ラット膵臓組織の迅速かつ費用対効果の高いRNA抽出
Summary
単離されたRNAの純度と完全性は、RNA依存アッセイにおいて重要なステップです。ここでは、少量の損傷を受けていない膵臓組織からRNAを抽出する実用的で迅速かつ安価な方法を提示する。
Abstract
抽出方法に関係なく、組織および細胞株の最適化されたRNA抽出は、1)均質化、2)RNAからのタンパク質の有効な変性、3)リボヌクレアーゼ不活性化、および4)DNA、タンパク質、および炭水化物からの汚染の除去の4つの段階で行われます。しかし、組織に高レベルのRNaseがある場合、RNAの完全性を維持することは非常に面倒です。自発的な自己分解は、それを損傷することなく、膵臓組織からRNAを抽出することは非常に困難になります。したがって、抽出プロセス中に膵臓組織の完全性を維持するために実用的なRNA抽出方法が必要です。既存のプロトコルの実験的および比較研究は、2分未満で20〜30mgのラット膵臓組織を得てRNAを抽出することによって行われた。結果は電気泳動によって評価された。実験は、結果の一般化のために3回行った。24時間に対して−80°CでのRNA安定化試薬に膵臓組織を浸漬すると、RNA抽出試薬を試薬として用いた場合に高い完全性RNAが生じ、。得られた結果は、スピンカラム結合を有する市販キットから得られた結果と同等であった。
Introduction
構造遺伝子データは、遺伝子発現を通じて機能産物に転写することができる。RNA解析は、異なる条件間で遺伝子発現の違いを発見するために使用されます。核酸を抽出する方法は数多くあります:グアニジニウム・チオシアネート、フェノールクロロホルムによる抽出、セルロース系クロマトグラフィー、シリカマトリックスによる抽出、およびアニオン交換11,2。2
遺伝子発現の適切な検出は、組織から分離されたRNAの完全性の影響を受けます。したがって、低品質RNAの補完的な分子試験は診断アプリケーションの結果を危険にさらす可能性があるため、さらなる試験を行う前に、組織から分離されたRNAの完全性を評価することが重要です。したがって、定量的RT-PCR、マイクロアレイ、リボヌクレアーゼ保護アッセイ、ノーザンブロット分析、RNAマッピング、およびcDNAライブラリ構築33、44など、さまざまな診断アプリケーションを用いた分子生物学的試験には高い完全性RNAが必要です。
RNAは、長期間保持された後、かなり不安定になります。10 kb 以上の長い mRNA フラグメントは、特に分解の影響を受けやすい5,,6。したがって、研究者は、精製されたRNAの完全性に影響を与える様々な要因を考慮する必要があります。RNAの純度は、RNases、タンパク質、ゲノムDNA、および酵素阻害剤汚染から保護されなければならない。さらに、RNAとUVの吸収率(260/280)は、電気泳動に対する最小の断片化で1.8~2.0の範囲内でなければなりません。最近開発された実験室の技術は、科学者がより実質的に7、8の分子分析7サンプルの完全性を評価することを可能にしました。
リボヌクレアーゼ(RNases)の量が多いため、他のタイプの組織よりも膵臓組織から損傷を受けていないRNAを抽出することははるかに困難です。しかし、既存の抽出方法、すなわち、RNasesを妨げる低温での腹腔および均質化からの膵臓組織の急速な放出は、有効でない787、8、9、10、11、12、13、14,13,14を証明している。11,12,9,10,,
本比較実験研究の目的は、既存の方法を修正し、比較して最も効率的な方法を決定することです。そのために、RNA抽出の様々なプロトコルを改変し、比較した。これは、膵臓組織の最小量を必要とする最も安価な方法を決定することを特に目的とした。
Protocol
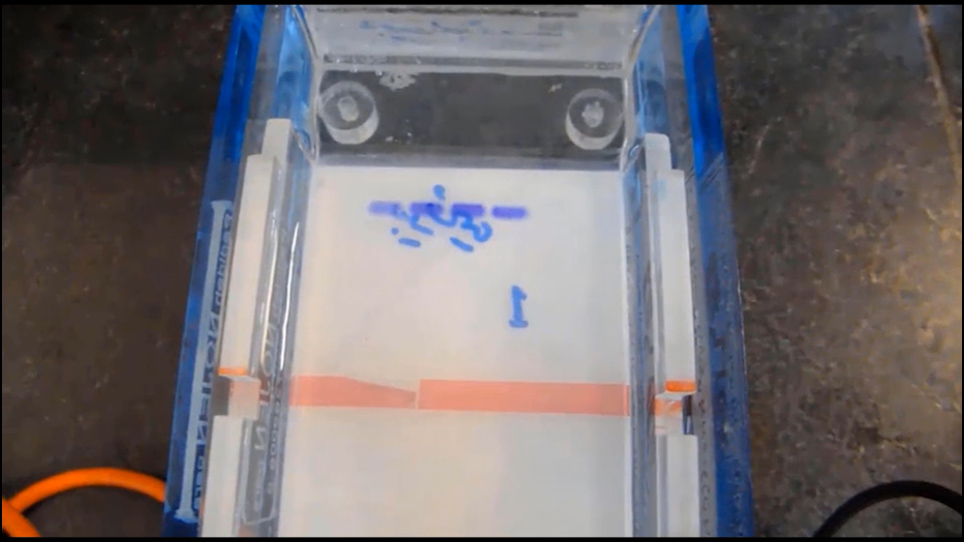
Representative Results
Discussion
分子生物学では、高品質のRNAを得ることが不可欠です。細胞および組織におけるリボヌクレアーゼ酵素の存在は、RNAを迅速に分解し、抽出を複雑にします。RNasesは共因子なしで機能する安定した酵素である。少量のRNaseはRNAを破壊するのに十分です。ラット膵臓組織が腹腔から取り出されるとき、強い洗剤によって外科器具を消毒し、十分に洗い流し、手術前にRNasesを不活性化するために240°…
Declarações
