מדידות אלקטרוכימיות של זרזים נתמכים באמצעות פוטנציוסטט /גלוונוסטאט
English
Share
Overview
מקור: המעבדה של ד”ר יורי רומן — המכון הטכנולוגי של מסצ’וסטס
potentiostat/galvanostat (המכונה לעתים קרובות פשוט potentiostat) הוא מכשיר המודד זרם בפוטנציאל יישומי (פעולה פוטנציסטטית) או מודד פוטנציאל בזרם מיושם (פעולה גלונוסטטית)(איור 1). זהו המכשיר הנפוץ ביותר באפיון האלקטרוכימי של אנודה וחומרי קתודה לתאי דלק, אלקטרוליזרים, סוללות, סופר-קבלים.
באופן קונבנציונלי, אלה אנודה וחומרי קתודה הם ממשק עם potentiostat באמצעות תא אלקטרוכימי שלוש אלקטרודה. האלקטרודה מובילה מן potentiostat מחוברים אלקטרודה הייחוס, אלקטרודה מונה (המכונה לעתים קרובות אלקטרודה עזר), ואת האלקטרודה עובד (אשר מכיל את חומר הבדיקה של עניין). התא האלקטרוכימי מתמלא בתמיסת אלקטרוליטים בעוצמה יונית גבוהה, כגון תמיסת חומצי, אלקליין או מלח. המדיה עבור פתרון זה כוח יוני גבוה הוא בדרך כלל מימית; עם זאת, עבור יישומים הדורשים חלונות פוטנציאליים גבוהים יותר של תא הפעלה, כגון סוללות וסופר-כובשים, נעשה שימוש לעתים קרובות במדיה שאינה מימית. התקשורת הסלולרית מנוטרלת בגז אינרטי (כדי למנוע תגובות צד לא רצויות) או בגז בדיקה (אם תגובת הבדיקה כוללת גז באחת האלקטרודות).
לחלופין, גשר מלח או קרום משמש כדי לשמור על קשר יוני אם שני חצי תאים הם להימדד אלקטרוליטים שונים. ב אלקטרוקטליזה הטרוגנית, סוג זה של תא “שני תאים” משמש לעתים קרובות אם מולקולת הבדיקה באלקטרודה העובדת מגיבה גם ב- counterelectrode. זה קורה לעתים קרובות כמו counterelectrode המועסק בדרך כלל הוא פלטינה, המהווה זרז פעיל מאוד עבור תגובות רבות. כאן, תאים תא יחיד ישמשו, שבו כל שלוש אלקטרודות נמצאים באותה מדיה.
וידאו זה יסביר את תהליך ליטוש אלקטרודה עובדת, הכנת דיו זרז, הרכבת דיו הזרז על האלקטרודה העובדת, הכנת התא האלקטרוכימי ולאחר מכן ביצוע מדידות אלקטרוכימיות. המדידות המבוצעות כוללות: וולטמטריה מחזורית (CV), וולטמטריה טאטומטרי טאטומטרי ליניארי (LSV), כרונופוטנטיומטריה (CP) וכרונואמפרומטריה (CA).
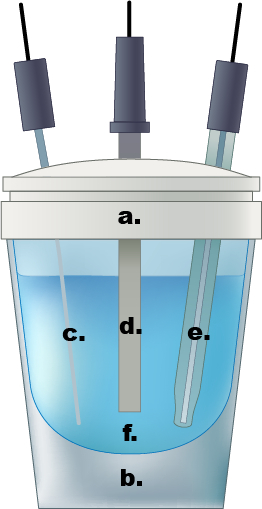
איור 1. דוגמה לתא אלקטרוכימי תא אחד. a.) כובע טפלון, ב.) תא זכוכית, ג.) אלקטרודה מונה חוט Pt, ד.) אלקטרודה עובדת, ה.) אלקטרודה התייחסות Ag/AgCl, נ.) 0.5 M תמיסה אלקטרוליט חומצה גופרתית מימית.
