डिजाइन, और प्रशासन हाथ का निर्माण सक्रिय सनसनीखेज टेस्ट (जल्दबाजी)
Summary
The Hand Active Sensation Test (HASTe) is a valid and reliable measure of haptic performance, which has been used successfully to identify impaired haptic touch in individuals with stroke. The purpose of this paper is to describe the design, fabrication and administration of the HASTe.
Abstract
The concept of personalizing neurologic rehabilitation, based on individual impairments, has experienced a recent surge. In parallel, the number of outcome measures of upper extremity motor performance has grown. However, clinicians and researchers lack practical, quantitative measures of the hand’s natural role as a receptor of the environment. The Hand Active Sensation Test (HASTe), developed by Williams and colleagues in 2006, is a valid and reliable measure of haptic performance. Though not available commercially, the HASTe can be fabricated from inexpensive materials, and it has been used successfully to identify impairments in haptic touch in individuals with stroke. (Williams, 2006). This paper presents the methods of design and fabrication of the HASTe testing kit, as well as a visual screen to be used during administration, and instructions for the tests administration and scoring.
Introduction
एक प्यार एक के हाथ का लग रहा है की कल्पना करो। यह calloused या चिकनी है? मजबूत या नाजुक? गर्म या ठंडा? आप इसे एक हाथ मिलाना में या उंगलियों intertwined के साथ पकड़ है? आप एक स्मृति पैदा किया है, तो यह संभावना haptic स्पर्श, या सक्रिय सनसनी कहा जाता है जो somatosensory जानकारी, विनती करने के लिए अपने हाथ की आवाजाही उपयोग करने की क्षमता पर आधारित है। Haptic स्पर्श के साथ निर्धारित किया जा सकता है कि लक्षण आकार, आकार, वजन, बनावट, सतह अनुपालन, और तापमान में शामिल हैं। Haptic रिसेप्टर्स वस्तुओं के मैनुअल अन्वेषण के दौरान सक्रिय कर रहे हैं, जो दोनों की त्वचा में पाए जाते हैं जो proprioceptors, मांसपेशियों, tendons, और जोड़ों, साथ ही त्वचा संबंधी रिसेप्टर्स, शामिल हैं। अलग हाथ कार्यों वस्तु विशेषताओं के निर्धारण में सहायता। उदाहरण के लिए, बार-बार बनावट गुणों का पर्दाफाश हो सकता है एक वस्तु के पार एक पार्श्व मलाई गति प्रदर्शन, या वस्तु वजन प्रकट हो सकता है हाथ में वस्तु उठाने। इसलिए, दोनों मैनुअल निपुणता और somatosensation haptic प्रदर्शन और मानवीय अनुभव के लिए महत्वपूर्ण हैं।
स्ट्रोक के बाद, दोनों somatosensory और मोटर impairments स्ट्रोक बचे के लगभग 70% केवल पेशियों के कुछ स्तर का सामना कर के साथ, एक Poststroke मोटर impairments। कम haptic प्रदर्शन में योगदान आम है और अच्छी तरह से परिभाषित कर रहे हैं। एक Somatosensory दोष स्ट्रोक भी आम हैं के बाद, 47 में होने वाली 89% व्यक्तियों के 2-4। शोधकर्ताओं त्वचीय और प्रग्राही दोष दोनों स्ट्रोक के बाद आम हैं सहमत हैं। पाठक केरी के द्वारा काम करता है के लिए भेजा है somatosensory डोमेन पर स्ट्रोक के परिणामों में से एक पूरी तरह से लक्षण वर्णन के लिए एट अल।, 2 Connell एट अल।, 5 और सुलिवन। 4
