An ATP Utilization Assay for Determining Bacterial Survival Under Antibiotics Treatment
Published: March 29, 2024
Abstract
Source: Wang, Liang-Chun, et al. Quantitative Examination of Antibiotic Susceptibility of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Aggregates Using ATP-utilization Commercial Assays and Live/Dead Staining. J. Vis. Exp. (2019).
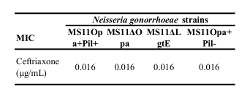
This video describes the simple ATP-measuring assay using luciferase glow reagent. This assay is used to quantify Neisseria gonorrhoeae survival after treatment with ceftriaxone.
Protocol
1. Viability quantification of GC aggregations
- Collect GC using a sterile applicator. Swab GC from the plate and re-suspend GC in pre-warmed broth(GCP, Table 1) supplemented with 4.2% NaHCO3 and 1% Kellogg solutions. Use spectrophotometry at a wavelength of 650 nm (an OD 650 of 1 = ~1 x 109 CFU/mL) to determine the concentration of suspended bacteria.
- Adjust the concentration of GC to ~1 x 108 CFU/mL.
- Add 99 µL of adjusted GC suspension into wells of a 96-well plate.
- Incubate the plate for 6 h at 37 °C with 5% CO2 to allow the bacteria to aggregate.
- Add 1 µL of serial diluted ceftriaxone (1000, 100, 50, 25, 12.5, 6.2, 3.1, 1.5, 0.8, 0.4, 0.2 µg/mL) into each well. Leave some wells untreated to serve as controls.
- Incubate the plate for 24 h at 37 °C with 5% CO2.
- Sonicate the suspension 3 times in each well for 5 s at 144 W and 20 kHz.
- Add 100 µL of commercially available ATP utilization glow reagent into each well, pipette up-and down for 3 times, and incubate for 15 min at 37 °C with 5% CO2.
- Carefully transfer 150 µL of mixture from each well into a new well in a 96-well black microplate and avoid introducing bubbles.
- Measure the absorbance of each well at 560 nm using the plate reader.
- Calculate the survival rate by the ratio of the reading obtained after serial ceftriaxone treatment to the reading from untreated wells.
2. Fluorescence microscopic analysis of Live/Dead of GC aggregates
- Collect GC using a sterile applicator. Swab GC from the plate and re-suspend GC in pre-warmed GCP media plus 1% Kellogg supplements.
- Determine the number of bacteria by spectrophotometry at a wavelength of 650 nm and adjust the concentration of GC to ~1 x 107 CFU/mL.
- Add 198 µL of GC suspension into in 8-well coverslip-bottom chambers.
- Incubate the chamber for 6 h at 37 °C with 5% CO2 to allow aggregation formation.
- Add 2 µL of ceftriaxone (100 µg/mL or various dilutions) into each well within each aggregation condition. Incubate for the desired time at 37 °C with 5% CO2.
- Add 0.6 µL of live/dead staining solution mixture into each well and incubate for 20 min at 37 °C with 5% CO2.
- Acquire Z-series images using a confocal microscope (an equivalent microscope can be used).
- Analyze the images using ImageJ software for measurement of the size of GC aggregates and the fluorescence intensity ratio FIR of live-to-dead staining in each aggregate.
Table 1: Recipe for 1 L of GCP Bacterial Growth Media.
Divulgazioni
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Materials
| 100x Kellogg's supplement | |||
| Agar | United States Biological | A0930 | |
| BacTiter Assay | Promega | G8232 | |
| Ceftriaxone | TCI | C2226 | |
| Difco GC medium base | BD | 228950 | |
| Ferric nitrate, nonahydrate | Sigma-Aldrich | 254223-10G | |
| Glucose | Thermo Fisher Scientific | BP350-1 | |
| BacLight live/dead staining | Invitrogen | L7012 | |
| MS11 Neisseria gonorrhoeae strain | kindly provided by Dr. Herman Schneider, Walter Reed Army Institute for Research | ||
| Sonicator | Kontes | Equivelent to 9110001 |
Tags
Citazione di questo articolo
An ATP Utilization Assay for Determining Bacterial Survival Under Antibiotics Treatment. J. Vis. Exp. (Pending Publication), e22010, doi: (2024).

