깊은 뇌 자극과 Saccadometry를 사용하여 정상 및 병적 뇌 기능을 연구하는
Summary
This paper describes the use of quantitative measurement of eye movements in conjunction with stimulation of focal areas of the deep brain in order to study physiology, pathophysiology, and the mechanisms of deep brain stimulation.
Abstract
The oculomotor system involves a large number of brain areas including parts of the basal ganglia, and various neurodegenerative diseases including Parkinson’s and Huntington’s can disrupt it. People with Parkinson’s disease, for example, tend to have increased saccadic latencies. Consequently, the quantitative measurement of saccadic eye movements has received considerable attention as a potential biomarker for neurodegenerative conditions. A lot more can be learned about the brain in both health and disease by observing what happens to eye movements when the function of specific brain areas is perturbed. Deep brain stimulation is a surgical intervention used for the management of a range of neurological conditions including Parkinson’s disease, in which stimulating electrodes are placed in specific brain areas including several sites in the basal ganglia. Eye movement measurements can then be made with the stimulator systems both off and on and the results compared. With suitable experimental design, this approach can be used to study the pathophysiology of the disease being treated, the mechanism by which DBS exerts it beneficial effects, and even aspects of normal neurophysiology.
Introduction
최근에는 1을 신경 결정 고레벨 메커니즘에 관한 정보를 얻고의 정량적 및 비 침습적 방법으로 반응 시간의 측정 값의 사용에 대한 관심이 증가되고있다. 광범위하게 연구 된 반응 시간이 한 가지 유형은 단속적 안구 지연이라고 알려진 시각적 자극의 제시에 단속적 움직임을 시작하는데 걸리는 시간이다. 안구 단속 운동은 우리가 신속하게 한 장소에서 다른 장소로 우리의 시선을 이동 때 발생하는 빠른 안구 운동이다. 이들은 일반적으로 두 개 또는 초당 3 인 주파수에서 발생하는, 우리는 신뢰성 안구 운동의 가장 흔한 유형이다. 각 단속적 효과에 또 다른 2보다는 시각적 인 세계에 하나의 큐 볼 수있는 결정이다.
눈의 움직임을 제어하는 신경 경로는 광범위하게 연구되었고, 상당히 잘 3 설명되어 있습니다. 민감한 전자 장비를 사용하여 안구 운동 기능의 측면과 정확히 될 수 objectively를 정량화. 이는 안구 운동 자체의 상세한 연구를 용이하게 또한 그들을 신경 생리 및 병리의 다른 영역을 조사하기위한 도구로서 이용 될 수있다.
안구 운동 측정은 질병 상태에 대한 유용한 정보를 제공 할 수 있습니다. 단속적 안구 안구 운동 최근, 예를 들면, 헌팅 4,5- 파킨슨 질환 -6,7- 비롯한 신경 퇴행성 질환의 잠재적 바이오 마커로서 많은 관심을 받아 왔으며, 이는 잘 단속적 안구 반응 시간은 이러한 조건에서 정상보다 느린 경향이 확립된다. 단속적 안구 운동 측정의 잠재적 용도는 진단 및 질병 추적에 보조를 포함한다. 단속적 안구 운동 작업 등 (시각적 자극에 반대 측에 가능한 한 빨리보고) antisaccade 또는 메모리 – 같은 더 복잡한 작업에의 (a 갑자기 나타나는 시각적 인 자극을 향해 오른쪽에서 왼쪽으로 또는 가능한 한 빨리보고) 간단한 prosaccade 범위 안내 단속적 (보고) 더 이상 존재하지 않는 대상의 기억 위치를 향해.