Somatosensory दोष कम पुनर्वास के परिणामों, 6 ऊपरी अंग समन्वय, 7 समारोह और जीवन की गुणवत्ता के लिए योगदान करते हैं। 8 हालांकि, Qusomatosensory दोष, विशेष रूप से सक्रिय सनसनी की antification कारण somatosensory नुकसान मोटर दोष से यों को कम स्पष्ट और अधिक कठिन है कि इस तथ्य के हिस्से में नैदानिक अभ्यास में कमी है। सक्रिय सनसनी यों करने के लिए विकसित किया गया है जो 9 उपाय Byl-Chyney शामिल -Boczai संवेदी discriminator (बीसीबी), 10 संशोधित नॉटिंघम संवेदी आकलन, 11 कार्यात्मक स्पर्श वस्तु मान्यता टेस्ट (fTORT), 12 मैनुअल फार्म धारणा परीक्षण (संवेदी जानकारी और अभ्यास टेस्ट के एक सबसेट), 13 की stereognosis घटक और Haptic वस्तु मान्यता टेस्ट (HORT)। 14 इन उपायों उपलब्ध हैं, बांह और हाथ में somatosensory दोष स्ट्रोक के बाद ऊपरी अंग समस्याओं से संबंधित हैं, की मांग की है, जो हाल ही में एक व्यवस्थित समीक्षा, वर्णन करने के लिए चिकित्सकों और शोधकर्ताओं वर्तमान में मान्य की कमी है कि यह निष्कर्ष निकाला और somatosensation के विश्वसनीय परीक्षण। 15 </समर्थन> इसलिए, haptic प्रदर्शन की चिकित्सकीय उपयोगी और parametrically ध्वनि उपायों की उपलब्धता को संबोधित आवश्यक है।
हाथ सक्रिय सनसनीखेज टेस्ट (जल्दबाजी) haptic स्पर्श का एक उपाय है, मूल रूप से 2006 में 16 जल्दबाजी में विलियम्स और उनके सहयोगियों द्वारा प्रकाशित वजन और बनावट भेदभाव के एक 18 आइटम मैच नमूना परीक्षण किया जाता है और में haptic दोष के प्रति संवेदनशील है स्ट्रोक के साथ व्यक्तियों (कम से कम 13 से सही मैचों ने संकेत दिया)। जल्दबाजी न्यूनतम मापदंड के रूप में haptic धारणा है, को मापने के लिए करना चाहता है के रूप में, व्यक्तियों समझ और हाथ से उठा और हाथ और परीक्षण के निर्देशों का पालन करने के लिए क्षमताओं की जरूरत है। कार्य, विकलांगता और स्वास्थ्य (आईसीएफ) मॉडल, 17 की अंतर्राष्ट्रीय वर्गीकरण में जल्दबाजी एक गतिविधि के स्तर की माप माना जाता है। जल्दबाजी परीक्षण किया हाथ प्रति प्रशासन के लिए 15-30 मिनट के बीच लेता है। जल्दबाजी के लाभ यह सस्ती है कि शामिल हैं, 2015 के लिए माल की कीमतों के कुल $ 100 में अनुमान लगाया गयाऔर निर्माण और इसे पैमाने "बिगड़ा" "बरकरार" या के अधिक आम डाइकोटोमस लक्षण वर्णन से प्रदर्शन के बारे में अधिक से अधिक संकल्प प्रदान करता है 18-बिंदु है कि करने के लिए आसान नहीं है।
इस पत्र का उद्देश्य जल्दबाजी के डिजाइन, निर्माण और प्रशासन का वर्णन है। यह मूल जल्दबाजी प्रकाशन से परीक्षण सेट अप करने के लिए अनुमान संभव है, यह पत्र एक दृश्य स्क्रीन और एक जल्दबाजी परीक्षण किट, दोनों परीक्षण के दौरान इस्तेमाल किया जाएगा fabricating के लिए विस्तृत तरीके प्रदान करता है। विधानसभा के लिए आवश्यक उपकरण, साथ ही सभी आवश्यक सामग्री की एक विस्तृत सूची सामग्री की तालिका में सूचीबद्ध है। प्रशासन और जल्दबाजी भी निम्नलिखित के रूप में प्रदान की जाती है स्कोरिंग के लिए निर्देश के साथ एक एकल पत्रक:
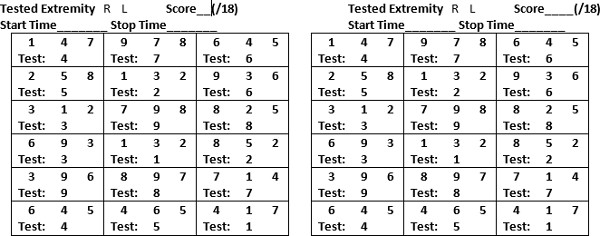
परिशिष्ट 1: जल्दबाजी प्रशासन के निर्देश और स्कोर शीट पार्टिसिपेंट आईडी #_______ Date_______
