恒流中原发性人类内皮细胞的肺炎球菌感染
Summary
本研究描述了在定义的流动条件下,在剪切应力下在分化人类原发内皮细胞表面产生的对冯·威勒布兰德因子字符串的肺炎球菌依从的微观监测。通过应用微分免疫染色程序,此协议可扩展到特定细胞结构的详细可视化和细菌定量。
Abstract
肺炎链球菌与内皮细胞表面的相互作用通过对美能敏感蛋白(如冯·威勒布兰德因子(VWF)在血液流动中介导。这种糖蛋白改变其分子构象,以响应剪切应力,从而暴露结合位点,用于广泛的宿主-配体相互作用。一般来说,在定义的剪切流下培养原发内皮细胞可以促进特定的细胞分化,并形成一个稳定且紧密相连的内皮层,类似于血管内壁的生理。.因此,对细菌病原体与涉及对肌敏感的蛋白质的宿主血管之间的相互作用的功能分析需要建立泵系统,以模拟已知影响表面的生理流动力。血管细胞。
本研究中使用的微流体装置使具有定义流速的流体能够连续和无脉冲再循环。计算机控制的气压泵系统通过生成连续、单向和控制的介质流,在内皮细胞表面应用定义的剪切应力。通过使用专为微观可视化而设计的特殊通道幻灯片,可以在流中微观监控和量化细胞和细菌附着物的形态变化。与静态细胞培养感染(一般要求在免疫标记和微观分析之前进行样品固定)不同,微流体滑道可实现基于荧光的蛋白质、细菌和细胞成分的检测样品固定后;系列免疫荧光染色;和直接荧光检测。结合荧光细菌和特定的荧光标记抗体,这种感染程序为与血管过程相关的大量科学应用提供了一个高效的多组分可视化系统。
Introduction
肺炎球菌感染的发病机制的特点是与细胞外基质化合物和人类血变成分的多样性相互作用,如质原和VWF1,2, 3,4,5,6,7,8 。多域糖蛋白VWF作为平衡血变的关键调节器,通过调解血栓细胞招募和纤维蛋白结合在血管血栓形成位9。功能,活跃的VWF对出血控制和伤口愈合的重要性证明了冯·威尔布兰德的疾病,一种常见的遗传性出血紊乱10。
球状VWF在人体血液系统中循环,浓度高达14.0微克/mL11,10。为了应对血管损伤,内皮韦贝尔帕拉德体(WBP)局部释放的VWF明显增加11,12。以前的研究表明,肺炎球菌粘附于人类内皮细胞及其产生的孔隙毒素肺炎溶血蛋白显著刺激发光VWF分泌13。血流的流体动力诱导机械反应VWF域的结构开放。在10dyn/cm2的流速下,VWF多变到长度高达几百微米的长蛋白串,仍然附着在子内皮10,12。
为了理解在剪切应力下产生的多面化VWF字符串在肺炎球菌与内皮表面相互作用中的功能,建立了基于微流体的细胞培养感染方法。使用一种微流体装置,采用软件控制的气压泵系统。这使得细胞培养基的连续、单向再循环具有定义的流速。因此,系统在内皮细胞表面应用了定义的剪切应力,内皮细胞仍附着在专用通道滑道内。这种方法能够模拟人类血管系统血流中的剪切力,在定义的恒定流动条件下,VWF字符串在分化的内皮细胞上生成。为此,内皮细胞在特定的通道幻灯片中培养(见材料表),这些细胞适用于流中的微小分析。微流体泵系统提供了在可融合的内皮细胞层上形成扩展 VWF 字符串所需的高度定义和控制的剪切应力情况。通过组胺补充刺激人类脐带静脉内皮细胞(HUVEC)的VWF分泌后,通过施加10 dyn/cm2的剪切应力(*)诱导弦形成。剪切应力定义为作用于细胞层的力。它是大约根据康尼什等人计算的。al.14与方程 1:
其中 = = 在 dyn/cm2中剪切应力 ,= 在 (dyn_s)/cm2中的粘度,h = 通道高度的一半,w = 通道宽度的一半,而 = = 流量(以 mL/min 表示)。
公式 1 的结果取决于所使用的不同幻灯片的不同高度和宽度(参见材料表)。在本研究中,使用了 0.4 μm 的 Luer 通道滑动,导致室滑动系数为 131.6(参见公式 2)。
37°C时介质的粘度为0.0072 dyn_s/cm2,剪切应力为10 dyn/cm2。这导致流量为 10.5 mL/min(参见公式 3)。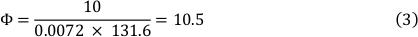
本文详细介绍了使用单向层流系统对宿主血管中细菌感染机制进行调查和可视化的微流体细胞培养过程的适应和进展。内皮层上的VWF字符串的生成也可以通过使用其他泵系统,能够应用连续和稳定的剪切应力15刺激。
在原发内皮细胞培养到流动汇合和刺激VWF弦形成后,在恒定的微观控制下,将表达红荧光蛋白(RFP)16的肺炎球菌添加到内皮细胞层中。使用VWF特异性荧光标记抗体,对内皮细胞表面的细菌附着在VWF串上进行微观可视化和实时监测长达三个小时。用这种方法,VWF作为促进细菌附着到血管内皮的粘附辅助因子的作用被确定8。
除了蛋白质分泌和构象变化的微观可视化外,该方法还可用于实时监测细菌感染过程的单步骤,并量化不同时间点的附着细菌数量。感染。特定的软件控制的泵系统还提供在定义的恒定流动条件下培养内皮细胞长达数天的可能性,并实现定义的脉冲介质流孵育。此外,该方法可以使用不同的单元格类型应用。调整染色方案还能够检测和可视化内化为真核细胞的细菌。
本手稿描述了这种高级实验协议,可用作一种定义、可靠和可重复的方法,用于对病理生理学过程进行高效和通用的表征。
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
模拟细菌与对美能敏感宿主蛋白(如 VWF)的相互作用,需要一个可渗透的细胞培养系统,该系统能够生成定义、单向和连续流动的液体,从而产生可靠的剪切应力.已经描述了几个微流体泵系统。Bergmann等人的综合综述总结了不同二维和三维细胞培养模型的关键方面17。
微流体技术是一种非常年轻的技术,始于20世纪90年代初,在微米甚至纳米尺?…
Divulgations
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
该项目由DFG(BE 4570/4-1)向S.B.提供资金。
Materials
| 1 mL Luer-syringe | Fisher Scientific | 10303002 | with 1 mL volume for gelatin injection using the luer-connection of the slides |
| 2 mL Luer-syringe | Sarstedt | 9077136 | For pieptting/injecting fluids into the luer connections of the channel chamber slides |
| Accutase | eBioscience now thermo fisher | 00-4555-56 | protease mix used for gentle detachment of endothelial cells |
| AlexaFluor350-conjugated Phalloidin | Abcam | ab176751 | no concentration available from the manufacturer, stock solution is sufficient for 300 tets, company recommends to use 100 µl of a 1:1000 dilution, blue fluorescence (DAPI-filter settings) |
| AlexaFluor488-conjugated goat-derived anti-mouse antibody | Thermo Fisher Sientific | A11001 | stock concentration: 2 mg/mL for immunostaining of human VWF in microfluidic slide after PFA fixation, green fluorescence |
