ウェーブフロントシェイピングを用いた光ファイバを介して複数の信号の伝送
Summary
We demonstrate the transmission of multiple independent signals through a multimode fiber using wavefront shaping employing a single spatial light modulator. By modulating the wavefront for each signal individually, spatially separated foci are transmitted. Potential applications are multiplexed data transfer in communications engineering and endoscopic light delivery in biophotonics.
Abstract
マルチモード光ファイバを介して複数の独立した光信号の伝送は、ファイバ内伝搬中の光の歪みを補償するために、波面整形を用いて達成されます。私たちの方法論は、光の波面を個別変調器の異なる領域で変調された単一の空間光変調器、光信号ごとに一つの領域を使用するデジタル光位相共役に基づいています。デジタル光位相共役アプローチは、繊維の波伝播挙動の完全な決意が行われる(例えば)他の波面成形アプローチよりも速くなると考えられます。それが唯一の光信号ごとに1キャリブレーションを必要とするのでこれとは対照的に、提示されたアプローチは、時間効率的です。提案手法は、通信工学における空間分割多重化のための潜在的に適切です。さらに応用分野は、特にOで、バイオフォトニクスにおける内視鏡の光配信されています生体組織内の単一の細胞が選択的に高い空間分解能と時間分解能で照明されなければならないptogenetics、。
Introduction
マルチモードファイバ(MMF)を介して複数の光信号の伝送は、通信技術1及びバイオフォトニクス2に明らかです。通信技術において、空間分割多重(SDM)は、複数のシングルモードファイバと比較して、限られた空間の高い利用の恩恵を受け、将来のデータ転送アプリケーション用の光ファイバの伝送容量を高めるために実行可能な解決策であると考えられています3。バイオフォトニクスでは、生物学的サンプルは、MMF内視鏡4を透過する光によって操作されています。例えば、MMFの内視鏡を使用して、個々のニューロンの独立した光制御は、脳5におけるニューロンネットワークを研究するために、光遺伝学のために重要です。しかし、MMF入力ファセットに投影される光は、outpuへの伝播中に歪みによるモードの混合分散の対象となりますMMFのトンファセット。その結果、光の伝搬は、信号伝送が困難な作るれ、変更されます。
波面整形方法6は 、 図7に示すように 、空間光変調器(SLM)を使用して、散乱媒体に適用し、光による伝播8時の散乱による歪みの補償を可能にしています。光フィードバック9を使用して出力を最適化する反復アプローチがあります。これらのアプローチは、変調器要素の多くに対応するために多数の反復の必要性と高い自由度のかかるかなりの時間です。別のアプローチは、完全にその送信行列10によって記述MMF内の歪みを決定することです。送信されるモードの数が多い場合、これは、同様に時間がかかるであろう。対照的に、デジタル光位相共役(DOPC)があると考えられています迅速かつ有利ここで、ほんの数焦点がMMFの出力面で生成されなければならないからです。位相共役アプローチは、生体組織12、13、14を介して集束またはイメージングのために実証されています。
これまで、DOPCは、単一の時間信号のみ15、16のために使用し、そしてMMF 17を通る光の透過のために適用しました。複数の独立した信号のDOPCのアプローチがなされていません。我々は、単相のみのSLM 18を用いて 、各信号のために整形する個々の波面を使用して複数の光信号の独立した伝送を提供する強化されたDOPC方法を開発しました。この目的のために、SLMは各信号に対して1つを送信する、領域に分割されます。提案された実験は、 図1に示されていますキャリブレーションは、実際の送信前)に行われる場合、)(b)に発生します。
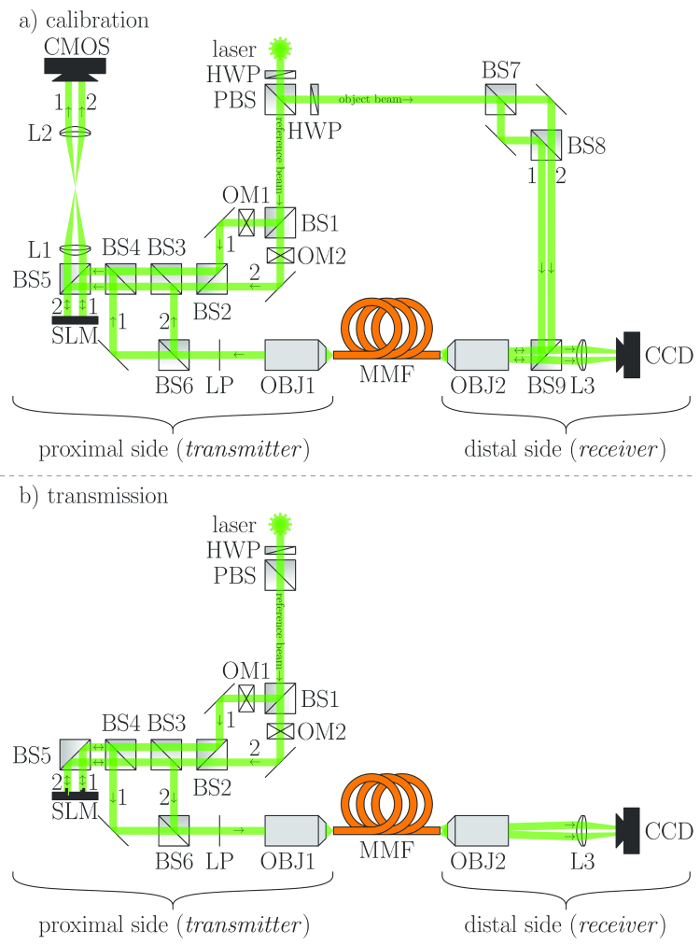
図1:実験セットアップ。 BS =ビームスプリッタ、CCD =電荷結合素子、OM =光変調器、CMOS =相補型金属酸化膜半導体、HWP =半波長板、L =レンズ、LP =直線偏光子、MMF =マルチモードファイバ、OBJ =顕微鏡対物レンズ、 PBSは=偏光ビームスプリッタ、SLM =空間光変調器(位相のみ) – (a)のキャリブレーションおよび(b)の伝送にのみ関連ビームが描かれている。この図の拡大版をご覧になるにはこちらをクリックしてください。
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
実験(プロトコルにおけるステップ1)の組立は、互いに対する光学部品の徹底的な位置合わせを必要とします。最も重要な側面は、高PBRを確保するためにSLM上に参照光の矩形発生です。
二つ以上の送信信号の設定を高めるために、追加のビームスプリッタを使用することができます。別の方法として、光ファイバベースの実装は、よりコンパクトで、システムはバイオ?…
