مفاعل حيوي متعدد التيار للتروية مدمج مع تجزئة المخرج لزراعة الخلايا الديناميكية
Summary
تقدم هذه الورقة طريقة لبناء وتشغيل نظام منخفض التكلفة متعدد القنوات لزراعة خلايا التروية لقياس ديناميكيات إفراز ومعدلات امتصاص المذابات في العمليات الخلوية. يمكن للنظام أيضا تعريض الخلايا لملفات تعريف التحفيز الديناميكية.
Abstract
تعمل بعض وظائف الخلايا والأنسجة ضمن النطاق الزمني الديناميكي من دقائق إلى ساعات يتم حلها بشكل سيئ بواسطة أنظمة الزراعة التقليدية. وقد طور هذا العمل نظاما منخفض التكلفة للمفاعل الحيوي للتروية يسمح بدمج وسط الاستزراع باستمرار في وحدة زراعة الخلايا وتقسيمه في وحدة المصب لقياس الديناميكيات على هذا النطاق. تم بناء النظام بالكامل تقريبا من الأجزاء المتاحة تجاريا ويمكن موازاته لإجراء تجارب مستقلة في لوحات زراعة الخلايا التقليدية متعددة الآبار في وقت واحد. توضح مقالة الفيديو هذه كيفية تجميع الإعداد الأساسي ، والذي لا يتطلب سوى مضخة حقنة واحدة متعددة القنوات وجامع أجزاء معدل لدمج ما يصل إلى ست ثقافات بالتوازي. كما يتم تقديم متغيرات مفيدة على التصميم المعياري تسمح بديناميكيات التحفيز التي يتم التحكم فيها ، مثل النبضات المذابة أو الملامح الشبيهة بالحرائك الدوائية. الأهم من ذلك ، عندما تنتقل الإشارات المذابة عبر النظام ، فإنها مشوهة بسبب تشتت المذاب. علاوة على ذلك ، يتم وصف طريقة لقياس توزيعات وقت الإقامة (RTDs) لمكونات إعداد التروية باستخدام جهاز تتبع باستخدام MATLAB. RTDs مفيدة لحساب كيفية تشويه الإشارات المذابة بسبب التدفق في نظام المقصورات المتعددة. هذا النظام قوي للغاية وقابل للتكرار ، لذلك يمكن للباحثين الأساسيين اعتماده بسهولة دون الحاجة إلى مرافق تصنيع متخصصة.
Introduction
تحدث العديد من العمليات البيولوجية الهامة في مزارع الخلايا والأنسجة على مقياس زمني من دقائق إلى ساعات 1,2,3. في حين أن بعض هذه الظواهر يمكن ملاحظتها وتسجيلها بطريقة آلية باستخدام المجهربفاصل زمني 4 أو التلألؤ الحيوي1 أو طرق أخرى ، فإن التجارب التي تنطوي على جمع عينات من المستنبتات الفائقة للتحليل الكيميائي غالبا ما يتم إجراؤها يدويا في مزارع الخلايا الثابتة. يحد أخذ العينات اليدوي من جدوى بعض الدراسات بسبب إزعاج النقاط الزمنية المتكررة أو بعد ساعات العمل. وتشمل أوجه القصور الأخرى في أساليب الزراعة الثابتة التجارب التي تنطوي على التعرض الخاضع للرقابة والعابرة للمحفزات الكيميائية. في الثقافات الثابتة ، يجب إضافة المحفزات وإزالتها يدويا ، وتقتصر ملفات تعريف التحفيز على تغييرات الخطوة بمرور الوقت ، بينما تضيف التغييرات المتوسطة أيضا مكونات متوسطة أخرى وتزيلها ، والتي يمكن أن تؤثر على الخلايا بطريقة غير منضبطة5. يمكن للأنظمة الموائعة التغلب على هذه التحديات ، لكن الأجهزة الحالية تشكل تحديات أخرى. تأتي أجهزة الموائع الدقيقة مع التكاليف الباهظة للمعدات المتخصصة والتدريب على الإنتاج والاستخدام ، وتتطلب أساليب التحليل الدقيق لمعالجة العينات ، ويصعب استرداد الخلايا من الأجهزة بعد التروية6. تم إنشاء عدد قليل من أنظمة الموائع الكبيرة لأنواع التجارب الموضحة هنا7،8،9،10 ، وهي مبنية من أجزاء مخصصة متعددة مصنوعة داخليا وتتطلب مضخات متعددة أو جامعي كسر. علاوة على ذلك ، فإن المؤلفين ليسوا على دراية بأي أنظمة متاحة تجاريا لزراعة خلايا التروية الموائع الكبيرة بخلاف المفاعلات الحيوية للخزانات المقلوبة لزراعة التعليق ، والتي تعد مفيدة للتصنيع الحيوي ، على الرغم من أنها ليست مصممة لنمذجة ودراسة علم وظائف الأعضاء.
