细胞外囊泡的量化和尺寸测定纳米粒子跟踪分析
Summary
我们演示了如何使用新型纳米粒子跟踪分析仪器来估计从小鼠围产层组织和人类血浆中分离出来的细胞外囊泡的大小分布和总颗粒浓度。
Abstract
细胞外囊泡(EV)的生理和病理生理作用已日益得到认可,使EV领域成为一个快速发展的研究领域。电动汽车隔离有许多不同的方法,每个方法都有明显的优缺点,影响电动汽车的下游产量和纯度。因此,通过选定的方法将EV准备从给定来源中分离出来,对于解释下游结果和比较实验室的结果非常重要。有各种方法来确定电动汽车的大小和数量,这些方法可以根据疾病状态或根据外部条件进行更改。纳米粒子跟踪分析 (NTA) 是用于单个 EV 的高通量分析的突出技术之一。在这里,我们提出了一个详细的协议,量化和大小确定EV从小鼠围产儿脂肪组织和人类血浆使用NTA的突破性技术,代表该领域的重大进展。结果表明,该方法可以提供可重复和有效的总粒子浓度和大小分布数据,用于使用不同方法从不同来源分离的电动汽车,如传输电子显微镜所证实的。该仪器的NTA改造将解决NTA方法标准化的需要,以提高电动汽车研究的严谨性和可重复性。
Introduction
细胞外囊泡 (EV) 是小 (0.03-2 μm) 膜绑定囊泡分泌几乎所有细胞类型1.它们通常被称为”外显子”、”微囊”或”凋形体”,这取决于它们的释放机制和大小2。虽然最初认为电动汽车只是消除细胞废物以维持平衡3的一种手段,但现在我们知道,它们也可以通过分子物质的转移参与细胞际交流,包括DNA、RNA(mRNA、microRNA)、脂质和蛋白质4、5,它们是正常生理学和病理过程的重要调节器。 5,6,7,8。
有许多不同的方法来隔离和量化电动汽车,这在其他地方已经描述9,10,11,12。使用的隔离协议以及电动汽车的来源可以极大地影响电动汽车的产量和纯度。即使是差异离心,长期被认为是外体隔离的”黄金标准”方法,也可能受到巨大的变异性,随后影响获得的EV种群和下游分析13。因此,EV隔离和量化的各种不同方法使得比较、复制和解释文献14中报道的实验结果变得困难。此外,EV 释放可以由细胞条件或各种外部因素调节。研究表明,电动汽车通过保护细胞免受细胞内应激15在维持细胞平衡方面发挥作用,因为一些研究表明,细胞压力会刺激EV分泌。例如,在细胞接触缺氧、内质视网膜应激、氧化应激、机械应激、香烟烟雾提取物和颗粒物空气污染16、17、18、19、20、21、22之后,EV释放量增加。EV 版本也已显示在体内进行了修改:小鼠受高脂肪饮食或禁食16小时释放更多的脂肪细胞EV23。要调查特定的治疗或条件是否改变 EV 释放,必须准确确定电动汽车的数量。对EV尺寸分布的评估也可能表明电动汽车的主要亚细胞起源(例如,晚期内分泌体/多血管体与等离子体膜的融合与等离子膜的萌芽)24。因此,需要采用强有力的方法来准确测量正在研究的电动汽车准备的总浓度和尺寸分布。
纳米粒子跟踪分析 (NTA) 是解决方案中电动汽车可视化和定性快速和高度敏感的方法。详细解释这种方法的原则,并与评估EV尺寸和浓度的替代方法进行比较,先前已描述25,26,27,28。简言之,在 NTA 测量期间,当电动汽车被激光束照射时,它们会被散射的光线所可视化。散射光通过显微镜聚焦在记录粒子运动的相机上。NTA 软件跟踪每个粒子的随机热运动(称为布朗运动),以确定扩散系数,该扩散系数用于使用斯托克斯-爱因斯坦方程计算每个粒子的大小。NTA于2011年首次应用于生物样本中的电动汽车测量。直到最近,只有两家主流公司提供商用 NTA 仪器29,直到采用 ViewSizer 3000(以下简称粒子跟踪仪器),它使用新型硬件和软件解决方案的组合来克服其他 NTA 技术的巨大局限性。
粒子跟踪仪器通过分析液体样品中的纳米粒子,通过分析其布朗运动来描述纳米粒子的特征,并通过分析引力沉降来描述较大的微米大小的粒子。该仪器独特的光学系统包括三个激光光源(450纳米、520纳米和635纳米)的多光谱照明,使研究人员能够同时分析各种粒子大小(例如外显子、微囊)。图 1显示了仪器设置的示意图。
在这里,我们演示了如何使用新型的 NTA 仪器对孤立的鼠标和人类 EV 进行颗粒大小分布和浓度测量。
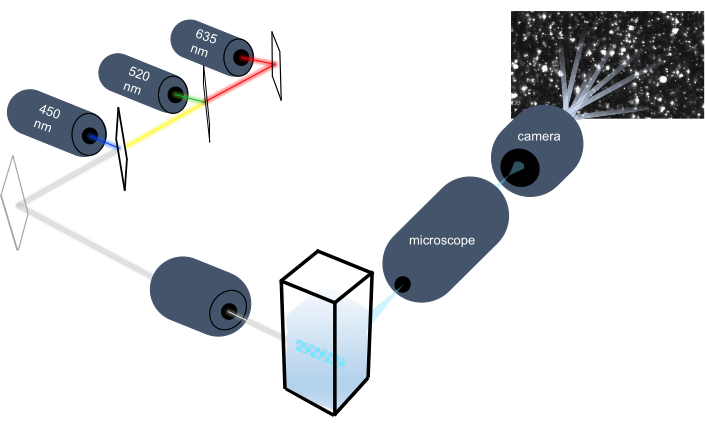
图1:粒子跟踪仪器光学系统。 NTA 仪器使用以下波长为 450 nm、520 nm、635 nm 的三种激光照明粒子。从单个粒子中检测和跟踪分散光的视频记录,由面向 90° 的数字摄像机从 cuvette 检测和跟踪。 请单击此处查看此图的较大版本。
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
在这里,我们演示了电动汽车 NTA 的协议,以同时测量各种颗粒大小的大小分布,并测量多分散样品中的总 EV 浓度。在这项研究中,小鼠围产层脂肪组织和人类血浆被用作电动汽车的来源。然而,从其他组织或生物液体(如血清、尿液、唾液、母乳、羊水和细胞培养超高纳特)中分离出来的EV也可用于NTA。聚苯乙烯珠标准的测量确保了仪器得到适当校准,并证明该 NTA 仪器能够正确测量纳米粒子的…
Divulgazioni
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