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The financial support by DFG (German research foundation, project CZ 55/30-1) for parts of this work is gratefully acknowledged.
Materials
| spatial light modulator | Holoeye | PLUTO‐VIS‐016 | |
| CMOS camera | Mikrotron | MC4082 | |
| diode‐pumped solid state laser | Laser Quantum | torus 532 | |
| CCD camera | IDS | U3‐3482LE‐M | CMOS camera; suitable as well |
| lens 1 | Qioptiq | G063204000 | |
| lens 2 | Qioptiq | G063203000 | |
| lens 3 | Thorlabs | AC508‐180‐A‐ML | |
| multimode fiber | Thorlabs | M14L02 | |
| beam splitters | Thorlabs | BS013 | 9x |
| polarizing beam splitters | Thorlabs | PBS251 | |
| mirrors | Thorlabs | PF10‐03‐P01 | 5x |
| microscope objectives | Thorlabs | RMS20X | 2x |
| half wave plates | Thorlabs | WPH10M‐532 | 2x |
| linear polarizer | Thorlabs | LPVISB050‐MP2 | |
| optical modulators | Thorlabs | MC2000B‐EC | 2x |
| linear and rotation stage for CMOS camera | Thorlabs | XYR1/M | |
| fiber connector | Thorlabs | S120‐SMA | 2x |
| reducing ring for microscope objectives | Qioptiq | G061621000 | 2x |
| xy adjustment for objective adapters | Qioptiq | G061025000 | 2x |
| z translation mount for fiber adapter | Thorlabs | SM1Z | 2x |
| rods for fiber alignment to objectives | Qioptiq | G061210000 | 8x |
| mounts for lenses 1 and 2 plus two phantom mounts | Qioptiq | G061047000 | 4x |
| rail carriers for objective and lens mounts | Qioptiq | G061372000 | 6x |
| rail for rail carriers | Qioptiq | G061359000 | 2x |
| adapter for CCD camera to 1 post | in-house | ||
| adapter for laser to 4 posts | in-house | ||
| mount for lens 3 | Thorlabs | LMR2/M | |
| mounts for half wave plates | Thorlabs | RSP1D/M | 2 |
| mounts for mirrors | Thorlabs | KM100 | 5x |
| mount for linear polarizer | Thorlabs | RSP05/M | |
| mounts for beam splitters and SLM | Thorlabs | KM100PM/M | 11x |
| clamping arms for beam splitters and SLM | Thorlabs | PM4/M | 11x |
| posts for mounts, rail carriers and adapters | Thorlabs | TR75/M | 29x |
| holders for posts | Thorlabs | PH50/M | 29x |
| pedestals for holders | Thorlabs | BE1/M | 29x |
| clamping forks for pedestals | Thorlabs | CF125 | 29x |
References
- Richardson, D. J., Fini, J. M., Nelson, L. E. Space-division multiplexing in optical fibres. Nat. Photonics. 7 (5), 354-362 (2013).