एसईटी: के साथ एक मेज (टेबल ~ 29 इंच ऊंची और कुर्सी सीट ~ 18 इंच ऊंची) पर परीक्षण भागीदार सीट, शुरू में, प्रमुख या उससे कम बिगड़ा ऊपरी सिरा मेज पर आराम और इकट्ठे दृश्य स्क्रीन के नीचे रखा। परीक्षण के दौरान, संगठन बनाए रखने के लिए संख्यात्मक क्रम में सभी वस्तुओं को रखने के लिए।
प्रदर्शन परीक्षण: पहले स्कोरिंग के लिए दो प्रदर्शन परीक्षणों प्रशासन। वस्तुओं ए और बी के साथ भागीदार प्रदान करते हैं और वस्तुओं को 'वजन तुलना करने के लिए उसे / उसे हिदायत। फिर, वस्तुओं ए और सी के साथ भागीदार प्रदान करते हैं और वस्तुओं को 'बनावट तुलना करने के लिए उसे / उसे हिदायत। केवल प्रदर्शन के परीक्षण के लिए प्रतिक्रिया की पेशकश।
रन परीक्षण: प्रत्येक के लिए अनुमति दी 5 मिनट की एक अधिकतम के साथ सिरा प्रति रन 18 परीक्षणों की जाएगी। मैन्युअल निर्दिष्ट परीक्षण वस्तु का पता लगाने के लिए भागीदार हिदायत प्रमुख या उससे कम बिगड़ा हाथ के साथ (नीचे तालिका में "परीक्षण") की पहचान की है, तो पूर्वइस एक ही हाथ से (नीचे प्रत्येक परीक्षण बॉक्स के भीतर अन्यथा गिने) तीन संभावित वस्तु मैचों में से प्रत्येक plore। संभव मैचों लेकिन कभी एक परीक्षण के भीतर दोनों के द्वारा, वजन या बनावट या तो द्वारा अलग अलग होंगे। एक जवाब निर्धारित करने की जरूरत के रूप में उसके मूल वस्तु का मैच खोजने और बताने के लिए प्रतिभागी को हिदायत / उसे वे कई बार के रूप में प्रत्येक वस्तु को छू सकता है। जो संपत्ति (बनावट या वजन) वस्तु के रूप में वह भागीदार सूचित नहीं करते या वह एक परीक्षण के भीतर से मेल खाते है, और वस्तुओं के मैनुअल अन्वेषण के साथ भागीदार की सहायता नहीं करते। नीचे दिए गए उस वस्तु की संख्या चक्कर द्वारा तालिकाओं में प्रत्येक परीक्षण के लिए प्रतिभागी का अंतिम जवाब का संकेत मिलता है। प्रतिभागी को कम बिगड़ा ऊपरी सिरा के साथ परीक्षण के पूरा होने के बाद अधिक बिगड़ा ऊपरी सिरा परीक्षण करें। नीचे तालिका का उपयोग कर, हाथ प्रति 18 परीक्षणों (नीचे परीक्षण के प्रति एक बॉक्स) की कुल से सही मैचों की संख्या निर्धारित करने से परीक्षण स्कोर।
मौखिक निर्देप्राप्तगुमप्रतिभागी को uctions: "मैन्युअल पहला परीक्षण वस्तु का पता लगाने के लिए एक हाथ का प्रयोग करें। फिर, वजन या बनावट लेकिन कभी एक परीक्षण के भीतर दोनों के द्वारा या तो द्वारा भिन्न है, जो तीन संभावित मैचों में से प्रत्येक का पता लगाएं। मैच का पता लगाएं। आप अपने जवाब निर्धारित करने की आवश्यकता के रूप में आप प्रत्येक वस्तु के रूप में कई बार छू सकता है। 18 परीक्षणों की जाएगी। आप प्रत्येक परीक्षण के लिए 5 मिनट की एक अधिकतम है। "
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
साक्ष्य, somatosensory वसूली कार्य विशेष प्रशिक्षण स्ट्रोक के बाद मोटर वसूली के लिए इसी तरह की आवश्यकता है कि पता चलता है। 18,19, 20 इसलिए, हम एक haptic रिसेप्टर के रूप में हाथों प्रदर्शन में सुधार करना है, तो haptic दोष प?…
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
इस काम के डॉ Borstad को TL1TR001069 पुरस्कार के माध्यम से OSU के CCTS कार्यक्रम में भाग द्वारा समर्थित किया गया। हम इस पांडुलिपि के अंतिम मसौदे के संपादन के साथ उसकी सहायता के लिए अमेलिया Siles, डीपीटी, एनसीएस उसकी बहुमूल्य माप अंतर्दृष्टि के लिए और सारा अलेक्जेंडर को स्वीकार करना होगा।