وكان المؤلفون قد أبلغوا سابقا عن تصميم نظام مفاعل حيوي منخفض التكلفة للإرواء يتكون بالكامل تقريبا من الأجزاء11 المتاحة تجاريا. تمكن النسخة الأساسية من النظام من الاحتفاظ بثقافات متعددة في صفيحة بئر في حاضنة CO2 ودمجها باستمرار مع وسيط من مضخة حقنة ، في حين يتم تقسيم تيارات وسط النفايات السائلة من الثقافات تلقائيا إلى عينات بمرور الوقت باستخدام جامع أجزاء مع تعديل مخصص. وبالتالي ، يتيح هذا النظام أخذ عينات آلية من المدخلات المتوسطة للثقافة الفائقة والمذابة المستمرة للثقافات بمرور الوقت. النظام هو macrofluidic ووحدات ويمكن تعديله بسهولة لتلبية احتياجات تصاميم التجارب الجديدة.
الهدف العام للطريقة المعروضة هنا هو بناء وتوصيف واستخدام نظام زراعة خلايا التروية الذي يتيح إجراء تجارب يتم فيها قياس معدلات إفراز أو امتصاص المواد بواسطة الخلايا بمرور الوقت ، و / أو تعرض الخلايا لإشارات مذابة دقيقة وعابرة. تشرح مقالة الفيديو هذه كيفية تجميع الإعداد الأساسي ، القادر على اختراق ما يصل إلى ست مزارع خلايا في وقت واحد باستخدام مضخة حقنة واحدة وجامع أجزاء معدلة. كما يتم عرض متغيرين مفيدين على النظام الأساسي يستخدمان مضخات وأجزاء إضافية للسماح بإجراء تجارب تعرض الخلايا لإشارات تركيز ذائبة عابرة ، بما في ذلك النبضات القصيرة والملامح الشبيهة بالحركية الدوائية12 ، كما هو موضح في الشكل 1.
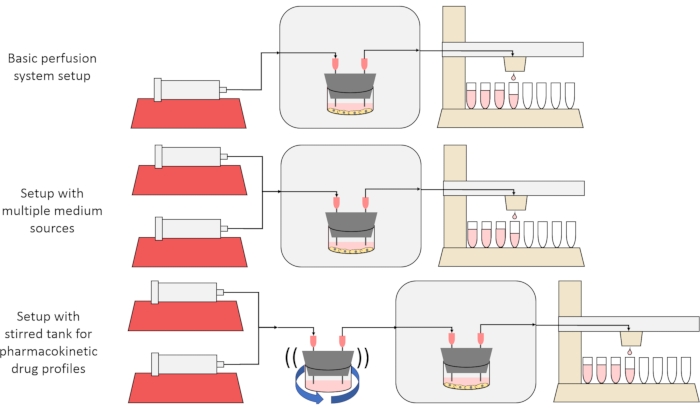
الشكل 1: ثلاثة اختلافات في تصميم نظام التروية. (أعلى) نظام التروية الأساسي. (الوسط) نظام التروية مع stopcock لمصادر متوسطة متعددة. (أسفل) نظام التروية مع خزان مقلب لتقليد حجم مختلط جيدا من التوزيع. يرجى النقر هنا لعرض نسخة أكبر من هذا الرقم.