这项工作得到了国家卫生研究院(ES030973-01A1,R01ES025225,R01DK066525,P30DK026687,P30DK063608)的支持。我们感谢霍里巴仪器公司博士杰弗里·博德科姆帮助校准仪器。
Materials
| 1X dPBS | VWR | 02-0119-1000 | To dilute samples |
| 100 nm bead standard | Thermo Scientific | 3100A | To test ViewSizer 3000 calibration |
| 400 nm bead standard | Thermo Scientific | 3400A | To test ViewSizer 3000 calibration |
| Centrifugal Filter Unit | Amicon | UFC901024 | To filter PBS diluent |
| Collection tubes, 2 mL | Qiagen | 19201 | For isolation of human plasma extracellular vesicles |
| Compressed air duster | DustOff | DPSJB-12 | To clean cuvettes |
| Cuvette insert | HORIBA Scientific | – | Provided with purchase of ViewSizer 3000 |
| Cuvette jig | HORIBA Scientific | – | To align magnetic stir bar while placing inserts inside cuvette; Provided with purchase of ViewSizer 3000 |
| De-ionized water | VWR | 02-0201-1000 | To clean cuvettes |
| Desktop computer with monitor, keyboard, mouse, and all necessary cables | Dell | – | Provided with purchase of ViewSizer 3000 |
| Ethanol (70-100%) | Millipore Sigma | – | To clean cuvettes |
| ExoQuick ULTRA | System Biosciences | EQULTRA-20A-1 | For isolation of human plasma extracellular vesicles |
| Glass scintillation vials with lids | Thermo Scientific | B780020 | To clean cuvettes |
| "Hook" tool | Excelta | – | Provided with purchase of ViewSizer 3000 |
| Lint-free microfiber cloth | Texwipe | TX629 | To clean cuvettes and cover work surface |
| Microcentrifuge tubes, 2 mL | Eppendorf | 22363344 | For isolation of human plasma extracellular vesicles |
| Stir bar | Sp Scienceware | F37119-0005 | |
| Suprasil Quartz cuvette with cap | Agilent Technologies | AG1000-0544 | Initially provided with purchase of ViewSizer 3000 |
| ViewSizer 3000 | HORIBA Scientific | – | Nanoparticle tracking instrument |
Riferimenti
- Colombo, M., Raposo, G., Théry, C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology. 30, 255-289 (2014).
- Hessvik, N. P., Llorente, A. Current knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cellular and molecular life sciences: CMLS. 75, 193-208 (2018).
- Johnstone, R. M., Adam, M., Hammond, J. R., Orr, L., Turbide, C. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 262, 9412-9420 (1987).
