15.11:
Bepalen van de pH van Zoutoplossingen
15.11:
Bepalen van de pH van Zoutoplossingen
The pH of a salt solution is determined by its component anions and cations. Salts that contain pH-neutral anions and the hydronium ion-producing cations form a solution with a pH less than 7. For example, in ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) solution, NO3− ions do not react with water whereas NH4+ ions produce the hydronium ions resulting in the acidic solution. In contrast, salts that contain pH-neutral cations and the hydroxide ion-producing anions form a solution with a pH greater than 7. For example, in sodium fluoride (NaF) solution, the Na+ is pH-neutral but the F– produces the hydroxide ions and forms the basic solution. The counterions of a strong acid or base are pH-neutral and salts formed by such counterions form a neutral solution with a pH equal to 7. For example, in KBr, The K+ cation is inert and will not affect pH. The bromide ion is the conjugate base of a strong acid, and so it is of negligible base strength (no appreciable base ionization). The solution is neutral.
Some salts contain both an acidic cation and a basic anion. The overall acidity or basicity of a solution is determined by the relative strength of the cation and anion, which can be compared using Ka and Kb. For example, in NH4F, the NH4+ ion is acidic and the F− ion is basic (conjugate base of the weak acid HF). Comparing the two ionization constants: Ka of NH4+ is 5.6 × 10−10 and the Kb of F− is 1.6 × 10−11, so the solution is acidic, since Ka > Kb.