Principles
Procedure
Results
This procedure will result in figures containing plots of measured current vs. potential for each of the four techniques. By convention for CV and LSV, the plots will also be outputted as measured current vs. potential despite the reality that these are transient techniques that measure current vs. the time derivative of potential.
Applications and Summary
CV, LSV, CP, and CA are indispensable techniques for determining the efficacy of new electrode materials for fuel cells, electrolyzers, batteries, and supercapacitors as well as for developing fields such as the selective partial oxidation or reduction of commodity chemicals. These methods allow for determining overpotentials of reactions on different electrode materials as compared to their thermodynamic equilibrium potentials. These methods also allow the volumetric or gravimetric capacitance of supercapacitors to be determined. Similarly, rates of charging/discharging of battery electrodes or supercapacitors can be determined with these techniques. These techniques also allow for the characterization of the electrochemical stability of the materials to be determined. Beyond these basic techniques, more advanced techniques include the combination of potentiometric techniques with in-situ methods such as IR and mass spectrometry.
Transcript
A potentiostat-galvanostat is the most commonly used instrument in electrochemical characterization, and is used to understand the effect of electrical changes on a chemical reaction.
A potentiostat-galvanostat is an instrument used in electrochemical systems. It measures current at an applied potential in potentiostat mode, or vice versa in galvanostat mode. For simplicity, the instrument is commonly called a potentiostat.
Oxidation-reduction, or redox, reactions occur at an electrode surface and involve the transfer of electrons. In particular, the loss of electrons in a chemical species is the case of oxidation, or the gain of electrons in the case of reduction. This redox event can be induced by an applied potential, E, also called voltage.
This video will demonstrate the set up and performance of electrochemical tests using a potentiostat.
In most cases, redox events are coupled to a potentiostat via a three-electrode cell. The three-electrode cell consists of a working electrode, counter or auxiliary electrode, and reference electrode. The working electrode is where the reaction of interest occurs, and the counter electrode is used to complete the electrical circuit.
An applied potential is measured against the reference electrode, which contains a redox system with a known, stable electrode potential, E. Common reference electrodes are the saturated calomel electrode, and the reversible hydrogen electrode, which are used for calibration purposes. The Ag/AgCl electrode is commonly used in electrochemical tests, and is interfaced with the electrolyte solution via a porous frit.
The electrochemical cell is filled with a high ionic strength electrolyte solution, such as an acidic, alkaline, or salt solution. The electrolyte solution prevents charge buildup at the electrodes.
In an electrochemical experiment, potential, current, time, and charge can all be manipulated or measured by the potentiostat. When the working electrode is acting as the cathode, electrons flow from the counter electrode to the working electrode. Positively charged ions, or cations, flow to the cathode. The reverse is true when the working electrode is acting as the anode. Negatively charged ions, or anions, flow to the anode.
By selecting the manipulated and measured parameters, a number of measurement techniques are possible. Chronoamperometry is a technique where a potential step is applied to the working electrode, and the resulting current change is measured as a function of time. When a potential step is large enough to cause an electrochemical reaction at the working electrode, the current changes. This technique can be used for many applications, such as the determination of diffusion coefficients in reaction kinetics.
Similarly, chronopotentiometry is a technique where a constant or varied current is applied, and the potential is measured as a function of time. The applied current causes electroactive species to be oxidized or reduced at a certain rate. This technique is used for a range of applications, such as the determination of reaction progress.
Voltammetry measures anodic and cathodic current with respect to an applied potential sweep. This measurement examines the addition or removal of electrons from a chemical species during the increase or decrease of potential at a constant rate. Cyclic voltammetry, or CV, is covered in depth separately in another video in this collection.
Now that the basics of voltammetry have been covered, the preparation of a three-electrode cell and a working electrode with a surface bound catalyst will be demonstrated in the laboratory. In this demonstration, catalyst ink will be prepared and measured, which consists of platinum nanoparticles in a carbon black support, with a Nafion binding agent. This system is representative of current fuel cell and battery research.
