三维培养试验探索肿瘤细胞浸润和卫星肿瘤形成
Summary
Cancer cells are embedded in a collagen gel and then sandwiched in an acellular fibrin gel to generate a 3D culture system in which the invasiveness and formation of satellite tumors may be monitored.
Abstract
在单层哺乳动物细胞培养被广泛用于研究各种生理和分子过程。然而,这种方法来研究生长的细胞往往会产生不希望的痕迹。因此,在一个三维(3D)环境的细胞培养,通常使用细胞外基质组分,成为一个有趣的选择,因为它接近相似的体内组织或器官中的原生。我们开发了使用两个室,即(i)一个三维细胞培养系统包含嵌入在胶原凝胶充当伪主macrospherical肿瘤和(ii)的周边无细胞隔室制成的纤维蛋白凝胶的癌细胞的中心隔室, 即细胞外基质组分从在中心使用的不同,其中,癌症细胞可以迁移(侵入前)和/或形成代表仲或卫星肿瘤微球肿瘤。卫星肿瘤的外围隔室的形成是显着相关与天然肿瘤细胞的已知攻击性或转移性原点,这使得这种三维培养系统是唯一的。这种细胞培养物的方法可以考虑以评估癌细胞侵袭和运动性,细胞 – 细胞外基质相互作用并作为评价抗癌药物性能的方法。
Introduction
调查癌细胞侵袭/迁移和随后的转移机构的基本和生物医学特征是强烈的研究1,2的主题。转移是癌症的最终阶段,临床管理仍然遥遥无期。在细胞和分子水平上更好地了解转移将使更有效的疗法3的发展。
转移细胞的几个属性可以在体外 4包括它们的干性和潜在的获得的过渡状态( 例如 ,上皮-间质转化)迁移和内部以及从原发肿瘤5侵入进行探讨。然而,侵袭/转移过程的体外评估一直是一个挑战,因为它几乎排除了血液/淋巴循环的贡献。在胶原凝胶中嵌入肿瘤碎片器官文化有页上一页狡猾被用于监测癌症的侵袭性。虽然肿瘤的复杂性被保留( 例如 ,非癌细胞的存在),肿瘤片段暴露于有限介质扩散,以采样变化,并且对基质细胞6的过度生长。另一种方法包括在细胞外基质(ECM),它模仿了三维(3D)细胞环境的组分中生长的癌细胞。的乳腺癌细胞系中胶原凝胶和/或基底膜衍生基质的扩散是之中三维细胞培养物的最佳表征的例子。通过使用特定的三维细胞培养物的环境中,在标准条件下生长的乳腺癌细胞中观察到的紊乱组件可被反向以自发形成乳腺腺泡和管状结构7-10的。此外,来自腺癌细胞的多细胞肿瘤球状体的形成使用不同的技术(聚集例如,悬滴,浮球体,琼脂嵌入)现在构成了最常用的三维细胞培养物测定法11-13。然而,该测定是由限制集合的癌细胞系可以形成球状体,并通过提供研究细胞在这些条件下,短周期的限制。
在这种可视化技术,我们这里所介绍其中感兴趣癌细胞嵌入在胶原凝胶,以允许可替代地涂覆有基底膜衍生矩阵的伪原发肿瘤的体外形成复杂的三维细胞培养物测定法。一旦形成,所述伪原发性肿瘤,然后夹在无细胞基质(在本例中纤维蛋白胶),它允许癌细胞跨越两个矩阵隔间之间的界面(参见图1)。有趣的是,从伪原发性肿瘤始发侵袭性癌细胞沿继发性肿瘤样结构出现在纤维蛋白胶。这样的三维培养系统提供调查所需的灵活性,例如,抗癌药物,基因表达和细胞-细胞和/或细胞-ECM相互作用14-16。
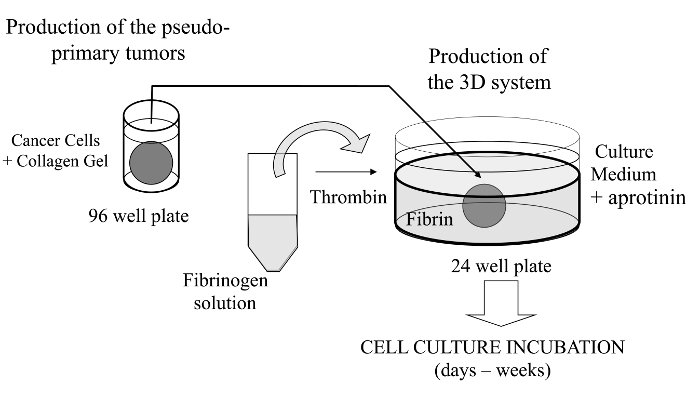
图 1: 该方法的概述 ,生成三维细胞培养系统作为癌症研究的模型方法的原理总结,请点击此处查看该图的放大版本。
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
作为一个重要的技术脚注,至关重要的是,没有间隙存在于中央和周边的凝胶之间的接口。否则,可能会降低细胞迁移/侵袭纤维蛋白凝胶的能力。如果凝血酶未被适当地稀释的胶原蛋白和纤维蛋白凝胶之间的空间可以培养的第24小时的过程中可形成。它也可能是测试可能导致的胶原蛋白凝胶的细胞系培养过程中收缩,从而导致相当大的空间都凝胶之间形成。当基质细胞中的胶原凝胶与癌细胞由于?…
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
Work partially funded by Prostate Cancer Canada (grant # D2014-4 to SG and CJD) and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (grant # MOP-111069 to SG). We would like to thank Dr. Richard Poulin for editorial assistance and Mrs. Chanel Dupont for technical assistance.
Materials
| Freeze-dried collagen | Sigma-Aldrich | C7661 | from rat tail tendon (soluble dispersion) or home-made (see Rajan et al., ref.#14) |