Calculating the pH of an Acidic Salt Solution
Aniline is an amine that is used to manufacture dyes. It is isolated as anilinium chloride, [C6H5NH3+]Cl, a salt prepared by the reaction of the weak base aniline and hydrochloric acid. What is the pH of a 0.233 M solution of anilinium chloride?
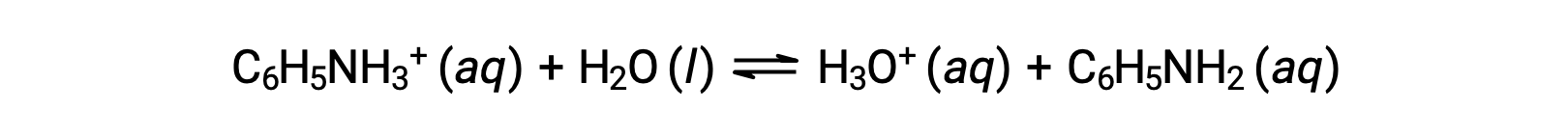
The Ka for anilinium ion is derived from the Kb for its conjugate base, aniline:
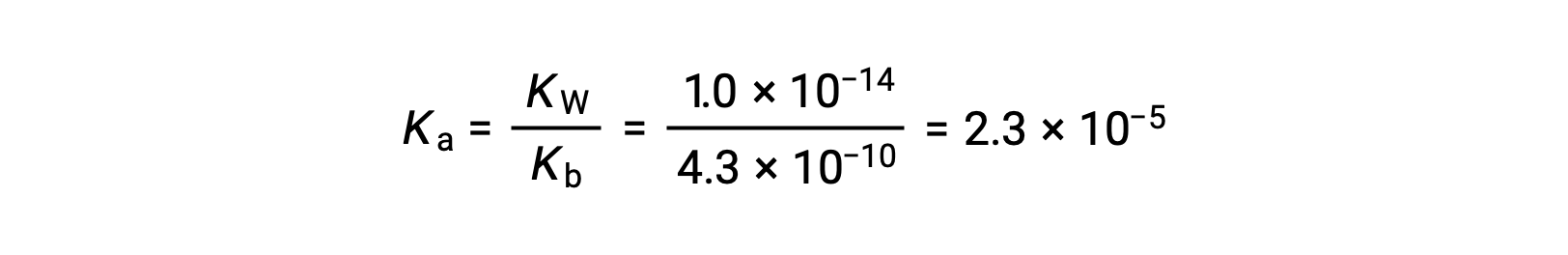
Using the provided information, an ICE table for this system is prepared:
| C6H5NH3+ (aq) | H3O+ (aq) | C6H5NH2 (aq) | |
| Initial Concentration (M) | 0.233 | ~0 | 0 |
| Change (M) | −x | +x | +x |
| Equilibrium Concentration (M) | 0.233 − x | x | x |
Substituting these equilibrium concentration terms into the Ka expression gives
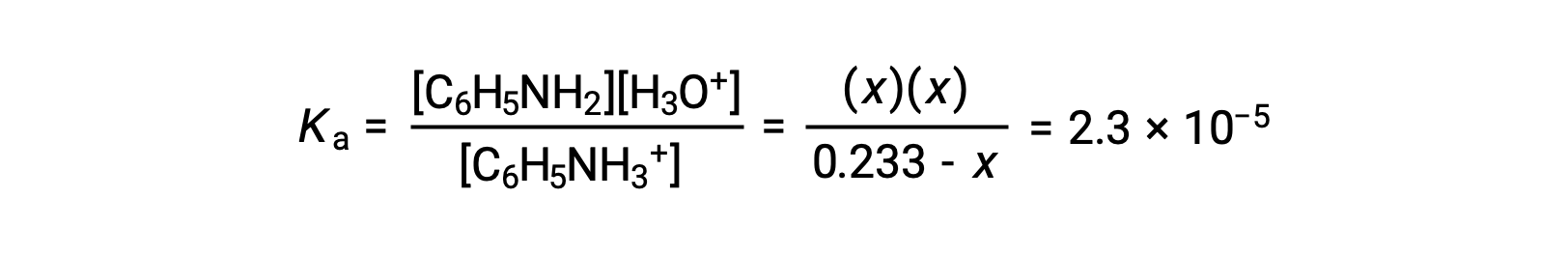
Assuming x << 0.233, the equation is simplified and solved for x:
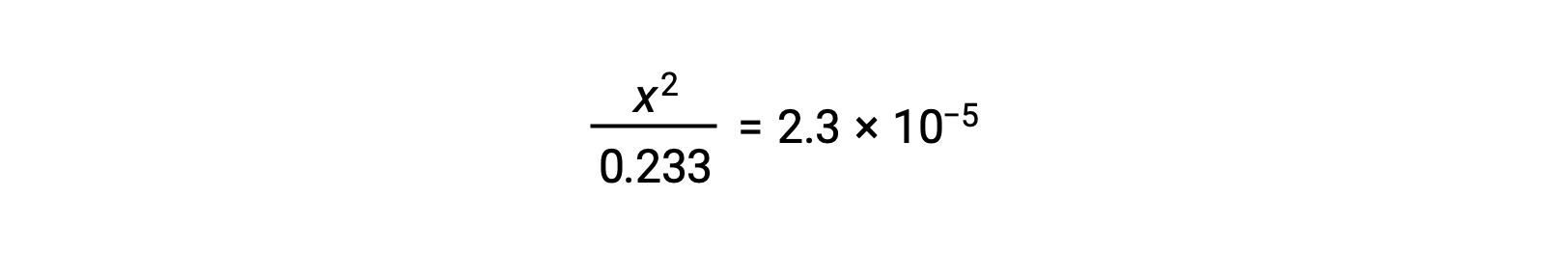

The ICE table defines x as the hydronium ion molarity, and so the pH is computed as
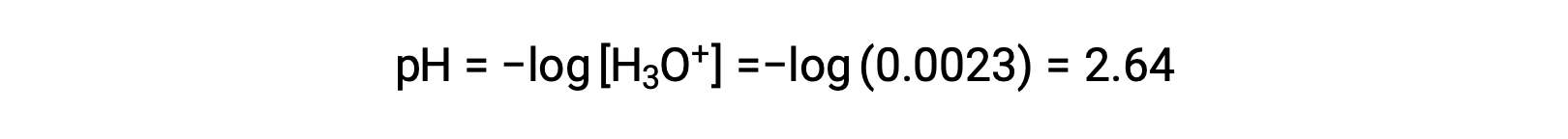
Hydrolysis of [Al(H2O)6]3+
Calculate the pH of a 0.10 M solution of aluminum chloride, which dissolves completely to give the hydrated aluminum ion [Al(H2O)6]3+ in solution.