| AlexaFluor568-conjugated goat-derived anti-rabbit-antibody | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A-11011 | stock concentration: 2 mg/mL for immunostaining of pneumococci in microfluidic slide after pFA fixation, red fluorescence |
| Bacto Todd-Hewitt-Broth | Becton Dickinson GmbH | BD 249210 | complex bacterial culture medium |
| Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) | Sigma Aldrich | A2153-25G | solubilized, for preparation of blocking buffer |
| Cell culture flasks with filter | TPP | 90026 | subcultivation of HUVEC in non-coated cell culture flasks of 25 cm2 surface |
| Centrifuge Allegra X-12R | Beckman Coulter Life Sciences | 392304 | spinning down of bacteria (volumes of > 2mL) |
| Centrifuge Allegra X-30 | Beckman Coulter Life Sciences | B06314 | spinning down of eukaryotic cells |
| Centrifuge Z 216 MK | Hermle | 305.00 V05 – Z 216 M | spinning down of bacteria (volumes of less than 2 mL) |
| Chloramphenicol | Carl Roth GmbH + Co. KG, Karlsruhe | 3886.2 | used in a concentration of 0.2 /mL for cultivation of pneumococci transformed with genetic construct carrying red fluorescent protein and chloramphenicol resistance cassette |
| Clamp for perfusion tubing | ibidi | 10821 | for holding the liquid in the tube bevor connecting the slide to the pump system |
| CO2-Incubator | Fisher Scientific | MIDI 40 | incubator size is perfectly adapted to teh size of the fluidic unit with connected channel slide and was used for flow cultivation at 37°C and 5% CO2 |
| CO2-Incubator | Sanyo | MCO-18 AIC | for incubation of bacteria and cells in a defined atmosphere at 5% CO2 and 37°C |
| Colombia blood agar plates | Becton Dickinson GmbH | PA-254005.06 | agar-based complex culture medium for S. pneumoniae supplemented with 7% sheep blood |
| Computer | Dell | Latitude 3440 | Comuter with pressure pump software |
| Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope (CLSM) | Leica | DMi8 | An inverse microscope with a stage covered by a heatable chamber and with a fluorescence unit equipped with fluorescence filter, Xenon-light source (SP8, DMi8) and DFC 365 FX Kamera (1392 x 1040, 1.4 Megapixel) |
| Di Potassium hydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4) | Carl Roth GmbH + Co. KG, Karlsruhe | 3904.1 | used for PBS buffer |
| Drying material | Merck | 101969 | orange silica beads for drying used in a glass bottle with a tubing adaptor |
| ECGM supplement Mix | Promocell | C-39215 | supplement mix for ECGM -medium, required for precultivation of endothelial cells: 0.02 mL/mL Fetal calf serum, 0.004 mL/ mL endothelial cell growth supplement, 0.1 ng / mL epidermal growth factor, 1 ng / mL basic fibroblast growth factor, 90 µg / mL heparin, 1 µg / mL Hydrocortisone |
| ECGMS | Promocell | C-22010 | ECGM supplemented with 5 % [w/w] FCS and 1 mM MgSO4 to increase cell adhesion |
| Endothelial Cell growth medium (ECGM, ready to use) | Promocell | C-22010 | culture medium of HUVECs, already supplemented with all components of the supplement mix |
| Fetal Calf Serum (FCS) | biochrome now Merck | S 0415 | supplement for cell culture, used for infection analyses |
