Exploración pélvica I: Evaluación de los genitales externos
English
Share
Overview
Fuente:
Alexandra Duncan, GTA, Praxis clínica, New Haven, CT
Cocinero de Tiffany, GTA, Praxis clínica, New Haven, CT
Jaideep S. Talwalkar, MD, medicina interna y Pediatría, Facultad de medicina de Yale, New Haven, CT
El examen pélvico puede sentir invasivo a los pacientes, por lo que es importante hacer todo lo posible para que pacientes se sienta cómodo y poder, más que vulnerables. Los clínicos deben ser conscientes de cómo se comunican, tanto verbal como no verbal y deben dar a sus pacientes control siempre que sea posible. Hay muchas maneras de hacerlo, desde cómo se coloca la mesa de examinación a cómo participa el paciente durante el examen. Como 1 de cada 5 pacientes puede han experimentado trauma sexual; por lo tanto, es importante evitar la activación de los pacientes, pero no siempre es posible saber quiénes son. El examen en este video muestra idioma neutro y técnicas que pueden emplearse con todos los pacientes para crear la mejor experiencia posible.
Es importante mantener al paciente cubierto siempre que sea posible y minimizar el contacto con extraño. Un médico debe tener cuidado al meter los dedos que no se utiliza para examinar al paciente para evitar el contacto accidental con el clítoris o el ano.
Antes de realizar el examen pélvico, examinadores deben averiguar cómo bien informados los pacientes sobre el título y sus propios cuerpos y establecer la expectativa de que los pacientes pueden comunicar preguntas o preocupaciones durante el examen. Mientras que siempre es importante evitar el lenguaje muy clínico, ciertas palabras coloquiales pueden cruzar la línea de cuidado para excesivamente íntimo durante este examen. Es útil evitar las palabras “touch” y “feel”, que puede sentir sexual en este contexto; en cambio, las palabras “evaluar,” “check”, “inspeccionar”, o “examinar” debe ser utilizado. Deben evitarse las palabras “cama” y “hoja” y “tabla” y “cuelgue” debe utilizarse en su lugar. También, un médico debe usar la palabra “reposapiés” en lugar de “estribos” para evitar que connota caballos. Es una buena idea para evitar decirle a pacientes para “relajarse”, porque es una orden difícil de un paciente seguir cuando ansioso. Pacientes para “suavizar” o “soltar” los músculos específicos puede ser más útil y tener un paciente hacer un Kegel ejercicio o maniobra de Valsalva puede servir como una técnica de relajación específicas.
Mejor práctica dicta evitar asunciones sobre el género de los pacientes, como pacientes con anatomía femenina se pueden identificar como otro género (por ejemplo, transgénero o genderqueer). Este video representa el enfoque de un paciente cuya historia ha revelado no hay denuncias específicas o factores de riesgo relacionados con la salud ginecológica.
El examen pélvico consta de tres partes: el examen visual y manual de los genitales externos, un examen de espéculo y un examen bimanual. Este video cubre la introducción al examen pélvico y el examen de los genitales externos. Para evitar la falta de resultados potenciales, se debe realizar el examen pélvico externo en un enfoque sistemático que consiste en dos componentes principales: una inspección visual de la vulva (figura 1) y palpación interna y evaluación de las glándulas y el tono.
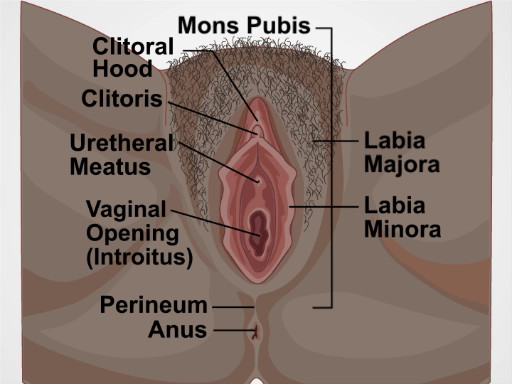
Figura 1. Diagrama de la vulva. Un diagrama que muestra los genitales externos con las estructuras etiquetadas.
Procedure
Applications and Summary
This video reviewed the introduction and setup for the pelvic exam, and how to visually inspect and examine the complete female external genitalia. Before performing the pelvic exam, examiners should find out how knowledgeable the patients are about the exam and their own bodies, and establish the expectation that the patients can communicate questions or concerns throughout the exam. The exam table should be positioned so the patient can see what is happening and can communicate with the examiner, and the patient should remain covered as much as possible to minimize feelings of vulnerability. The examiner can give the patient a hand mirror and instruct how to position it to follow along with the exam, and educate the patient about their structures throughout the exam (when appropriate).
