执行显微镜安装的Y形切割测试
Summary
Y形切割测量软材料中与断裂相关的长度尺度和能量。以前的设备是为台式测量而设计的。该协议描述了一种设备的制造和使用,该设备水平定向设置,并通过光学显微镜提供原位观察以及故障量化所需的精细定位能力。
Abstract
Y形切割最近被证明是一种很有前途的方法,通过该方法可以了解材料的阈值长度尺度和失效能量,以及存在过量变形能量时的失效响应。这些研究中使用的实验装置是垂直定向的,需要繁琐的步骤来调整Y形腿之间的角度。垂直方向禁止在标准光学显微镜中进行可视化。该协议提出了一个Y形切割装置,该设备水平安装在现有的倒置显微镜载物台上,可以在三维(X-Y-Z)中进行调整以落在物镜的视野内,并允许轻松修改腿之间的角度。后两个功能是这种实验技术的新功能。所提出的设备测量切削力的精度在1 mN以内。在测试该技术的参考材料聚二甲基硅氧烷(PDMS)时,测量的切削能量为132.96 J/m 2(32°腿角,75 g预紧力),发现其误差在先前垂直设置下的测量误差范围内(132.9 J/m 2 ± 3.4 J/m2)。该方法适用于软合成材料、组织或生物膜,并可能为它们在失效期间的行为提供新的见解。这项工作中的零件列表、CAD 文件和详细说明为轻松实施这一强大技术提供了路线图。
Introduction
非线性连续介质力学提供了一个关键的镜头,通过它来理解导致软固体失效的能量集中1。然而,准确预测这种破坏还需要描述有助于在裂纹尖端2,3处产生新表面的微观结构特征。处理此类描述的一种方法是在失效4,5期间对裂纹尖端进行原位可视化。然而,在典型的远场断裂测试中,裂纹钝化使得通过展开高度变形的材料(可能超出显微镜的视场6)来获取原位数据具有挑战性。Y形切割为微观结构可视化提供了一种独特的替代方案,因为它将大变形区域集中在刀片7的尖端。此外,我们小组以前的工作表明,这种独特的实验方法可以深入了解远场撕裂和接触介导的加载条件之间的失效响应差异7。
这里介绍的设备中使用的Y形切割方法在几十年前首次被描述为天然橡胶的切割方法8。该方法包括通过预加载的Y形试件推切固定刀片。在“Y”的交点处是裂纹尖端,它是在测试之前通过将矩形的一部分分成两个相等的“腿”来创建的(图1B和图2D)。这种切割方法的主要优点包括减少摩擦对测量的切削能量的贡献,可变的刀片几何形状(即,裂纹尖端几何形状的约束),故障率的控制(通过样品位移率),以及单独调整切割,C和撕裂,T,能量贡献对总能量G切割(即 改变超过切割阈值的失效能量)8.后一种贡献以切削能量的简单闭式表达式表示9
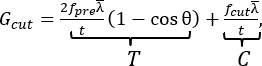 等式 (1)
等式 (1)
它使用实验选择的参数,包括样品厚度、t、平均腿应变、预紧力、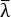 fpre 以及腿与切割轴之间的角度 θ。切割力f切割是用Zhang等人9中详述的仪器测量的。值得注意的是,这里介绍的装置包括一种新的、简单而准确的机制,用于调整支腿角度θ,并确保样品居中。虽然这两个功能对于显微镜安装的设置都至关重要,但该机制也可能通过提高易用性而有利于Y形切割测试的未来垂直实施。
fpre 以及腿与切割轴之间的角度 θ。切割力f切割是用Zhang等人9中详述的仪器测量的。值得注意的是,这里介绍的装置包括一种新的、简单而准确的机制,用于调整支腿角度θ,并确保样品居中。虽然这两个功能对于显微镜安装的设置都至关重要,但该机制也可能通过提高易用性而有利于Y形切割测试的未来垂直实施。
自Rivlin和Thomas10引入的独立于样品的断裂几何形状的早期成功以来,在确定软固体的适当失效标准方面一直在取得进展。已经使用了临界能量释放率10,内聚区定律11以及各种形式的压力或远距离能量方法12,13,14。最近,Zhang和Hutchens利用后一种方法,证明具有足够小半径刀片的Y形切割可以产生软断裂7的阈值失效条件:阈值失效能量和阈值长度尺度,在均匀,高弹性聚二甲基硅氧烷(PDMS)中从数十到数百纳米不等。这些结果与连续介质建模和缩放理论相结合,以发展这些材料中切割和撕裂之间的关系,从而证明了Y形切割在提供对所有软失效模式的见解方面的实用性。然而,许多材料类别的行为,包括耗散和复合材料,仍未被探索。预计其中许多将在高于可见光波长的长度尺度上表现出微观结构控制效应。因此,本研究设计了一种装置,该装置允许首次在Y形切割期间对这些影响进行近距离的视觉表征(例如,在复合材料中,包括软组织,或耗散过程,预计在微米到毫米长度尺度上15)。
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
这里报道的水平Y形切割设备可实现 原位 成像功能,并提高了这种故障技术的易用性。该设备包括模块化/便携式设计,用于从显微镜上快速安装/拆卸,并连续、预先对齐的支腿角度调整。所有CAD文件,所需材料和程序都包括在内,以促进此方法的实施。在许多情况下(刀片支架、样品支架、称重传感器支架、安装框架),3D打印部件可以很容易地针对给定的材料/刀片或特定的称重传感器/?…
Declarações
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
我们要感谢James Phillips博士,Amy Wagoner-Johnson博士,Alexandra Spitzer和Amir Ostadi对这项工作的建议。资金来自伊利诺伊大学厄巴纳-香槟分校机械科学与工程系提供的启动补助金。M. Guerena,J. C. Peng,M. Schmid和C. Walsh都因其在该项目上的工作而获得了高级设计荣誉。
Materials