- Théry, C., Ostrowski, M., Segura, E. Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nature Reviews Immunology. 9, 581-593 (2009).
- Yáñez-Mó, M., et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. 4, 27066 (2015).
- Lo Cicero, A., Stahl, A., Raposo, G. Extracellular vesicles shuffling intercellular messages: for good or for bad. Current Opinion in Cell Biology. 35, 69-77 (2015).
- Raposo, G., Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. The Journal of Cell Biology. 200, 373-383 (2013).
- Mathivanan, S., Ji, H., Simpson, R. J. Exosomes: extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. Journal of Proteomics. 73, 1907-1920 (2010).
- Zhang, M., et al. Methods and technologies for exosome isolation and characterization. Small Methods. 2, 1800021 (2018).
- Szatanek, R., et al. The methods of choice for extracellular vesicles (EVs) characterization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 18, (2017).
- Erdbrügger, U., Lannigan, J. Analytical challenges of extracellular vesicle detection: A comparison of different techniques. Cytometry. Part A: The Journal of the International Society for Analytical Cytology. 89, 123-134 (2016).
- Konoshenko, M. Y., Lekchnov, E. A., Vlassov, A. V., Laktionov, P. P. Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles: General Methodologies and Latest Trends. BioMed Research International. 2018, 1-27 (2018).
- Cvjetkovic, A., Lötvall, J., Lässer, C. The influence of rotor type and centrifugation time on the yield and purity of extracellular vesicles. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. 3, (2014).
- Taylor, D. D., Shah, S. Methods of isolating extracellular vesicles impact down-stream analyses of their cargoes. Methods. 87, 3-10 (2015).
- Desdín-Micó, G., Mittelbrunn, M. Role of exosomes in the protection of cellular homeostasis. Cell Adhesion & Migration. 11, 127-134 (2017).
- Kanemoto, S., et al. Multivesicular body formation enhancement and exosome release during endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 480, 166-172 (2016).
- Benedikter, B. J., et al. Cigarette smoke extract induced exosome release is mediated by depletion of exofacial thiols and can be inhibited by thiol-antioxidants. Free Radical Biology & Medicine. 108, 334-344 (2017).
- Saeed-Zidane, M., et al. Cellular and exosome mediated molecular defense mechanism in bovine granulosa cells exposed to oxidative stress. PloS One. 12, 0187569 (2017).
- Wang, K., et al. Mechanical stress-dependent autophagy component release via extracellular nanovesicles in tumor cells. ACS Nano. 13, 4589-4602 (2019).
- King, H. W., Michael, M. Z., Gleadle, J. M. Hypoxic enhancement of exosome release by breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 12, 421 (2012).
- Bonzini, M., et al. Short-term particulate matter exposure induces extracellular vesicle release in overweight subjects. Environment Research. 155, 228-234 (2017).
- Neri, T., et al. Particulate matter induces prothrombotic microparticle shedding by human mononuclear and endothelial cells. Toxicology In Vitro. 32, 333-338 (2016).
- Flaherty, S. E., et al. A lipase-independent pathway of lipid release and immune modulation by adipocytes. Science. 363, 989-993 (2019).
- van Niel, G., D’Angelo, G., Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology. 19, 213-228 (2018).
- Dragovic, R. A., et al. Sizing and phenotyping of cellular vesicles using Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology, and Medicine. 7, 780-788 (2011).
- Saveyn, H., et al. Accurate particle size distribution determination by nanoparticle tracking analysis based on 2-D Brownian dynamics simulation. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science. 352, 593-600 (2010).
- Vander Meeren, P., Kasinos, M., Saveyn, H. Relevance of two-dimensional Brownian motion dynamics in applying nanoparticle tracking analysis. Methods in Molecular Biology. , 525-534 (2012).
- Filipe, V., Hawe, A., Jiskoot, W. Critical evaluation of Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) by NanoSight for the measurement of nanoparticles and protein aggregates. Pharmaceutical Research. 27, 796-810 (2010).
- Bachurski, D., et al. Extracellular vesicle measurements with nanoparticle tracking analysis – An accuracy and repeatability comparison between NanoSight NS300 and ZetaView. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. 8, 1596016 (2019).
- Varga, Z., et al. Hollow organosilica beads as reference particles for optical detection of extracellular vesicles. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 16, 1646-1655 (2018).
- Serrano-Pertierra, E., et al. Extracellular vesicles: Current analytical techniques for detection and quantification. Biomolecules. 10, (2020).
- Maguire, C. M., Rösslein, M., Wick, P., Prina-Mello, A. Characterisation of particles in solution – a perspective on light scattering and comparative technologies. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials. 19, 732-745 (2018).
- Bohren, C. F., Huffman, D. R. . Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles. , (1983).

