Mouse Ileal Loop Model: A Surgical Model to Study Intestinal Permeability in the Mouse
Abstract
Source: Boerner, K., et al. Functional Assessment of Intestinal Permeability and Neutrophil Transepithelial Migration in Mice using a Standardized Intestinal Loop Model. J. Vis. Exp. (2021)
This video demonstrates the generation of an ileal loop model to study intestinal permeability in a mouse model. This method provides a live model to understand the epithelial barrier function and consequent immune response.
Protocol
All procedures involving animal models have been reviewed by the local institutional animal care committee and the JoVE veterinary review board.
1. Generation of the ileal loop
- Skin preparation: Scrub fur of the abdominal midline with alcohol swabs or gauze sponge soaked with 70% Ethanol. Do not wet a wide area of fur with alcohol to prevent hypothermia.
- Using scissors, perform a midline laparotomy. Make a vertical incision in the middle of the abdomen (about 2 cm in length) and expose the peritoneum. Be careful to not injure intra-abdominal organs.
- Place pre-cut wet cotton gauze over the exposed intra-abdominal cavity.
- Use wet cotton swabs to mobilize and exteriorize the caecum. Carefully place the caecum on the wet cotton gauze.
NOTE: Caecum is localized in the left caudal quadrant of the abdominal cavity in most mice independent of the sex of the animal. - Use wet cotton swabs to mobilize and gently exteriorize the ileum of which the terminal section (distal end) is attached to the caecum (Figure 1B).
- Deploy at least 6 cm of terminal ileum on the wet cotton gauze without disruption of the mesenteric vessels and blood supply. Blood supply is maintained if there is no bleeding, and the tissue maintains its pink color (Figure 1B).
NOTE: Avoid drying of exposed tissues by maintaining tissues moist all the time with warm HBSS (every 2 – 3 min) using 10 mL syringe pre-attached to a yellow feeding tube. - Close to the caecum, identify the major artery in the mesentery, supplying blood to the ileum. Then locate two ligation sites in the mesentery that are free of critical blood vessels.
- Using blunt tissue forceps, firmly grab the terminal ileum (closest to the caecum) and using fine tip forceps, fenestrate the mesentery avoiding blood vessels. Place silk suture across the perforation and tie a surgical knot to create the first ligation (distal end of the loop).
- Use the ruler to measure 4 cm away from the first ligature and create the second ligature (proximal end of the loop) as mentioned in step 2.8 (Figure 1C).
- With fine scissors carefully cut next to each ligation to isolate the 4 cm ileal loop, keeping intact blood supply and mesenteric membrane.
NOTE: Cut off both ends of the exteriorized segment of the iLoop, then flush gently as a necessary step that prevents interference with luminal contents (fecal matter), thus facilitating even dispersion of FITC-dextran or chemotactic stimuli across the entire length of the isolated segment as well as allowing for more accurate quantification of leukocytes by flow cytometry. This procedure also allows uniform distension of the mucosa after injection of specified volumes of reagent and better reproducibility between animals. - Gently flush the content of the ileal loop segment with warm HBSS using a flexible yellow feeding tube attached to a 10 mL syringe.
- Ligate the two cut ends of the flushed ileal loop using silk suture.
- Use a 1 mL syringe with 30 G needle to slowly inject 250 µL of reagent such as FITC-dextran or chemokine into the intestinal lumen. The ileal loop will inflate causing a moderate distension of the mucosa (Figure 1D).
NOTE: Inject reagent into the loop lumen on the opposite side of the mesenteric artery. Be careful not to pull out the ileal loop from the animal while injecting to avoid tearing blood vessels and induce bleeding. - Using wet cotton swabs, gently put back the ileal loop, proximal ileum, and caecum.
- Use a needle holder, anatomical forceps and 3.0 non-absorbable silk sutures with reverse cutting needle to close the abdominal wall.
- Place the animal in a temperature-regulated anesthesia chamber for the incubation period.
