Exploración de la tiroides
English
Teilen
Übersicht
Fuente: Richard Glickman-Simon, MD, profesor asistente, Departamento de salud pública y medicina comunitaria, Tufts University School of Medicine, MA
La glándula tiroides se encuentra en la tráquea anterior del cuello entre el cartílago cricoides (arriba) y la muesca del suprasternal (abajo) (figura 1). Consiste en un lóbulo derecho e izquierdo conectado por un istmo. El istmo abarca al segundo, tercero, y cuarto traqueales anillos y los lóbulos de la curva posteriorly alrededor de los lados de la tráquea y el esófago. La glándula normal, peso de 10-25 g, es generalmente invisible en la inspección y a menudo difíciles de palpar. Un bocio es un agrandamiento tiroideo por cualquier causa. Además de evaluar su tamaño, es importante palpar la tiroides por su forma, movilidad, consistencia y sensibilidad. Una tiroides normal es suave, liso, simétrico y no blanda, y se desliza hacia arriba un poco al tragar. La ampliación simétrica de un suave, lisa tiroides sugiere hipotiroidismo endémico debido a la deficiencia de yodo o una de dos enfermedades autoinmunes frecuentes: enfermedad de Graves o tiroiditis de Hashimoto. Los nódulos tiroideos son comunes y generalmente accidental; sin embargo, el 10% de nódulos de la tiroides resultan para ser malignos. Pueden ser únicas o múltiples y frecuentemente son firmes y no blanda. Típicamente, un bocio blando, simétrico indica tiroiditis.
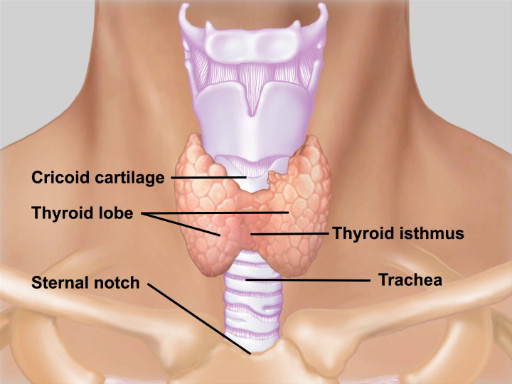
Figura 1. Anatomía de la glándula tiroides. Ilustración de la ubicación y anatomía de la glándula tiroides con respecto a las estructuras del cuello.
Enfermedad tiroidea raramente se manifiesta como un bocio palpable en aislamiento. Las hormonas tiroideas sirven para mantener la homeostasis principalmente por estimulación metabolismo celular en todo el cuerpo. Por lo tanto, hipo e hipertiroidismo están asociados con una variedad de síntomas y hallazgos físicos (tabla 1). Es importante tener en cuenta que esta afección puede ser eutiroideo (niveles normales de hormonas tiroideas), hipertiroidismo o hipotiroidismo. Dolores de cabeza o trastornos visuales pueden sugerir un trastorno tiroideo secundario a un adenoma pituitario
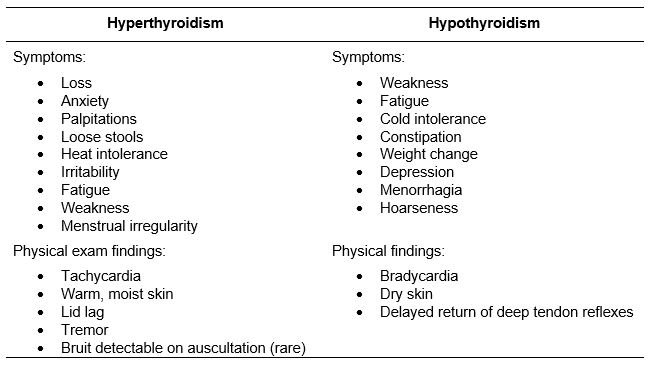
Tabla 1. Los síntomas y hallazgos físicos para hypo – e hiper-tiroidismo.
Verfahren
Applications and Summary
An enlarged thyroid gland, or goiter, is most often associated with normal thyroid gland function (euthyroid), but may be associated with hyper- or hypothyroid conditions. Therefore, thyroid abnormality found on physical examination should prompt a careful evaluation for the systemic signs and symptoms associated with both high and low thyroid hormone levels. A normal thyroid can be difficult to palpate, particularly in patients with large necks. However, its location can be precisely determined by identifying the bony and cartilaginous landmarks nearby: the cricoid cartilage above and the suprasternal notch below. In addition to an increase in size, the gland may show asymmetry, nodularity, or tenderness. Symmetrical goiters and thyroid nodules are not uncommon, and their detection should always prompt further investigation.