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
本研究は、シラーズ医科大学(グラント93-01-01-7178\03-07-2014)によって財政的に支援されました。私たちは、ビデオを編集するためのサイラズ医科大学、医学、バーチャルスクール、eラーニングの卓越性センターの医学部のゾモロディアン氏とロスタミ氏に感謝します。
Materials
| Agarose | Merck | 116801 | Germany |
| Atoclave | Teb Zaim | Iran | |
| Centrifuge | Sigma | Germany | |
| Chloroform | Merck | 107024 | Germany |
| Diethylpyrocarbonate (DEPC)-treated water | Sigma | Germany | |
| EDTA | sigma | 60-00-4 | Germany |
| Electrophoresis tank | Payapajoohesh | Iran | |
| Eppendorf microTube | Extragene | Taiwan | |
| EtBr | sigma | E 8751 | Germany |
| Ethanol | Merck | 81870 | Germany |
| Falcon Tube | Extragene | Taiwan | |
| Formaldehyde | Merck | 344198 | Germany |
| Formamide | Merck | 344206 | Germany |
| Homogenizer-sunicator | Microson XL 2000 | USA | |
| Isopropanol | sigma | 19516 | Germany |
| Ketamine hydrochloride | sigma | 1867-66-9 | Germany |
| Laminar Flow Hood | Jal Tajhiz | Iran | |
| Mgnetic stirrer | Labrotechnik | USA | |
| Microcentrifuge | Eppendorf | Germany | |
| Micropipette Tips | Extragene | Taiwan | |
| MOPS | sigma | 85022106 | Germany |
| Na AC | Merck | 567422 | Germany |
| NaOH | Merck | 109137 | Germany |
| Oven | Teb Zaim | Iran | |
| PH meter | Knick | Germany | |
| RNA Later/RNA stabilization reagent | Qiagen | 76104 | USA |
| Surgical instrument | Agn Thos | German made | |
| Syringes | AvaPezeshk | Iran | |
| TriPure reagent/RNA extraction reagent | Roche | 11667157001 | USA |
| Vortex | Labinco | Netherland | |
| Water bath | Memmert | Germany | |
| zylazine | sigma | 7361-61-7 | Germany |
Referências
- McCarthy, B., Hoyer, B. Identity of DNA and diversity of messenger RNA molecules in normal mouse tissues. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 52 (4), 915-922 (1964).
- Tan, S. C., Yiap, B. C. DNA, RNA, and protein extraction: the past and the present. BioMed Research International. 2009, (2009).