| Buy Parts | |||
| 1" OD Pulley | McMaster Carr | 3434T75 | Pulley for Wire Rope (Larger) |
| 100 g Micro Load Cell | RobotShop | RB-Phi-203 | |
| 1K Resistor | Digi-Key | CMF1.00KFGCT-ND | 1 kOhms ±1% 1 W Through Hole Resistor Axial Flame Retardant Coating, Moisture Resistant, Safety Metal Film |
| 1M Resistor | Digi-Key | RNF14FAD1M00 | 1 MOhms ±1% 0.25 W, 1/4 W Through Hole Resistor Axial Flame Retardant Coating, Safety Metal Film |
| 3/8" OD Pulley | McMaster Carr | 3434T31 | Pulley for Wire Rope |
| 4" Clear Protractor with Easy Read Markings | S&S Worldwide | LR3023 | |
| Breadboard | ECEB | N/A | |
| IC OPAMP ZERO-DRIFT 2 CIRC 8DIP | Digi-Key | LTC1051CN8#PBF-ND | |
| M2 x 0.4 mm Nut | McMaster Carr | 90592A075 | Steel Hex Nut |
| M2 x 0.4 mm x 25 mm | McMaster Carr | 91292A032 | 18-8 Stainless Steel Socket Head Screw |
| M2 x 0.4 mm x 8 mm | McMaster Carr | 91292A832 | 18-8 Stainless Steel Socket Head Screw |
| M3 x 0.5 mm x 15 mm | McMaster Carr | 91290A572 | Black-Oxide Alloy Steel Socket Head Screw |
| M3 x 0.5 mm x 16 mm | McMaster Carr | 91294A134 | Black-Oxide Alloy Steel Hex Drive Flat Head Screw |
| M3 x 0.5 mm, 4 mm High | McMaster Carr | 90576A102 | Medium-Strength Steel Nylon-Insert Locknut |
| M4 x 0.7 mm Nut | McMaster Carr | 90592A090 | Steel Hex Nut |
| M4 x 0.7 mm x 15 mm | McMaster Carr | 91290A306 | Black-Oxide Alloy Steel Socket Head Screw |
| M4 x 0.7 mm x 16 mm | McMaster Carr | 91294A194 | Black-Oxide Alloy Steel Hex Drive Flat Head Screw |
| M4 x 0.7 mm x 18 mm | McMaster Carr | 91290A164 | Black-Oxide Alloy Steel Socket Head Screw |
| M4 x 0.7 mm x 20 mm | McMaster Carr | 91290A168 | Black-Oxide Alloy Steel Socket Head Screw |
| M4 x 0.7 mm x 20 mm | McMaster Carr | 92581A270 | Stell Raised Knurled-Head Thumb Screw |
| M4 x 0.7 mm x 30 mm | McMaster Carr | 91290A172 | Black-Oxide Alloy Steel Socket Head Screw |
| M4 x 0.7 mm x 50 mm | McMaster Carr | 91290A193 | Black-Oxide Alloy Steel Socket Head Screw |
| M4 x 0.7 mm, 5 mm High | McMaster Carr | 94645A101 | High-Strength Steel Nylon-Insert Locknut |
| M5 x 0.8 mm Nut | McMaster Carr | 90592A095 | Steel Hex Nut |
| M5 x 0.8 mm x 16 mm | McMaster Carr | 91310A123 | High-Strength Class 10.9 Steel Hex Head Screw |
| M5 x 0.8 mm x 35 mm | McMaster Carr | 91290A195 | Black-Oxide Alloy Steel Socket Head Screw |
| M5 x 0.8 mm, 13 mm Head Diameter | McMaster Carr | 96445A360 | Flanged Knurled-Head Thumb Nut |
