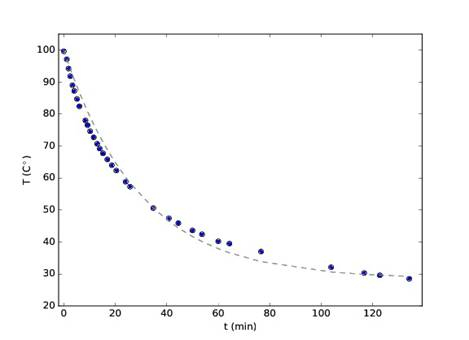
Figure 1. Plot of temperature versus time. The blue dots indicate the experimental data, and the dashed line represents theoretical data based on Newton's law of cooling.
Applications and Summary
A pair of headphones kept in a bag always tends to become knotted-this is an increase in entropy caused by carrying the bag around. It is necessary to do work on the headphones to un-knot them and decrease the entropy (this can be thought of as a “reversible process”). The most efficient heat engine cycle allowed by physical laws is the Carnot cycle. The second law states that not all heat supplied to a heat engine can be used to do work. The Carnot efficiency sets the limiting value on the fraction of heat that can be used. The cycle consists of two isothermal processes followed by two adiabatic processes. A refrigerator, which is essentially just a heat pump, is also a classic example of the second law. Refrigerators move heat from one location at a lower temperature (the “source”) to another location at a higher temperature (the “heat sink”) using mechanical work. According to the second law, heat cannot spontaneously flow from a colder location to a hotter one; thus, work (energy) is required for refrigeration.
Newton’s law of cooling was demonstrated by a beaker full of water at 100 °C cooling down to room temperature, which led to an increase in the entropy of the water-air system. By measuring the temperature of the water as a function of time over a period of 135 min, it was possible to confirm that the cooling of the water was exponential in form. The cooling constant of the water sample was found by solving the cooling equation using collected data.
成績單
Entropy is a fundamental thermodynamic principle used to describe heat transfer in a system.
The term Entropy is often considered a measure of the “disorder” of a system and the second law of thermodynamics states that if the system is undergoing an irreversible process, then the entropy of the system will always increase.
Think about gas trapped in a container with known volume, pressure and temperature. The gas molecules can have an enormous number of possible configurations. If the container is opened, the gas molecules escape and the number of configurations increases dramatically, essentially approaching infinity. Therefore S, which denotes entropy, definitely increased after opening the container. Thus, ΔS, or the change in entropy,is greater than zero.
Similarly, entropy also increases when hot water is left at room temperature and allowed to cool down. In this video, we will illustrate how to measure the change in entropy of a system during such cooling experiments.
Before learning how to do the experiment and gather data, let’s learn some laws and equations that allow us to calculate rate of temperature change and increase in entropy during cooling experiments.
Newton’s Law of Cooling states that the rate of temperature change of an object is proportional to the difference between its own temperature and the temperature of the surroundings. Using calculus, this relationship can be converted into this equation, where lower case t represents time, Ts denotes temperature of the surroundings, T0 is the initial temperature, and k is a constant that depends on the characteristics of the object and its surroundings.
Using this equation, one can calculate the temperature of a cooling system at any time if all the other variables are known. This equation also shows that temperature is an exponential function of time. Thus, when a hot object, like a glass of hot water, is placed in a cooler environment, its temperature will decrease at an exponential rate until it reaches the temperature of the surroundings.
Now, let’s see how to calculate the change in entropy, or ΔS. Let’s rewind to when the water was hot.
When talking about entropy, we must first define the system. Here, the system is the glass of water plus the air in the room. So the change in entropy of the system, or ΔStotal is a sum of the change in entropies of these individual components. Mathematically, the change in entropy is defined as heat gained or lost, denoted by Q, divided by the temperature.
In this scenario, we know that heat leaves water, thus ΔS for water decreases. On the contrary, the surrounding air gains heat. Therefore, ΔSair increases. From the second law of the thermodynamics, we know the change in entropy of the total system must be positive.
Now let’s see how to conduct an experiment to test these theoretical predictions of Newton’s Law of Cooling and the second law of thermodynamics.
To begin, fill a large beaker with between 500 mL to one L of water. Place the beaker on a hot plate, and heat the water to boiling. Once the water boils, turn off the heating element.
Then, carefully remove the beaker from the hot plate, and place it on the table on top of paper towels. The paper towels will act as insulation between the water and the cool table. Measure the temperature of the water using the thermometer.
Start the stopwatch, and record the temperature of the water every minute for the first 20 minutes.
For the next 20 minutes, record the temperature every 5 minutes.
Stop taking measurements when the water has come close to room temperature. Then, plot the data points in a graph of temperature of the water versus time.
Now let’s analyze the data obtained. The initial temperature of the water was 100 degrees, at 35 minutes the temperature dropped to 50.6, and the surrounding temperature was 28.5 degrees. Plug in these values into Newton’s Law of Cooling, and solve for the cooling constant k.
Now using the calculated value for k, plot the equation as a continuous function. If we lay our measured data points on this chart, we can see that the theoretical and experimental functions follow an almost identical path.
Now let’s talk about entropy. As we know, the total change in entropy, or delta S, is equal to the entropy change for the water plus the room.
The change in entropy equals Q, or the amount of heat transferred from the hot water to the air, divided by T, so the change in entropy can be calculated if Q is known.
Q can be calculated using the relationship between mass, m, specific heat, c, and the change in temperature in Kelvin, delta T. Using the values for water the amount of heat released by the water, Q can be calculated and used to solve for delta S.
Thus, the experimental data shows that the entropy of the total system has increased since heat was transferred from the water to the air molecules in the room. This validates the second law of thermodynamics.
Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics describe a wide range of occurrences in nature and engineering.
A refrigerator is essentially a heat pump, and removes heat from one location at a lower temperature, the heat source, and transfers it to another location, the heat sink, at a higher temperature.
According to the second law, heat cannot spontaneously flow from a colder location to a hotter one. Thus, work, or energy, is required for refrigeration.
A campfire is another example of entropy changes in real life. The solid wood used as fuel burns and turns into a disordered pile of ash. In addition, water molecules and carbon dioxide gas are released.
The atoms in the vapors spread out in an expanding cloud, with infinite disordered arrangements. Thus, the entropy change from burning wood is always positive.
You’ve just watched JoVE’s introduction to entropy and the second law of thermodynamics. You should now understand the basic concept of entropy, Newton’s Law of Cooling, and examples of entropy changes in everyday life. Thanks for watching!