- Peirson, S. N., Butler, J. N. RNA extraction from mammalian tissues. Circadian Rhythms: Methods and Protocols. , 315-327 (2007).
- Skidmore, A. F., Beebee, T. J. Characterization and use of the potent ribonuclease inhibitor aurintricarboxylic acid for the isolation of RNA from animal tissues. Biochemical Journal. 263 (1), 73-80 (1989).
- Mukhopadhyay, T., Roth, J. A. Isolation of total RNA from tissues or cell lines: visualization in gel. RNA Isolation and Characterization Protocols. , 55-59 (1998).
- Raeymaekers, L. Quantitative PCR: theoretical considerations with practical implications. Analytical Biochemistry. 214 (2), 582-585 (1993).
- Sparmann, G., Jäschke, A., Loehr, M., Liebe, S., Emmrich, J. Tissue homogenization as a key step in extracting RNA from human and rat pancreatic tissue. Biotechniques. 22 (3), 408 (1997).
- Kiba, T., et al. High-quality RNA extraction from rat pancreas for microarray analysis. Pancreas. 35 (1), 98-100 (2007).
- Gill, S. S., Aubin, R. A., Bura, C. A., Curran, I. H., Matula, T. I. Ensuring recovery of intact RNA from rat pancreas. Molecular Biotechnology. 6 (3), 359-362 (1996).
- Hernandez, G. E., Mondala, T. S., Head, S. R. Assessing a novel room temperature RNA storage medium for compatibility in microarray gene expression analysis. Biotechniques. 47 (2), 667 (2009).
- Mullin, A. E., Soukatcheva, G., Verchere, C. B., Chantler, J. K. Application of in situ ductal perfusion to facilitate isolation of high-quality RNA from mouse pancreas. Biotechniques. 40 (5), 617 (2006).
- Li, D., et al. A modified method using TRIzol reagent and liquid nitrogen produces high-quality RNA from rat pancreas. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology. 158 (2), 253-261 (2009).
- Griffin, M., Abu-El-Haija, M., Abu-El-Haija, M., Rokhlina, T., Uc, A. A simplified and versatile method for obtaining high quality rna from pancreas. Biotechniques. 52 (5), 332 (2012).
- Jun, E., et al. Method optimization for extracting high-quality RNA from the human pancreas tissue. Translation Oncology. 11 (3), 800-807 (2018).
- Green, M. R., Sambrook, J. J. How to win the battle with RNase. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols. (2), 101857 (2019).
- Li, D. -. S., Yuan, Y. -. H., Tu, H. -. J., Dai, L. -. j. A protocol for islet isolation from mouse pancreas. Nature Protocols. 4 (11), 1649 (2009).
- Armstrong, J. A., Schulz, J. R. J. Agarose gel electrophoresis. Current Protocol: Essential Laboratory Techniques. (1), 1-20 (2008).
- Aranda, P. S., LaJoie, D. M., Jorcyk, C. Bleach gel: a simple agarose gel for analyzing RNA quality. Electrophoresis. 33 (2), 366-369 (2012).
- Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F., Maniatis, T. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold spring harbor laboratory press. , (1989).
- Potenza, N., et al. Hybridase activity of human ribonuclease-1 revealed by a real-time fluorometric assay. Nucleic Acids Research. 34 (10), 2906-2913 (2006).
- Jackson, D., Lewis, F., Taylor, G., Boylston, A., Quirke, P. Tissue extraction of DNA and RNA and analysis by the polymerase chain reaction. Journal of Clinical Pathology. 43 (6), 499-504 (1990).
- Quesada, I., Tudurí, E., Ripoll, C., Nadal, &. #. 1. 9. 3. ;. Physiology of the pancreatic α-cell and glucagon secretion: role in glucose homeostasis and diabetes. Journal of Endocrinology. 199 (1), 5-19 (2008).
- Quertinmont, E., Nicaise, C., Gustot, T., Deviere, J. Tissue Homogenization with the MagNA Lyser Instrument for Total RNA Extraction Using the TriPure Reagent. Liver (mg). 100 (100), 100 (2004).
- Dastgheib, S., Irajie, C., Assaei, R., Koohpeima, F., Mokarram, P. Optimization of RNA extraction from rat pancreatic tissue. Iranian Journal of Medical Sciences. 39 (3), 282 (2014).