- Kreysing, M., et al. Dynamic operation of optical fibres beyond the single-mode regime facilitates the orientation of biological cells. Nat. Commun. 5 (5481), 1-6 (2014).
- Winzer, P. J. Scaling optical fiber networks: Challenges and solutions. Opt. Photonics News. 26 (3), 28-35 (2015).
- Cižmár, T., Dholakia, K. Shaping the light transmission through a multimode optical fibre: complex transformation analysis and applications in biophotonics. Opt. Express. 19 (20), 18871-18884 (2011).
- Boyden, E. S., Zhang, F., Bamberg, E., Nagel, G., Deisseroth, K. Millisecond-timescale, genetically targeted optical control of neural activity. Nat. Neurosci. 8 (9), 1263-1268 (2005).
- Philipp, K., et al. Volumetric HiLo microscopy employing an electrically tunable lens. Opt. Express. 24 (13), 15029-15041 (2016).
- Büttner, L., Leithold, C., Czarske, J. Interferometric velocity measurements through a fluctuating gas-liquid interface employing adaptive optics. Opt. Express. 21 (25), 30653-30663 (2013).
- Vellekoop, I. M. Feedback-based wavefront shaping. Opt. Express. 23 (9), 12189-12206 (2015).
- Mahalati, R. N., Askarov, D., Wilde, J. P., Kahn, J. M. Adaptive control of input field to achieve desired output intensity profile in multimode fiber with random mode coupling. Opt. Express. 20 (13), 14321-14337 (2012).
- Caravaca-Aguirre, A. M., Niv, E., Conkey, D. B., Piestun, R. Real-time resilient focusing through a bending multimode fiber. Opt. Express. 21 (10), 12881-12887 (2013).
- Cižmár, T., Dholakia, K. Exploiting multimode waveguides for pure fibre-based imaging. Nat. Commun. 3, 1027 (2012).
- Yaqoob, Z., Psaltis, D., Feld, M. S., Yang, C. Optical phase conjugation for turbidity suppression in biological samples. Nat. Photonics. 2 (2), 110-115 (2008).
- Ma, C., Xu, X., Liu, Y., Wang, L. V. Time-reversed adapted-perturbation (TRAP) optical focusing onto dynamic objects inside scattering media. Nat. Photonics. 8 (12), 931-936 (2014).
- Lee, K., Lee, J., Park, J. H., Park, J. H., Park, Y. One-wave optical phase conjugation mirror by actively coupling arbitrary light fields into a single-mode reflector. Phys. Rev. Lett. 115 (15), 153902 (2015).
- Cui, M., Yang, C. Implementation of a digital optical phase conjugation system and its application to study the robustness of turbidity suppression by phase conjugation. Opt. Express. 18 (4), 3444-3455 (2010).
- Hillman, T. R., et al. Digital optical phase conjugation for delivering two-dimensional images through turbid media. Sci. Rep. 3, (2013).
- Papadopoulos, I. N., Farahi, S., Moser, C., Psaltis, D. Focusing and scanning light through a multimode optical fiber using digital phase conjugation. Opt. Express. 20 (10), 10583-10590 (2012).
- Czarske, J. W., Haufe, D., Koukourakis, N., Büttner, L. Transmission of independent signals through a multimode fiber using digital optical phase conjugation. Opt. Express. 24 (13), 15128-15136 (2016).
- Kim, M. K. Principles and techniques of digital holographic microscopy. SPIE Rev. 1 (1), 01800501-01800550 (2010).
- Gu, R. Y., Mahalati, R. N., Kahn, J. M. Design of flexible multi-mode fiber endoscope. Opt. Express. 23 (21), 26905-26918 (2015).
- Katz, O., Small, E., Bromberg, Y., Silberberg, Y. Focusing and compression of ultrashort pulses through scattering media. Nat. Photonics. 5 (6), 372-377 (2011).