The equation for the reaction and Ka are:
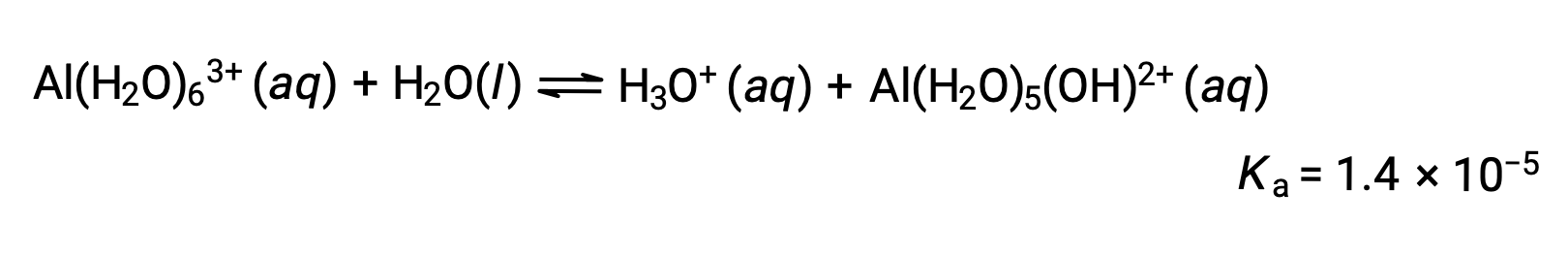
An ICE table with the provided information is
| Al(H2O)63+ (aq) | H3O+ (aq) | Al(H2O)5(OH)2+ (aq) | |
| Initial Concentration (M) | 0.10 | ~0 | 0 |
| Change (M) | −x | +x | +x |
| Equilibrium Concentration (M) | 0.10 − x | x | x |
Substituting the expressions for the equilibrium concentrations into the equation for the ionization constant yields:

Assuming x << 0.10 and solving the simplified equation gives:
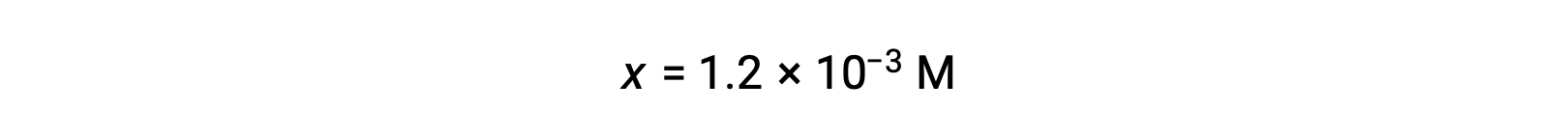
The ICE table defined x as equal to the hydronium ion concentration, and so the pH is calculated to be 2.92, and the solution is acidic.
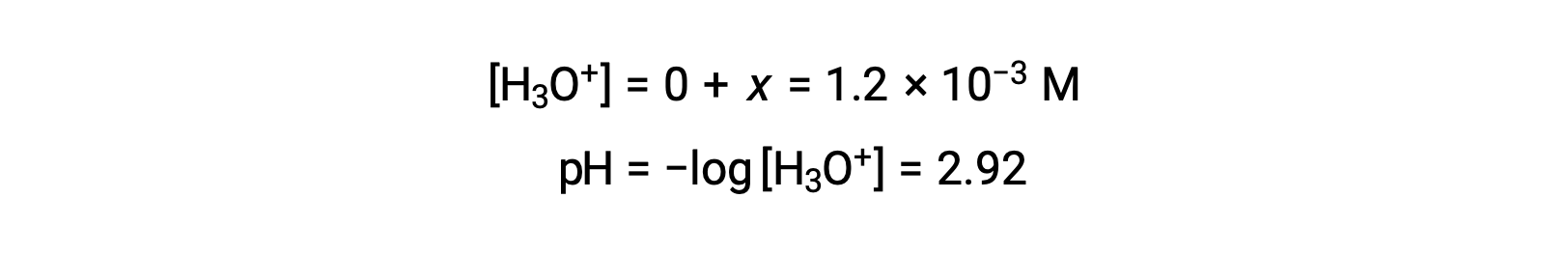
This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Section 14.4: Hydrolysis of Salts.