| M5 x 0.8 mm, 5 mm High | McMaster Carr | 90576A104 | Medium-Strength Steel Nylon-Insert Locknut |
| Solidworks | Dassault Systemes | CAD software | |
| Wiring Kit | ECEB | N/A | |
| XYZ Axis Manual Precision Linear Stage 60 mm x 60 mm Trimming Bearing Tuning Platform Sliding Table | OpticsFocus | N/A | |
| Make Parts | |||
| Angle adjustment system- arm | 3D Printing | solidworks: arms_arm_single.SLDPRT QTY: 2 Setting: Fast/0.2 mm layer height |
|
| Angle adjustment system- arms stationary | 3D Printing | solidworks: arms_stationary.SLDPRT QTY: 1 Setting: Fast/0.2 mm layer height |
|
| Angle adjustment system- link | 3D Printing | solidworks: arms_arm_link.SLDPRT QTY: 2 Setting: Fast/0.2 mm layer height |
|
| Angle adjustment system- slider | 3D Printing | solidworks: arms_slider.SLDPRT QTY: 1 Setting: Fast/0.2 mm layer height |
|
| Angle adjustment system- spacer | 3D Printing | solidworks: arms_front_spacer.SLDPRT QTY: 1 Setting: Fast/0.2 mm layer height |
|
| Clip- Blade clip | 3D Printing | solidworks: Blade clip.SLDPRT QTY: 1 Setting: Fine/0.1 mm layer height |
|
| Clip- Blade clip mount | 3D Printing | solidworks: Blade clip mount.SLDPRT QTY: 1 Setting: Fine/0.1 mm layer height |
|
| Frame arm | 3D Printing | solidworks: frame arm.SLDPRT QTY: 2 Setting: Fast/0.2 mm layer height |
|
| Mounting platform | Laser Cut Acrylic | solidworks: mounting platform.SLDPRT QTY: 1 |
|
| Pulley arm (left) | 3D Printing | solidworks: pulley arm_Mirror.SLDPRT QTY: 1 Setting: Fast/0.2 mm layer height |
|
| Pulley arm (right) | 3D Printing | solidworks: pulley arm.SLDPRT QTY: 1 Setting: Fast/0.2 mm layer height |
|
| Sample holder and tab- Clamp | 3D Printing | solidworks: Clamp.SLDPRT QTY: 1 Setting: Fast/0.2 mm layer height |
|
| Sample holder and tab- Sample holder | 3D Printing | solidworks: Sample holder.SLDPRT QTY: 1 Setting: Fast/0.2 mm layer height |
|
| Sample holder and tab- Tab | 3D Printing | solidworks: Tab.SLDPRT QTY: 2 per test Setting: Fine/0.1 mm layer height, no brim |
|
| Vertical adjust system- Inner slide | 3D Printing | solidworks: Inner slide.SLDPRT QTY: 1 Setting: Fast/0.2 mm layer height |
|
| Vertical adjust system- Outer slide | 3D Printing | solidworks: Outer slide.SLDPRT QTY: 1 Setting: Fast/0.2 mm layer height |
Referências
- Long, R., Hui, C. -. Y. Crack tip fields in soft elastic solids subjected to large quasi-static deformation – A review. Extreme Mechanics Letters. 4, 131-155 (2015).