| Fibrinogen (freeze-dried) | Sigma-Aldrich | F8630 | Type I-S, 65-85% protein with ≥75% of protein is clottable |
| Thrombin | EMD Chemicals Inc. | 605157 | Gibbstown, NJ; NIH units/mg dry weight |
| Growth factor-reduced Matrigel | Corning | 356234 | Previously from BD Biosciences |
| Aprotinin | Sigma-Aldrich | A6279 | solution at 5-10TIU/ml (Trypsin Inhibitor Unit) |
| Micro-spoons | Fisher Scientific | 2140115 | Fisherbrand Handi-Hold Microspatula |
| 96 well plate, round base | Sarstedt | 3925500 | |
| 24 well plate | Sarstedt | 3922 | |
| Dulbecco's modified Eagle's Medium | Sigma Chemical, Co. | D5546 | DMEM |
| Fetal Bovine Serum | VWR | CAA15-701 | FBS, Canadian origin. |
| Trypsin-EDTA | Sigma Chemical, Co. | T4049 | |
| Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution | Sigma Chemical, Co. | H8264 | HBSS |
References
- Alizadeh, A. M., Shiri, S., Farsinejad, S. Metastasis review: from bench to bedside. Tumour Biol. 35 (9), 8483-8523 (2014).
- Roudsari, L. C., West, J. L. Studying the influence of angiogenesis in in vitro cancer model systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. , (2016).
- Bill, R., Christofori, G. The relevance of EMT in breast cancer metastasis: Correlation or causality. FEBS Lett. 589 (14), 1577-1587 (2015).
- Kimlin, L. C., Casagrande, G., Virador, V. M. In Vitro Three-Dimensional (3D) Models in Cancer Research: an Update. Mol Carcinog. 52 (3), 167-182 (2013).
- Obenauf, A. C., Massagué, J. Surviving at a Distance Organ-Specific Metastasis. Trends Cancer. 1 (1), 76-91 (2015).
- Sykes, J. A., Fogh, J. Separation of Tumor Cells from Fibroblasts. Human Tumor Cells In Vitro. 1, 1-22 (1975).
- Lang, S. H., Stark, M., Collins, A., Paul, A. B., Stower, M. J., Maitland, N. J. Experimental Prostate Epithelial Morphogenesis in Response to Stroma and Three-Dimensional Matrigel Culture. Cell Growth Differ. 12 (12), 631-640 (2001).
- Debnath, J., Muthuswamy, S. K., Brugge, J. S. Morphogenesis and Oncogenesis of MCF-10A Mammary Epithelial Acini Grown In Three-Dimensional Basement Membrane Cultures. Methods. 30 (3), 256-268 (2003).
- Shaw, L. M. Tumor cell invasion assays. Methods Mol. Biol. 294, 97-105 (2005).