بسبب التشتت والانتشار داخل التدفق ، تصبح الإشارات المذابة مشوهة أو “ملطخة” أثناء انتقالها عبر نظام التدفق. ويمكن تحديد هذا التشويه كميا من خلال استخدام توزيعات وقت الإقامة (RTDs)13. تشرح هذه المقالة كيفية إجراء تجارب التتبع على مكونات نظام التروية (الشكل 2)، وتوفر البرامج النصية MATLAB لإنشاء RTDs من البيانات المقاسة. ويمكن الاطلاع على شرح مفصل لهذا التحليل في الورقة السابقةللمؤلفين رقم 11. تناسب نصوص MATLAB الإضافية الوظائف المناسبة ل RTDs وتستخرج المعلمات الفيزيائية ، وتؤدي التفاف الإشارة باستخدام RTDs للتنبؤ بكيفية انتشار وتشويه إدخال الإشارة المذاب من قبل المستخدم من خلال نظام التروية14.
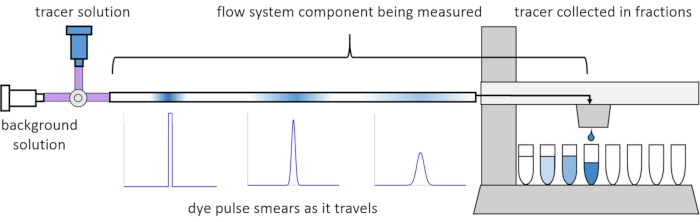
الشكل 2: توزيعات وقت الإقامة. يتم قياس RTDs لمكونات نظام التدفق ، مثل طول الأنابيب هذا ، عن طريق إدخال نبضة من المقتفي إلى النظام وقياس كيفية “تلطيخها” بحلول الوقت الذي تخرج فيه إلى الكسور التي تم جمعها. وقد عدل هذا الرقم من Erickson et al.11. يرجى النقر هنا لعرض نسخة أكبر من هذا الرقم.
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
يصف هذا العمل تجميع وتشغيل نظام زراعة خلايا التروية مع مصادر متوسطة متعددة تم إثباتها مع مثال محدد تم فيه قياس ديناميكيات التعبير الجيني المدفوع ب NF-κB استجابة لنبضة عابرة من TNF-α. تم قياس ونمذجة RTDs لمكونات نظام التروية ، وتم استخدام التفاف الإشارة للتنبؤ بكل من تعرض الخلايا لنبضة TNF-α وتوزي…
Divulgations
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
تم إجراء هذا البحث بدعم بموجب رقم المنحة. R01EB012521 و R01EB028782 و T32 GM008339 من المعاهد الوطنية للصحة.
Materials
| 18 Gauge 1 1/2- in Disposable Probe Needle For Use With Syringes and Dispensing Machines | Grainger | 5FVK2 | |
| 293T Cells | ATCC | CRL-3216 | HEK 293T cells used in the Representative Results experiment. |
| 96-Well Clear Bottom Plates, Corning | VWR | 89091-010 | Plates for measuring dye concentrations in RTD experiments and GLuc in representative results experiment. |
| BD Disposable Syringes with Luer-Lok Tips, 5 mL | Fisher Scientific | 14-829-45 | |
| BioFrac Fraction Collector | Bio-Rad | 7410002 | Fraction collector that can be used for a single stream, or modified using our method to enable collection from multiple streams. |
| Clear High-Strength UV-Resistant Acrylic 12" x 12" x 1/8" | McMaster-Carr | 4615T93 | This sheet is cut using a laser cutter according to the DXF file in the supplemental materials to produce the multi-head dispenser that can be attached to the BioFrac fraction collector. |
| Coelenterazine native | NanoLight Technology | 303 | Substrate used in Gaussia luciferase bioluminescence assay in representative results. |
| Corning Costar TC-Treated Multiple Well Plates, size 48 wells, polystyrene plate, flat bottom wells | Millipore Sigma | CLS3548 | Used to grow and perfuse 293T cells in representative results. |
| Corning Costar Flat Bottom Cell Culture Plates, size 12 wells | Fisher Scientific | 720081 | Can be plugged and used as a stirred tank to produce pharmacokinetic profiles in perfusion. Can also contain cells for perfusion. |
| DMEM, high glucose | ThermoFisher Scientific | 11965126 | |
| Epilog Zing 24 Laser | Cutting Edge Systems | Epilog Zing 24 | Laser cutter used to produce multi-head dispenser from acrylic sheet. Other laser cutters may be used. |