뇌 심부 자극은 여러 신경 학적 상태에 대한 효과적인 치료이다. 이는 가장 일반적으로 진전, 강성, 운동 완만 및 운동 이상증을 포함하여, 파킨슨 병의 운동 증상을 치료하는 데 사용된다. 그것은 또한 강박 장애 덜 흔히 신경 병성 통증, 간질, 정신 및 조건 및 근긴장 태성 진전 등을 포함하는 다른 운동 장애에 사용된다. 그것은 과학자들이 생체 내에서 인간 두뇌의 깊은 구조에 직접 전기 액세스 할 수 있으며, 따라서 실험 신경을위한 소중한 기회를 제공하는 유일한 설정입니다. 대상의 다양한 조건에 따라 자극은 안구 경로에 관여하는 많은의 기저핵에서 여러 위치에 포함하여 처리된다. 이 연구는 다양한 자극을 전달하기 위해 DBS 시스템을 이용하여 수행 될 수 있음을 의미소정의 뇌의 위치 및 눈 추적 장치에 기록하고, 그 효과를 분석한다. 실험 패러다임에 따라, 이러한 연구는, 영역의 생리학에 관한 정보가 자극되는 질환 또는되는 DBS가 특정 환경에서 작동 메커니즘의 효과를 얻을 수있다. 이 문서는 깊은 뇌 자극 환자에서 단속적 안구 운동 안구 운동 검사에 대한 일반적인 접근 방법을 설명합니다.
안구 추적 장치의 몇 가지 다른 유형을 사용할 수 있습니다. 이 프로토콜에 기재된 연구 휴대용 saccadometer 수평 단속적 안구 안구의 움직임을 기록하는데 사용되었다. 휴대용 saccadometers 세션 특히 심각한 운동 장애로 고통받는 사람들을 위해, 파킨슨 병 환자에게 더 편안한 것을 의미를 머리 받침 (도 1 참조)를 필요로하지 않는 장점이있다. 여기에 사용 된 saccadometer 경량 약 5cm 폭 10cm 높이입니다. saccadometer의 measu직접 적외선 oculography 사용하여 입술 안구 운동 : 내측 안각 이용 빛 앞에 위치하는 적외선 소스 및 센서 밀리 초 간격으로 안구의 회전 위치를 확립하기 위해 각막 반사. 분석을위한 양질의 데이터를 획득하기 위해 saccadometer 적어도 12 비트의 해상도를 갖는 적어도 1 kHz의 속도로 샘플링한다. 여기에 사용 된 saccadometer에서 시각적 자극에 의해 생성 된 빛의 세 개의 빨간색 13 CD를 m -2 점이었다 저전력 레이저 내장, 하나의 중간 선에 자리하고 ± 10도에서 다른 두 일부 0.1도 subtending의 각 지점 (즉, ) 오른쪽과 왼쪽.
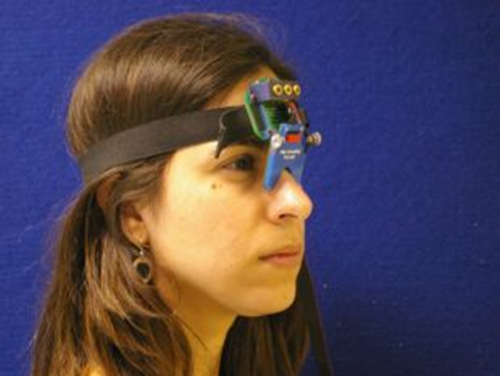
그림 1. Saccadometer. 머리 saccadometer 탄성 밴드에 부착 코의 다리에 휴식 탑재. 네 개의 소형 레이저는 시각적 대상 프로젝트매트 표면 및 참가자의 눈 움직임에에의 각 눈의 코 측에 차동 적외선 반사율 센서에 의해 측정된다. 레이저 표적이 머리를 이동하면, 헤드 레스트는 필요하지 않습니다. 이 그림의 더 큰 버전을 보려면 여기를 클릭하십시오.
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
좋은 품질 단속적 안구 운동 데이터를 획득에서 가장 중요한 요소는 참가자의 지시가 명확하고 정확한 것을 보장한다. antisaccadic 작업에 대한 설명은 완전히 명확하지 않은 경우, 예를 들어, 학습자는 대신 prosaccades를 실행할 가능성이있다. 참가자가 명확하게 자극을 볼 수 없습니다 또는 saccadometer 정확하게 눈의 위치를 측정 할 수없는 경우 녹음도 부패 할 수있다. 데이터 품질이 낮은 것으로…
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
Dr. Antoniades was supported by the National Institute of Health Research (NIHR) and by the Dementias and Neurodegenerative Diseases Research Network (DENDRON) and by the Wellcome Trust. Dr FitzGerald was supported by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Oxford Biomedical Research Centre.
Materials
| Saccadometer device ( Ober Consulting Poland) |
| Computer with Windows environment |
| Software, Latency Meter for downloading the raw data from the saccadometer. |
References
- Leigh, R. J., & Kennard, C. Using saccades as a research tool in the clinical neurosciences. Brain. 127, 460-477 (2004).