Materials
| Equipment Needed for Assembly | |||
| Tape measure | To measure lengths of materials | ||
| PVC saw | To cut PVC pieces to appropriate lengths given below | ||
| Scissors | To cut paper, cork and laminating material | ||
| Scale accurate to 0.1 ounce | To determine exact weight of test objects | ||
| Sharpie Permanent Marker | To label test item number and weight | ||
| Visual Screen Materials | Company | Catalog Number | |
| 0.5-inch PVC Pipe (Sch. 40 Plain-End Pipe) | Home Depot | 530048 | 104 inches total, will be cut into four 10-inch and three 20-inch pieces |
| 0.5-inch PVC Tee (Sch. 40 SxSxS Tee) | Home Depot | 406005RMC | Two pieces |
| PVC Elbow (Lasco 0.5-inch Dia 90 degree PVC Sch 40 Side Outlet Elbow) | Home Depot | 413005RMC | Two pieces |
| Pillowcase | One to be hung from the PVC frame as a visual shield | ||
| ACCO Binder Clips, Medium | amazon.com | 72050 | Two to hold the pillowcase to the PVC frame |
| Testing Kit Materials | |||
| 1.5-inch PVC Sch. 40 DWV Plain End Pipe | Home Depot | 531111 | 85 inches total, will be cut into 21 4-inch pieces |
| Quartet Cork Roll, 1/16-inch thick | amazon.com | NA | 1 roll, 24×48 inches, will be cut into 42 4×7-inch pieces to cover all test and example items |
| Oatey all purpose cement for CPVC and PVC | Home Depot | 308213 | 8 ounce can, to use to adhere cork, paper and end caps to PVC test items |
| Avery Self-Adhesive Laminating Roll | amazon.com | 73610 | One 24×600-inch roll, will be cut into six 4×7-inches pieces to cover cork on six test objects |
| Brown Builder's Paper | Home Depot | 35140 | One roll, will be cut into six 4×7-inch pieces to cover cork on six test objects |
| 3M Pro Grade 9 Sandpaper | Home Depot | 25060P-G | One piece 4×7 inches, to use to cover one example item |
| Ranger Glossy Cardstock | amazon.com | NA | One 8.5×11-inch, 10-Pack, white, will be cut into two 4×7-inch pieces to cover example items |
| Marblex-durable self modeling clay in moist form | amaco.com/shop/ | X-242 | One 5-pound package, used to achieve correct weights of test objects |
| Medium density polyethylene packing foam | amazon.com | NA | One foam sheet, 220 poly, charcoal, 2x24x18 inches, to fill the remaining space in test objects after clay has been inserted |
| Knock Out Plug for 1.5-inch PVC | Home Depot | 85000 | 42 caps to seal the ends of the 21 test items |
| Sterilite 6-quart plastic storage box | Home Depot | 16428960 | One to store/transport test objects |
References
- Nakayama, H., Jgtgensen, H., Stig, K., Raaschou, H. O., Olsen, T. S. Recovery of upper extremity function in stroke patients: the Copenhagen Stroke Study. Age (SD). 74, 12 (1994).