The examiner should first provide an overview of the exam, and explain every step as the exam progresses, letting the patient know before the examiner makes contact with the patient's genitalia. First, the external genitalia is examined, including the glands and muscle tone of the vagina. The examiner should take note of any potential findings (including taking swabs of any unusual discharge elicited). Any markings or potential signs of domestic or intimate partner violence should be documented, though examiners should remember that some of their patients may engage in rough sex, and bruising may not be indicative of violence.
Beyond asking clarifying questions, the examiner should not discuss concerns or follow-up testing while the exam is ongoing. Following the components covered in this video, the pelvic examination is typically followed by two additional components, the speculum and bimanual exams. After the speculum and bimanual exams, the examiner should step out to allow the patient to get dressed. The examiner can then reenter the room to discuss concerns and next steps, as having those conversations while the patient is unclothed and vulnerable heightens anxiety.
When an exam has normal findings, the examiner should always tell the patient that "everything appears healthy and normal." This simple statement relieves anxiety and empowers patients to equate their body structures as normal.
References
- Black M.C., Basile K.C., Breiding M.J., Smith S.G., Walters M.L., Merrick M.T., Chen J., Stevens M.R. The National Intimate Partner and Sexual Violence Survey (NISVS): 2010 Summary Report. Atlanta, GA: National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2011).
Transcript
The pelvic examination is performed for diagnostic, screening and treatment purposes as a part of gynecologic, obstetric and sexual health care. A comprehensive pelvic exam includes assessment of the external genitalia-which will be discussed in this video, followed by examination of the vagina and cervix with a speculum-to be covered in the video titled Pelvic Exam Part II; and a bimanual evaluation of the pelvic organs-reviewed in Part III of this series.
Here, we will first discuss how to introduce this exam to a patient. Subsequently, we will review the steps for external genitalia assessment, which includes inspection as well as digital evaluation.
Before discussing the physical examination steps, let’s review how to introduce this exam to a patient, the set-up necessary and a few general considerations. The pelvic exam can feel invasive to patients, so it is important to do everything possible to make them feel comfortable and empowered, rather than vulnerable. Right at the start you must establish an expectation of comfort and ask your patient to communicate their questions and concerns during the visit. If the patient has had a pelvic exam before, you should inquire about that experience. Reassure the patient by saying something like “Dialogue”.
Before beginning with the procedure, it is important that you introduce and summarize the exam, “Dialogue”. Remember, that while it is always important to avoid extremely clinical language, certain colloquial words can cross the line from being caring to being overly intimate during this exam. It is helpful to avoid the words “touch” and “feel,” which can feel sexualized in this context; instead, the words “assess,” “check,” “inspect,” or “examine” should be used. The words “bed” and “sheet” should be avoided, and “table” and “drape” should be used instead. Also, a clinician should use the word “footrests” rather than “stirrups”. It’s a good idea to avoid telling patients to “relax” because it’s a hard order for a patient to follow when they’re anxious. Practicing clinicians often utilize a chaperone for their own or the patient’s comfort, and based on institutional policies. However, in this video demonstration we will not be using a chaperone. Ask the patient to change into a gown and specify how they should dress-underwear off, and gown open in the back. Also provide the patient with a drape to place over their lap and step out of the room to give them privacy.
Set up all the supplies you will need, before beginning the exam. If you will be using lubricant at any point make sure to squeeze it onto a clean area before beginning, as you cannot touch the packets or bottle once you are wearing gloves. Make sure to have a trashcan, a working light, and a stool near the exam table.Give the patient a hand mirror so they can follow along with the exam and say, “Dialogue”. Pull out the footrests and ask the patient to place their feet over them. Raise the back of the exam table to 45-60° and ask the patient to sit back. This modified lithotomy position allows the patient to see the examiner and facilitates the examination, as the patient’s internal organs sink into the pelvic basin making them much easier to assess.