| Fisherbrand Sterile Syringes for Single Use, Luer-Lock, 20 mL | Fisher Scientific | 14-955-460 | |
| Fisherbrand Sterile Syringes for Single Use, Luer-Lock, 60 mL | Fisher Scientific | 14-955-461 | |
| Fisherbrand Premium Microcentrifuge Tubes: 1.5mL | Fisher Scientific | 05-408-129 | Microcentrifuge tubes for collecting fractions. |
| Fisherbrand Round Bottom Disposable Borosilicate Glass Tubes with Plain End | Fisher Scientific | 14-961-26 | Glass tubes for collecting fractions. |
| Fisherbrand SureOne Micropoint Pipette Tips, Universal Fit, Non-Filtered | Fisher Scientific | 2707410 | 300 ul pipette tips that best fit the multi-head dispenser and tubing to act as dispensing tips. |
| Gibco DPBS, powder, no calcium, no magnesium | Fisher Scientific | 21600010 | Phosphate buffered saline. |
| Labline 4625 Titer Shaker | Marshall Scientific | Labline 4625 Titer Shaker | Orbital shaker used to keep stirred tanks mixed. |
| Masterflex Fitting, Polycarbonate, Four-Way Stopcock, Male Luer Lock, Non-Sterile; 10/PK | Cole-Parmer | EW-30600-04 | Used to join multiple inlet streams for RTD experiments and cell culture experiments. |
| Masterflex Fitting, Polycarbonate, Straight, Female Luer x Cap; 25/PK | Masterflex | UX-45501-28 | |
| Masterflex Fitting, Polypropylene, Straight, Female Luer to Hosebarb Adapters, 1/16" | Cole-Parmer | EW-45508-00 | |
| Masterflex Fitting, Polypropylene, Straight, Male Luer Lock to Hosebarb Adapter, 1/16" ID | Cole-Parmer | EW-45518-00 | |
| Masterflex Fitting, Polypropylene, Straight, Male Luer Lock to Plug Adapter; 25/PK | Masterflex | EW-30800-30 | |
| Masterflex L/S Precision Pump Tubing, Platinum-Cured Silicone, L/S 14; 25 ft | Masterflex | EW-96410-14 | |
| MATLAB | MathWorks | R2019b | Version R2019b. Newer versions may also be used. Some older versions may work. |
| NE-1600 Six Channel Programmable Syringe Pump | New Era Pump Systems | NE-1600 | |
| Rack Set F1 | Bio-Rad | 7410010 | Racks to hold collecting tubes in the fraction collector. |
| Recombinant Human TNF-alpha (HEK293-expressed) Protein, CF | Bio-Techne | 10291-TA-020 | Cytokine used to stimulate 293T cells in representative results. |
| Saint Gobain Solid Stoppers, Versilic Silicone, Size: 00, Bottom 10.5mm | Saint Gobain | DX263015-50 | Fits 48-well plates. |
| Saint Gobain Solid Stoppers, Versilic Silicone, Size: 4 Bottom 21mm | Saint Gobain | DX263027-10 | Fits 12-well plates. |
| Sodium Hydroxide, 10.0 N Aqueous Solution APHA; 1 L | Spectrum Chemicals | S-395-1LT | |
| SolidWorks | Dassault Systems | SolidWorks | CAD software used to create the multi-head dispenser DXF file. |
| Varioskan LUX multimode microplate reader | ThermoFisher Scientific | VL0000D0 | Plate reader. |
| Wilton Color Right Performance Color System Base Refill, Blue | Michaels | 10404779 | Blue food dye containing Brilliant Blue FCF, used as a tracer in RTD experiments. Absorbance spectrum peaks at 628 nm. |
References
- Welsh, D. K., Yoo, S. H., Liu, A. C., Takahashi, J. S., Kay, S. A. Bioluminescence imaging of individual fibroblasts reveals persistent, independently phased circadian rhythms of clock gene expression. Current Biology. 14 (24), 2289-2295 (2004).