To begin, weigh 7.5 mg of metal/carbon black catalyst in a fume hood, and add it to a glass vial. Dilute the catalyst with 1 mL of water and add 100 μL of Nafion 117, then cap the vial.
Sonicate the mixture on ice for at least 10 min to ensure uniform dispersion and complete mixing of the carbon black support with the Nafion. While the ink is sonicating, prepare the working electrode, which is a 3-mm glassy carbon disk.
Clean and polish the electrode by gently rubbing it in a swirling, circular motion on a soft pad covered with 0.05 μm colloidal alumina solution. After polishing, rinse the electrode copiously with deionized water to remove the alumina.
Next, 7 mL of ink is dripped onto the polished, vertically oriented glassy carbon electrode. Dry the working electrode under vacuum at room temperature. Then dry it at 80 °C for one hr if the catalyst nanoparticles are air stable.
First, fill the glass electrochemical cell with 10 mL of the electrolyte. Cap the electrochemical cell with a Teflon cap with openings for the three electrodes. De-gas the electrolyte for at least 30 min with ultra high purity nitrogen gas in order to remove redox-active oxygen. Allow the nitrogen to bubble lightly throughout the experiment.
Remove the Ag/AgCl reference electrode from its 3 M NaCl storage solution. Rinse the electrode thoroughly with deionized water, and place it into the electrochemical cell.
Next, rinse the platinum wire counter electrode and the dried working electrode with deionized water, and insert them into the cell. Ensure that the electrodes do not touch. Turn on the potentiostat, and connect the leads to the reference and counter electrodes.
Perform at least 20 conditioning cycles by running cyclic voltammetry scans between the upper and lower potential limits at 50 mV per second. This step ensures that the electrode surfaces are fully hydrated.
Linear sweep voltammetry, or LSV, can be performed by specifying the initial and final potentials, and the scan rate. The scan rate for LSV is typically less than that for CV. The result is a plot of potential vs. current with oxidation or reduction events visualized as peaks in the scan. In this case, the perchlorate in the electrolyte was reduced on the catalyst surface in the cathodic scan.
To perform chronoamperometry, select it as the technique, then specify the fixed potential as well as the time. The result is a plot of current vs. time. The initial decay is due to capacitive discharging, while the steady state portion is essentially a straight line. Chronoamperometry is potentiostatic and thus after the initial asymptotic decay of the capacitative effects, the current attributed to surface reactions can be isolated.
Finally, chronopotentiometry is performed in a series of current steps, where one current is specified for a certain length of time. Each time the current switches from zero to the working current, there is an initial asymptotic change in potential, followed by a steady state. After each on/off cycle, the stable catalyst material requires the same over-potential to drive the specified current.
Electrochemical measurements with a potentiostat are widely used in analysis and fabrication.
Electrochemistry is used to analyze the binding of probe molecules to electrodes. In this example, electrodes were patterned within microfluidic channels, and functionalized with single stranded DNA. When the DNA was hybridized with the complimentary strand, the redox couple was blocked at the electrode surface.
DNA hybridization was then measured by connecting the electrodes to the potentiostat using three probe electrodes.
Impedance measurements, a measure of the resistance to current flow, showed that increasing complimentary DNA concentration resulted in increased impedance, and therefore increased hybridization.
Next, electrochemical processes were used to monitor and characterize the growth of biofilms on an electrode. For this, a three-electrode cell was assembled, with the electrolyte being the cell broth.
The growth of the biofilm was monitored using chronoamperometry, in order to achieve an exact measurement and reproducible culture conditions.
Electrochemical techniques can also be used in the fabrication of thin films and layers on an electrode surface. Electrical signals trigger localized environments at the electrode surface, which can induce the self-assembly of materials.
In this example, the deposition of biomaterials was performed using electrodeposition. Chitosan, a biopolysaccharide, undergoes a sol-gel transition at the electrode surface, creating a film.
You’ve just watched JoVE’s introduction to potentiometry. You should now understand how to set up a typical three-electrode cell, and perform basic electrochemical tests.
Thanks for watching!