- Carpenter, R. H. The neural control of looking. Curr Biol. 10, R291-293 (2000).
- Leigh, R. J., & Zee, D. S. The Neurology of Eye Movements. New York: Oxford University Press, (2006).
- Antoniades, C. A., Xu, Z., Mason, S. L., Carpenter, R. H., & Barker, R. A. Huntington's disease: changes in saccades and hand-tapping over 3 years. Journal of Neurology. 257, 1890-1898 (2010).
- Blekher, T.M., Yee, RD., Kirkwood, SC., Hake, AM., Stout, JC., Weaver, MR., Foroud, TM. Oculomotor control in asymptomatic and recently diagnosed individuals with the genetic marker for Huntington's disease. in Vision Research. Vol. 44 2729-2736 (2004).
- Chan, F., Armstrong, I. T., Pari, G., Riopelle, R. J., & Munoz, D. P. Deficits in saccadic eye-movement control in Parkinson's disease. Neuropsychologia. 43, 784-796 (2005).
- Antoniades, C. A., Demeyere, N., Kennard, C., Humphreys, G. W., & Hu, M. T. Antisaccades and executive dysfunction in early drug-naive Parkinson's disease: The discovery study. Mov Disord. (2015).
- Antoniades, C. et al. An internationally standardised antisaccade protocol. Vision Res. 84, 1-5 (2013).
- Ober, J. K. et al. Hand-Held system for ambulatory measurement of saccadic durations of neurological patients. . In: Modelling and Measurement in Medicine. (2003).
- Temperli, P. et al. How do parkinsonian signs return after discontinuation of subthalamic DBS? Neurology. 60, 78-81 (2003).
- Antoniades, C. A. et al. Deep brain stimulation: eye movements reveal anomalous effects of electrode placement and stimulation. PLoS ONE. 7, e32830 (2012).
- Yugeta, A. et al. Effects of STN stimulation on the initiation and inhibition of saccade in Parkinson disease. Neurology. 74, 743-748 (2010).
- Terao, Y., Fukuda, H., Ugawa, Y., & Hikosaka, O. New perspectives on the pathophysiology of Parkinson's disease as assessed by saccade performance: a clinical review. Clin Neurophysiol. 124, 1491-1506 (2013).
- Temel, Y., Visser-Vandewalle, V., & Carpenter, R. H. Saccadic latency during electrical stimulation of the human subthalamic nucleus. Curr Biol. 18, R412-414 (2008).
- Antoniades, C. A. et al. Deep brain stimulation abolishes slowing of reactions to unlikely stimuli. J Neurosci. 34, 10844-10852 1065-14.2014(2014).
- Rivaud-Pechoux, S. et al. Improvement of memory guided saccades in parkinsonian patients by high frequency subthalamic nucleus stimulation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 68, 381-384 (2000).
- Takikawa, Y., Kawagoe, R., Itoh, H., Nakahara, H., & Hikosaka, O. Modulation of saccadic eye movements by predicted reward outcome. Experimental brain research. Experimentelle Hirnforschung. 142, 284-291 (2002).
- Dorris, M. C., & Munoz, D. P. A neural correlate for the gap effect on saccadic reaction times in monkey. Journal of Neurophysiology. 73, 2558-2562, (1995).
- Hanes, D. P., & Schall, J. D. Countermanding saccades in macaque. Visual Neuroscience. 12, 929-937, (1995).
- Opris, I., Barborica, A., & Ferrera, V. P. On the gap effect for saccades evoked by electrical microstimulation of frontal eye fields in monkeys. Experimental brain research. Experimentelle Hirnforschung. 138, 1-7 (2001).
- Takagi, M., Frohman, E. M., & Zee, D. S. Gap-overlap effects on latencies of saccades, vergence and combined vergence-saccades in humans. Vision Res. 35, 3373-3388 (1995).
- Schall, J. D. Neuronal activity related to visually guided saccades in the frontal eye fields of rhesus monkeys: comparison with supplementary eye fields. Journal of Neurophysiology. 66, 559-579 (1991).
- Pare, M., & Hanes, D. P. Controlled movement processing: superior colliculus activity associated with countermanded saccades. J Neurosci. 23, 6480-6489 (2003).