- Slootman, J., et al. Quantifying rate-and temperature-dependent molecular damage in elastomer fracture. Physical Review X. 10, 041045 (2020).
- Zhao, X., et al. Soft materials by design: Unconventional polymer networks give extreme properties. Chemical Review. 121 (8), 4309-4372 (2021).
- Mzabi, S., Berghezan, D., Roux, S., Hild, F., Creton, C. A critical local energy release rate criterion for fatigue fracture of elastomers. Journal of Polymer Science Part B: Polymer Physics. 49 (21), 1518-1524 (2011).
- Chen, Y., Mellot, G., Van Luijk, D., Creton, C., Sijbesma, R. P. Mechanochemical tools for polymer materials. Chemical Society Reviews. 50, 4100-4140 (2021).
- Hui, C. -. Y., Jagota, A., Bennison, S. J., Londono, J. D. Crack blunting and the strength of soft elastic solids. Proceedings of the Royal Society A Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Science. 459 (2034), 1489-1516 (2003).
- Zhang, B., Hutchens, S. B. On the relationship between cutting and tearing in soft elastic solids. Soft Matter. 17, 6728-6741 (2021).
- Lake, G. J., Yeoh, O. H. Measurement of rubber cutting resistance in the absence of friction. International Journal of Fracture. 14, 509-526 (1978).
- Zhang, B., Shiang, C. -. S., Yang, S. J., Hutchens, S. B. Y-shaped cutting for the systematic characterization of cutting and tearing. Experimental Mechanics. 59, 517-529 (2019).
- Rivlin, R. S., Thomas, A. G. Rupture of rubber. I. Characteristic energy for tearing. Journal of Polymer Science. 10 (3), 291-318 (1953).
- Elices, M., Guinea, G. V., Gómez, J., Planas, J. The cohesive zone model: Advantages, limitations and challenges. Engineering Fracture Mechanics. 69 (2), 137-163 (2002).
- Taylor, D. . The Theory of Critical Distances. , (2007).
- Williams, J. G. Stress at a distance fracture criteria and crack self-blunting in rubber. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics. 68, 33-36 (2015).
- Talamini, B., Mao, Y., Anand, L. Progressive damage and rupture in polymers. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids. 111, 434-457 (2018).
- Long, R., Hui, C. -. Y., Gong, J. P., Bouchbinder, E. The fracture of highly deformable soft materials: A tale of two length scales. Annual Review of Condensed Matter Physics. 12, 71-94 (2021).
- Gent, A. N., Wang, C. Cutting resistance of polyethylene. Journal of Polymer Science: Part B: Polymer Physics. 34 (13), 2231-2237 (1996).
- Chen, X., Nadiarynkh, O., Plotnikov, S., Campagnola, P. J. Second harmonic generation microscopy for quantitative analysis of collagen fibrillar structure. Nature Protocols. 7, 654-669 (2015).
- Pan, B., Qian, K., Xie, H., Asundi, A. Two-dimensional digital image correlation for in-plane displacement and strain measurement: A review. Measurements Science and Technology. 20 (6), 062001 (2009).