Transkript
The thyroid physical examination is helpful for a clinician as it aids in narrowing down the differential diagnoses related to its anatomical pathology. The thyroid gland produces the thyroid hormones, which serve to maintain homeostasis throughout the body, primarily by stimulating cellular metabolism. Knowledge of the thyroid gland’s location and function is essential for diagnosing the commonly encountered pathologies, which are associated with its malfunctioning. The assessment of this gland should proceed in a systematic fashion, and this video will show the steps of this physical examination in detail.
The first step in examining the thyroid is to correctly locate it and understand its function, so before demonstrating the steps, let’s briefly review thyroid anatomy and physiology.
The thyroid gland is located in the neck, anterior to the trachea between the cricoid cartilage and the suprasternal notch. It consists of a right and left lobe connected by an isthmus. The isthmus covers the second, third, and fourth tracheal rings, and the lobes curve posteriorly around the sides of the trachea and esophagus.
The normal gland weighs 10-25 g, and is usually invisible on inspection and often difficult to palpate. Conversely, a goiter, which is an enlarged thyroid, is visible and palpable. In addition to assessing the goiter’s size, one must also palpate it for its shape, mobility, consistency, and tenderness. A normal thyroid is soft, smooth, symmetrical, and non-tender, and it slides upward slightly when swallowing. Symmetrical enlargement of a soft, smooth thyroid suggests endemic hypothyroidism due to iodine deficiency or one of two autoimmune disorders: Grave’s disease or Hashimoto’s thyroiditis Thyroid tenderness may be associated with the latter two conditions.
It should be noted that a goiter might be euthyroid, which indicates normal thyroid hormone levels, hyperthyroid, or hypothyroid. However, hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism rarely manifests as a palpable goiter in isolation. Therefore, diagnosing thyroid disease requires a detailed understanding of the symptoms and physical exam findings associated with these conditions.
Other than goiter, thyroid nodules may also be palpable. These are common and usually incidental. However, 10% turn out to be malignant. They may be single or multiple, and are most often firm and non-tender.
Now that you have an idea of the structure and function of the thyroid gland, let’s go over the sequence of inspection and palpation steps for a thorough evaluation of this vital organ. Before the exam, thoroughly sanitize your hands using a disinfecting solution in view of the patient. Briefly explain the procedure you will perform.
Begin with inspection. Ask the patient to tip their head slightly back, and carefully inspect the anterior neck. If visible, the thyroid appears between the cricoid cartilage, which lies just beneath the protuberance of the thyroid cartilage also known as the Adam’s apple, and the suprasternal notch marked by the midline depression where the upper end of the sternum and clavicles meet. Check for symmetry, diffuse swelling, and obvious masses.
Offer the patient a cup of water and request to take a sip and swallow. Observe as the cricoid cartilage, thyroid cartilage, and thyroid gland move up and down. Next, proceed to palpation. Traditionally, this is done while standing behind the patient. Reach around with both hands and use your fingers to identify the landmarks from top to bottom. Start by feeling the mobile hyoid bone just beneath the mandible. Moving downwards, feel the thyroid cartilage with its superior notch, followed by the cricoid cartilage. Further down, you will feel the tracheal rings, and lastly the suprasternal notch.
After identifying the landmarks, place your index fingers just below the cricoid cartilage. Ask the patient to take another sip of water and swallow as before, and feel for the thyroid isthmus rising up under your finger pads. The isthmus is not always palpable, but if it is, feel for size, shape, and consistency. Also note any nodularity or tenderness. Lastly, palpate the thyroid lobes. Using the fingers of your right hand, gently move the trachea to the left and feel for the right lobe in the space between the trachea and sternomastoid muscle. Similarly examine the left lobe. If a goiter is detected, listen for a bruit by placing the stethoscope over the lateral lobes. If a bruit is present, it most likely indicates hyperthyroidism.
You’ve just watched JoVE’s demonstration of a comprehensive thyroid examination. You should now understand the anatomical location of the thyroid, how a goiter presents itself, what to look for during inspection, and finally the landmarks that help in thyroid palpation.
Remember, goiters and nodules are not uncommon. However, their detection should always prompt further investigation for the systemic signs and symptoms associated with hyper- and hypothyroidism. As always, thanks for watching!