- Carey, L. M., Matyas, T. A. Frequency of discriminative sensory loss in the hand after stroke in a rehabilitation setting. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine. 43, 257-263 (2011).
- Winward, C. E., Halligan, P. W., Wade, D. T. Somatosensory recovery: A longitudinal study of the first 6 months after unilateral stroke. Disability & Rehabilitation. 29, 293-299 (2007).
- Sullivan, J. E., Hedman, L. D. Sensory Dysfunction Following Stroke: Incidence, Significance, Examination, and Intervention. Topics in Stroke Rehabilitation. 15, 200-217 (2008).
- Connell, L. A., Lincoln, N. B., Radford, K. A. Somatosensory impairment after stroke: frequency of different deficits and their recovery. Clinical Rehabilitation. 22, 758 (2008).
- Winward, C. E., Halligan, P. W., Wade, D. T. Current practice and clinical relevance of somatosensory assessment after stroke. Clinical rehabilitation. 13, 48-55 (1999).
- Torre, K., et al. Somatosensory-related limitations for bimanual coordination after stroke. Neurorehabilitation and neural repair. , (2013).
- Nichols-Larsen, D. S., Clark, P. C., Zeringue, A., Greenspan, A., Blanton, S. Factors influencing stroke survivors’ quality of life during subacute recovery. Stroke. 36, 1480-1484 (2005).
- Borstad, A. L., Nichols-Larsen, D. S. Assessing and treating Higher-level Somatosensory Impairments Post Stroke. Topics in Stroke Rehabilitation. 21, 290-295 (2014).
- Byl, N., Leano, J., Cheney, L. K. The Byl-Cheney-Boczai Sensory Discriminator: reliability, validity, and responsiveness for testing stereognosis. Journal of Hand Therapy. 15, 315-330 (2002).
- Lincoln, N. B., Jackson, J. M., Adams, S. A. Reliability and revision of the Nottingham Sensory Assessment for stroke patients. Physiotherapy. 84, 358-365 (1998).
- Carey, L. M., Nankervis, , et al. . , (2006).
- Ayres, A. J. . Sensory integration and praxis test (SIPT). , (1989).
- Kalisch, T., Tegenthoff, M., Dinse, H. R. Improvement of sensorimotor functions in old age by passive sensory stimulation. Clinical Interventions in Aging. 3, 673 (2008).
- Meyer, S., Kattunen, A. H., Thijs, V., Feys, H., Verheyden, G. How do somatosensory deficits in the arm and hand relate to upper limb impairment, activity, and participation problems after stroke? A systematic Review. Physical Therapy. 94, (2014).
- Williams, P. S., Basso, D. M., Case-Smith, J., Nichols-Larsen, D. S. Development of the Hand Active Sensation Test: reliability and validity. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 87, 1471-1477 (2006).
- . . International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF). , (2001).
- McDonnell, M. N., Hillier, S. L., Miles, T. S., Thompson, P. D., Ridding, M. C. Influence of combined afferent stimulation and task-specific training following stroke: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Neurorehabilitation and neural repair. 21, 435-443 (2007).
- Byl, N. N., Pitsch, E. A., Abrams, G. M. Functional outcomes can vary by dose: learning-based sensorimotor training for patients stable poststroke. Neurorehabilitation and neural repair. 22, 494 (2008).
- Carey, L., Macdonell, R., Matyas, T. A. SENSe: Study of the Effectiveness of Neurorehabilitation on Sensation A Randomized Controlled Trial. Neurorehabilitation and neural repair. 25, 304-313 (2011).