- Nelson, C. M., Bissell, M. J. Modeling Dynamic Reciprocity: Engineering Three-Dimensional Culture Models of Breast Architecture, Function, and Neoplastic Transformation. Semin Cancer Biol. 15 (5), 342-352 (2005).
- Hedlund, T. E., Duke, R. C., Miller, G. J. Three-Dimensional Spheroid Cultures of Human Prostate Cancer Cell Lines. Prostate. 41 (3), 154-165 (1999).
- Le, V. M., Lang, M. D., Shi, W. B., Liu, J. W. A Collagen-Based Multicellular Tumor Spheroid Model for Evaluation of the Efficiency of Nanoparticle Drug Delivery. Artif. Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 15, 1-5 (2014).
- Neto, A. I., et al. A Novel Hanging Spherical Drop System for the Generation of Cellular Spheroids and High Throughput Combinatorial Drug Screening. Biomater Sci. 3 (4), 581-585 (2015).
- Janvier, R., Sourla, A., Koutsilieris, M., Doillon, C. J. Stromal Fibroblasts are Required for PC-3 Human Prostate Cancer Cells to Produce Capillary-like Formation of Endothelial Cells in a Three-dimensional Co-culture System. Anticancer Res. 17 (3A), 1551-1557 (1997).
- Doillon, C. J., Gagnon, E., Paradis, R., Koutsilieris, M. Three-dimensional Culture System as a Model for Studying Cancer Cell Invasion Capacity and Anticancer Drug Sensitivity. Anticancer Res. 24 (4), 2169-2177 (2004).
- Gobeil, S., Zhu, X., Doillon, C. J., Green, M. R. A Genome-Wide shRNA Screen Identifies GAS1 as a Novel Melanoma Metastasis Suppressor Gene. Genes Dev. 22 (21), 2932-2940 (2008).
- Rajan, N., Habermehl, J., Coté, M. F., Doillon, C. J., Mantovani, D. Preparation Of Ready-To-Use, Storable And Reconstituted Type I Collagen From Rat Tail Tendon For Tissue Engineering Applications. Nat Protoc. 1 (6), 2753-2758 (2007).
- Horie, M., et al. Characterization of Human Lung Cancer-associated Fibroblasts in Three-dimensional In Vitro Co-culture Model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 423 (1), 158-163 (2012).
- Banyard, J., et al. Identification of Genes Regulating Migration and Invasion Using a New Model of Metastatic Prostate Cancer. BMC Cancer. 30 (14), 387 (2014).
- Palumbo, J. S., Degen, J. L. Fibrinogen and Tumor Cell Metastasis. Haemostasis. 31, 11-15 (2001).
- Dvorak, H. F. Tumor Stroma, Tumor Blood Vessels, and Antiangiogenesis Therapy. Cancer J. 21 (4), 237-243 (2015).
- Luoto, K. R., Kumareswaran, R., Bristow, R. G. Tumor Hypoxia as a Driving Force in Genetic Instability. Genome Integr. 4 (1), 5 (2013).
- Das, V., Bruzzese, F., Konečný, P., Iannelli, F., Budillon, A., Hajdúch, M. Pathophysiologically Relevant In Vitro Tumor Models for Drug Screening. Drug Discov Today. 20 (7), 848-855 (2015).
- Longati, P., et al. 3D Pancreatic Carcinoma Spheroids Induce a Matrix-rich, Chemoresistant Phenotype Offering a Better Model for Drug Testing. BMC Cancer. 13 (95), (2013).
- Tan, P. H., Chia, S. S., Toh, S. L., Goh, J. C., Nathanm, S. S. Three-dimensional Spatial Configuration of Tumour Cells Confers Resistance to Chemotherapy Independent of Drug Delivery. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. , (2013).
- Koutsilieris, M., Reyes-Moreno, C., Choki, I., Sourla, A., Doillon, C., Pavlidis, N. Chemotherapy Cytotoxicity of Human MCF-7 and MDA-MB 231 Breast Cancer Cells is Altered by Osteoblast-Derived Growth Factors. Mol Med. 5 (2), 86-97 (1999).
- Lang, N. R., et al. Biphasic Response of Cell Invasion to Matrix Stiffness in Three-Dimensional Biopolymer Networks. Acta Biomater. 13, 61-67 (2015).

