偶发编码方式
English
Share
Overview
资料来源: 实验室的乔纳森 Flombaum — — 约翰 · 霍普金斯大学
长期记忆是人类认知的关键特征,它一直在实验心理学研究的一个突出重点。许多范例,旨在挖掘长期记忆依靠询问参与者学习或研究内容,然后测试内存有关的内容。这是一种好方法如果你想要理解记忆是如何支持教育成就,例如,在那里明确的学习过程的一部分。可是,在日常生活中,人们往往形成新的记忆 — — 很多的持续了很长时间 — — 顺便说一句.人们不记得他们读一本杂志,时刻遇见了一个伙伴,或者最喜欢的故事情节因为他们尝试。不知怎的丰富的经验只是获取编码到内存随着生命的流逝。要研究长期记忆的这一边,实验心理学家使用一种叫做附带编码的范式。
范式是对于调查的各种经验,往往会产生较强的长期记忆尤其有用。研究者所认为的那种接触他们要求的经验 — — 个人、 纯粹智力、 深或浅,例如。附带编码模式可以用来对比长期记忆的形成在不同种类的订婚期间通过改变用于公开个人对刺激的覆盖任务。一个封面任务是参与者被问到随后测试完全不知道那记忆任务中刺激的任务。
该视频演示使用附带编码范式和两个不同封面任务探讨长期记忆,当明确研究的刺激不要求的标准程序。
Procedure
Results
An influential effect in the domain of long-term memory is that objects are more likely to be remembered when incidental processing is more elaborate, especially when it is personal. Memory performance in a surprise test is therefore usually worse among participants exposed to the letter ‘C’ task and age-matched participants exposed to the more personal “have you ever touched it” task. Figure 5 graphs this result, which suggests that encoding into memory is not a random process, but instead, one that is influenced by the kinds of interactions a person is engaged in.
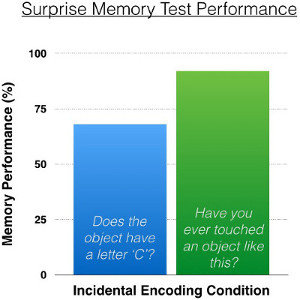
Figure 5. Memory performance in a surprise state discrimination task as a function of incidental encoding cover task, either impersonal and superficial (blue) or personal and more elaborate (green). Elaborate and personal interactions are more likely to lead to strong long-term memory through incidental exposure.
Applications and Summary
Incidental encoding followed by surprise memory testing is the primary vehicle of current research into the mechanisms of long-term memory formation, attempts to improve memory, and attempts to understand memory disorders like Alzheimer’s disease, in particular. It is well established that intentional encoding in Alzheimer’s disease is extremely impaired. For example, if patients try to remember stimuli, because they know they will be tested later, then they remember very little compared with controls. This can be shown by exposing patients to images just as they would be in the incidental-encoding task, but instructing them to try to remember each image because they will be tested later. In contrast, Alzheimer’s patients have better memory for images encoded incidentally in tasks that involve emotional or personal processing of the stimulus. This suggests that some kinds of incidental processing leads to stronger memories than even intentional encoding, and it suggests that activation of emotion areas in the brain may foster memory encoding.
Transcript
A great deal of our daily experiences gets encoded into long-term memory incidentally, as life goes by, without us explicitly trying to encode it.
For example, people do not remember the moment they first met a friend because they try to; rather, they just do.
Such implicit long-term memory is studied with an incidental encoding paradigm, which enables memories to be formed without the participant being asked to specifically remember a series of images.
This encoding is accomplished through the use of a cover task, where images are shown, but individuals are not explicitly told to remember them. At a later time, they are surprised with a memory test of the images.
This video demonstrates methods for investigating implicit long-term memory, including how to design stimuli and perform an experiment involving an incidental encoding paradigm, as well as how to analyze the data and interpret the results.
A typical incidental encoding experiment has two phases. The first consists of the encoding phase, where participants are exposed to a large set of pictures of real-world, everyday objects.
During this session, images are individually shown on the screen for 2 sec, with an inter-image interval of 1 sec. Half the participants are asked to do a cover task where they evaluate the object in an impersonal, and relatively superficial way by determining if there is a letter ‘c’ in its name.
The other half of the participants are asked to complete a more personal and detailed evaluation of the object by determining if they have ever touched the object on the screen. Note that including two cover tasks allows researchers to investigate whether the type of object engagement differentially affects incidental encoding into long-term memory.
The second phase of the experiment is the surprise memory recall test. All participants are randomly shown two images of the same object: one is the same as what was presented during the cover task, while the other is slightly different. Participants are asked to choose the image they think they previously saw.
In this case, the dependent variable is the number of correct choices during the recall test. Memory performance is expected to be greater for those who completed the more personal cover task, compared to the impersonal one.
To begin the experiment, greet the participant in the lab and explain the general procedures that will be used for the task.
During the experiment, have the participant sit comfortably in front of the screen and keyboard. Randomly assign participants to one of the two cover tasks, and instruct them to press the ‘Y’ key to respond yes or the ‘N’ key for no after the image is presented.
After judging 100 objects in the initial encoding phase, allow the participant to have a 20-min break.
When the break is over, explain to the participant that there is a final memory recall test, where two objects will appear and they must choose the one they think they saw during the initial phase by pressing the left or right arrow keys this time.
During this final recall phase, have each participant complete 100 paired trials, with the incidental objects presented in random order.
To analyze the results, compute the proportion of correct responses made by all of the participants during the surprise memory test phase and graph the results. Note that chance level is 50%, since there were only two choices.
Notice that incidental encoding into memory occurred during both cover tasks; however, having a more personal engagement with the presented items strengthened the formation of memories.
Now that you are familiar with an incidental encoding paradigm, let’s take a look at other ways experimental psychologists use the task to investigate long-term memory formation.
The incidental encoding paradigm is used to investigate the memory deficits caused by diseases such as Alzheimer’s. Patients remember very little compared with healthy controls when they are asked to study and remember images.
However, if an incidental encoding paradigm with a personal or emotional cover task is used, patients have a much better memory, suggesting that activation of emotion areas in the brain may foster memory encoding.
Other researchers have combined incidental encoding paradigms with functional magnetic resonance imaging to elucidate the brain regions involved in memory formation of emotional items, including the amygdala, hippocampus, and other medial temporal lobe structures.
You’ve just watched JoVE’s introduction to incidental encoding. Now you should have a good understanding of how to setup and perform an experiment, as well as analyze and assess the results.
Thanks for watching!