After the patient is comfortable, wash your hands thoroughly. Sit down on the stool near end of the exam table, and put on gloves. Then, place the back of your hand on the end of the table over the drape and ask the patient to slide down until they can feel the back of your hand. Next, ask them to extend their knees sideways. Now, using both your hands, fold the drape up toward the patient’s pubic bone. Then, request the patient to hold it in place using their free hand. Next, ask the patient to bring the mirror next to one of their knee. Place two fingers near, but not touching, the patient’s vulva and say, “Dialogue”. To put the patient at ease and avoid muscle spasm, establish a non-invasive contact first, “Dialogue”.
The structures evaluated during visual inspection include: mons pubis, which overlies the pubic symphysis, the labia majora that appear as rounded folds and are composed of adipose tissue, and more internally, the labia minora, the clitoris and the clitoral hood. Between the labia minora, there are two opening: the uretheral meatus and the vaginal opening, known as the introitus. The term perineum describes the tissue between the introitus and the anus. During the exam visually assess for the following: the pattern of hair growth, rashes, lesions, moles, masses, and discharge. Also look for potential signs of domestic violence such as scarring, burns, or bruising; signs of female genital mutilation; hemorrhoids; skin tags; fissures; and other irregularities.
To view these structures, position the index and middle fingers of dominant hand in a “peace” sign and keep the other fingers tucked. With the pads of your index and middle fingers, separate the labia minora and majora on one side to inspect the entirety of the sulcus. Keep your hand low and take care to avoid accidental extraneous contact with the clitoris by keeping fingers that aren’t being used tucked in. Using the same two fingers, separate the labia minora to view the vaginal introitus and urethral opening. Then, rotate your wrist up and use the back of the two fingers to retract the clitoral hood and view the clitoral shaft. Lastly, make a fist, and using the back of your fist pull away one buttock to view the anus. If you notice a mole or freckle, point it out to the patient and let them know they should regularly check it for changes, just as they would with moles elsewhere on their body.
The next part of the exam is the digital assessment of the vestibular glands, the vagina and the cervix. To start, first lubricate the turn your dominant index finger. Let the patient know you will be placing a finger in their vagina. In palm down position, place the lubricated finger into the vaginal introitus to just beyond your first knuckle. Then gently pinch the tissue between your thumb and the inserted finger at five and seven o’clock positions to assess the Bartholin’s glands located posteriorly. Watch the patient’s face for signs of discomfort and note if you feel any palpable masses.
Next, apply posterior pressure and rotating your palm up. Then using the thumb and middle finger separate the labia minora to visually inspect the urethral meatus and the openings of the paraurethral or Skene glands-located bilaterally next to the urethral meatus. Note the signs of inflammation and presence of discharge. Express the Skene’s glands by tapping gently upward with your index finger at one and eleven o’clock positions. If the glands are infected they discharge into the urethra, so finish by making a gentle beckoning motion at twelve o’clock to check if the glands release any discharge, which is absent in this case.
Then, release the labia and insert your finger farther to locate the cervix; assess its depth and direction. This will help you choose the correct speculum size and also help you decide where to angle the speculum during the other part of the exam.If you can easily locate the cervix while sitting down, the patient may need a short speculum. If you cannot easily locate the cervix, then you might have to stand up and the use a medium or a longer speculum.
Next, perform digital vaginal assessment. Slide your index finger halfway out and then rotate to palm down position. Subsequently, insert your middle finger by placing it over the top of your index finger and then place them side-by-side.Now, drop your wrist and pull down toward the perineum to make space above your fingers. Next, ask the patient to perform the Valsalva maneuver by bearing down as if having a bowel movement and assess cystocele, which refers to anterior bladder prolapse. Following that, lift your wrist up to apply anterior pressure toward the bladder until space underneath the fingers can be seen. Again, ask the patient to bear down while assessing for rectocele denoted by rectal herniation into the back wall of the vagina.
Next, lower your wrist so the fingers are flat and centered and gently separate them. This will also help in choosing the right speculum for the following part of this exam. If you’re having difficulty in separating your fingers, the exam should be performed with a small size speculum.Finally, assess the tone of the pubococcygeal muscle by asking the patient to squeeze around your fingers as if they are stopping the flow of urine. This maneuver is called the Kegel’s exercise. A firm squeeze represents a healthy and toned pelvic floor. Remove your fingers and discard the gloves. This completes the first part of the pelvic exam.
You’ve just watched JoVE’s video on the approach to the pelvic examination and assessment of the external genitalia. In this video, we reviewed how to introduce the pelvic exam to a patient, demonstrated the inspection of the external genitalia, and showed the steps to be performed during the digital assessment of the cervix and vagina. As always, thanks for watching!