- Talaei, K., et al. A mathematical model of the dynamics of cytokine expression and human immune cell activation in response to the pathogen Staphylococcus aureus. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology. 11, 711153 (2021).
- Kemas, A. M., Youhanna, S., Zandi Shafagh, R., Lauschke, V. M. Insulin-dependent glucose consumption dynamics in 3D primary human liver cultures measured by a sensitive and specific glucose sensor with nanoliter input volume. FASEB Journal. 35 (3), 21305 (2021).
- Muzzey, D., van Oudenaarden, A. Quantitative time-lapse fluorescence microscopy in single cells. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology. 25, 301-327 (2009).
- Calligaro, H., Kinane, C., Bennis, M., Coutanson, C., Dkhissi-Benyahya, O. A standardized method to assess the endogenous activity and the light-response of the retinal clock in mammals. Molecular Vision. 26, 106-116 (2020).
- Battat, S., Weitz, D. A., Whitesides, G. M. An outlook on microfluidics: the promise and the challenge. Lab on a Chip. 22 (3), 530-536 (2022).
- Petrenko, V., Saini, C., Perrin, L., Dibner, C. Parallel measurement of circadian clock gene expression and hormone secretion in human primary cell cultures. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (117), e54673 (2016).
- Yamagishi, K., Enomoto, T., Ohmiya, Y. Perfusion-culture-based secreted bioluminescence reporter assay in living cells. Analytical Biochemistry. 354 (1), 15-21 (2006).
- Watanabe, T., et al. Multichannel perfusion culture bioluminescence reporter system for long-term detection in living cells. Analytical Biochemistry. 402 (1), 107-109 (2010).
- Murakami, N., Nakamura, H., Nishi, R., Marumoto, N., Nasu, T. Comparison of circadian oscillation of melatonin release in pineal cells of house sparrow, pigeon and Japanese quail, using cell perfusion systems. Brain Research. 651 (1-2), 209-214 (1994).
- Erickson, P., Houwayek, T., Burr, A., Teryek, M., Parekkadan, B. A continuous flow cell culture system for precision cell stimulation and time-resolved profiling of cell secretion. Analytical Biochemistry. 625, 114213 (2021).
- Saltzman, W. M. . Drug Delivery: Engineering Principles for Drug Therapy. , (2001).
- Fogler, H. S. . Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering. 4th edn. , (2006).
- Conesa, J. A. . Chemical Reactor Design: Mathematical Modeling and Applications. , (2019).
- Toson, P., Doshi, P., Jajcevic, D. Explicit residence time distribution of a generalised cascade of continuous stirred tank reactors for a description of short recirculation time (bypassing). Processes. 7 (9), 615 (2019).
- Tamayo, A. G., Shukor, S., Burr, A., Erickson, P., Parekkadan, B. Tracking leukemic T-cell transcriptional dynamics in vivo with a blood-based reporter assay. FEBS Open Biology. 10 (9), 1868-1879 (2020).
- Newell, B., Bailey, J., Islam, A., Hopkins, L., Lant, P. Characterising bioreactor mixing with residence time distribution (RTD) tests. Water Science and Technology. 37 (12), 43-47 (1998).
- Dubois, J., Tremblay, L., Lepage, M., Vermette, P. Flow dynamics within a bioreactor for tissue engineering by residence time distribution analysis combined with fluorescence and magnetic resonance imaging to investigate forced permeability and apparent diffusion coefficient in a perfusion cell culture chamber. Biotechnology and Bioengineering. 108 (10), 2488-2498 (2011).
- Gaida, L. B., et al. Liquid and gas residence time distribution in a two-stage bioreactor with cell recycle. HAL Open Science. , (2008).
- Rodrigues, M. E., Costa, A. R., Henriques, M., Azeredo, J., Oliveira, R. Wave characterization for mammalian cell culture: residence time distribution. New Biotechnology. 29 (3), 402-408 (2012).
- Olivet, D., Valls, J., Gordillo, M. A., Freixó, A., Sánchez, A. Application of residence time distribution technique to the study of the hydrodynamic behaviour of a full-scale wastewater treatment plant plug-flow bioreactor. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology. 80 (4), 425-432 (2005).