Representative Results
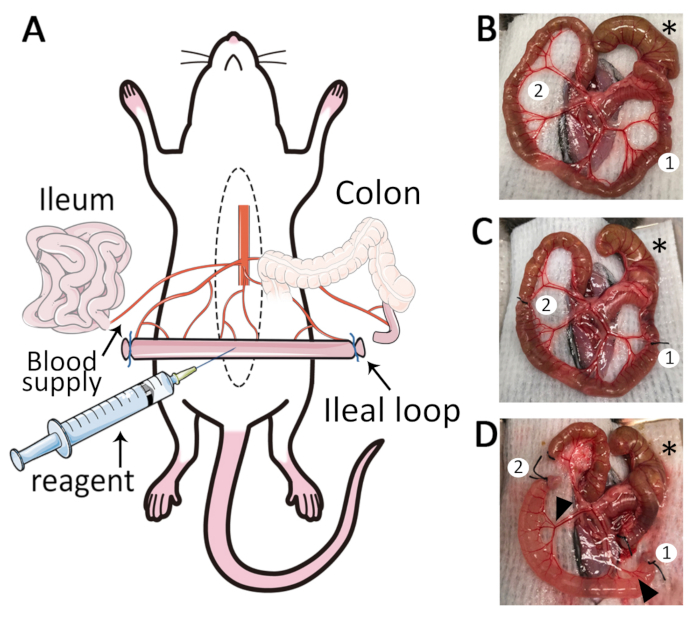
Figure 1: The ileal loop model. (A) Schematic overview of the ileal loop model. Median laparotomy is performed on mice under anesthesia and placed on a temperature-controlled surgery board. (B) Exteriorization of the caecum (*), ileum and mesentery. Two adequate sites for ligation are identified (1,2). (C) Isolate a segment of 4 cm length: the first ligature (1) is placed close to the ileo-caecal junction, and a second ligature (2) is placed 4 cm away from the first ligature. (D) Two small incisions are made in the mesentery (1, 2) to create a 4 cm length ileal loop. After removal of luminal content and ligation of cut-ends, reagents such as fluorescent markers and chemo-attractants can be injected into the lumen. The ileal loop is well vascularized (black arrowheads).
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Materials
| Equipment and Material | |||
| BD Alcohol Swabs | BD | 326895 | |
| BD PrecisionGlide Needle, 25G X 5/8" | BD | 305122 | |
| BD PrecisionGlide Needle, 30G X 1/2" | BD | 305106 | |
| BD 1ml Tuberculin Syringe Without Needle | BD | 309659 | |
| 15ml Centrifuge Tube | Corning | 14-959-53A | |
| Corning 96-Well Solid Black Polystyrene Microplate | FisherScientific | 07-200-592 | |
| Corning Non-treated Culture Dish, 10cm | MilliporeSigma | CLS430588 | |
| Cotton Tip Applicator (cotton swab), 6", sterile | FisherScientific | 25806 2WC | |
| Dynarex Cotton Filled Gauze Sponges, Non-Sterile, 2" x 2" | Medex | 3249-1 | |
| EZ-7000 anesthesia vaporizer (Classic System, including heating units) | E-Z Systems | EZ-7000 | |
| Moria Fine Scissors | FST | 14370-22 | |
| Puralube Vet Ointment, Sterile Ocular Lubricant | Dechra | 12920060 | |
| Ring Forceps (blunt tissue forceps) | FST | 11103-09 | |
| Roboz Surgical 4-0 Silk Black Braided, 100 YD | FisherScientific | NC9452680 | |
| Semken Forceps (anatomical forceps) | FST | 1108-13 | |
| Sofsilk Nonabsorbable Coated Black Suture Braided Silk Size 3-0, 18", Needle 19mm length 3/8 circle reverse cutting | HenrySchein | SS694 | |
| Student Fine Forceps, Angled | FST | 91110-10 | |
| 10ml Syringe PP/PE without needle | Millipore Sigma | Z248029 | |
| Yellow Feeding Tubes for Rodents 20G x 30 mm | Instech | FTP-20-30 | |
| Solutions and Buffers | |||
| Hanks' Balanced Salt Solution | Corning | 21-023-CV | |
| Phosphate-Buffered Saline without Calcium and Magnesium | Corning | 21-040-CV | |
| Isoflurane | Halocarbon | 12164-002-25 | |