| FITC-conjugated goat anti-human VWF antibody | Abcam | ab8822 | stock concentration: 10 mg/mL, for immunodetection of globular and multimerized VWF in flow |
| Fluidic Unit | ibidi | 10903 | fluidic unit for flow cultivation |
| Gelatin (porcine) | Sigma Aldrich | G-1890-100g | for precoating of microslide channel surface |
| histamine dihydrochloride | Sigma Aldrich | H-7250-10MG | for induction of VWF secretion from endothelial Weibel Palade Bodies |
| Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cell (HUVEC) | Promocell | C-12203 Lot-Nr. 396Z042 | primary endothelial cells from pooled donor, stored crypcoserved in liquid nitrogen |
| Human VWF-specific antibody derived from mouse (monoclonal) | Santa Cruz | sc73268 | stock concentration: 200 µg/mL for immunostaining of VWF in microfluidic slide after PFA fixation |
| Injection Port | ibidi | 10820 | for injection of histamin or bacteria into the reservoir tubing during the flow circulation |
| Light microscope | Zeiss | Axiovert 35M | inverse light microscope for control of eukaryotic cell detachement and cell counting using a 40 x water objective allowing 400 x magnification |
| Luer-slides I0.4 (ibiTreat472microslides) | ibidi | 80176 | physically modified slides for fludic cultivation (μ–Slide I0.4Luer with a channel hight of 0.4 mm, a channel volume of 100 μl, a growth area of 2.5 cm and a coating area of 25.4 cm2) suitable for all kinds of flow assay, the physical treatment generates a hydrophilic and adhesive surface. |
| Magnesium sulfate (MgSO4, unhydrated) | Sigma Aldrich | M7506-500G | For preparation of ECGMS medium |
| Microfluidic Pump | ibidi | 10905 | air pressure pump |
| Neubauer cell counting chamber | Karl Hecht GmbH&Co KG | 40442002 | microscopic counting chamber for HUVECs |
| Paraformaldehyde 16% (PFA) | Electron Microscopy Sciences | 15710-S | for cross linking of samples |
| Perfusion Set | ibidi | 10964 | Perfusion Set Yellow/Green has a tubing diameter of 1.6 mm, a tube length of 50 cm, a total working volume of 13.6 mL, a dead tube volume of 2.8 mL and a reservoir size of 10 mL. combined with the µ-slide L0.4Luer, at 37°C and a viscosity of 0.0072 dyn x s/cm2 a flow rate range of 3.8mL/min up to 33.9 mL/min and shear stress between 3.5 dyn/cm2 and 31.2 dyn/cm2 can be reached. with 50 cm lenght for microfluidic |
| Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) | the solution was prepared using the following chemicals: 0.2 g/L KCl, 1.44 g/L Na2HPO4, 0.24 g/L KH2PO4 , pH 7.4 | ||
| Plastic cuvettes | Sarstedt | 67,741 | (2 x optic) for OD measurement at 600 nm |
| Pneumococcus-specific antiserum | Pineda | raised in rabbit using heat-inactivated Streptococcus pneumoniae NCTC10319 and D39, IgG-purified using proteinA-sepharose column. | |
| Polystyrene or Styrofoam plate | this is a precaution step to avoid cold stress on the cells seeded in the channel slides. Any type of styrofoam such as packaging box-material can be used. The plate might by 0.5 cm thick and should have a size of 20 cm2. | ||
| Potassium chloride (KCl) | Carl Roth GmbH + Co. KG, Karlsruhe | 6781.1 | used for PBS buffer |
| Pump Control Software (PumpControl v1.5.4) | ibidi | v1.5.4 | Computer software for controlling the pressure pump, setting the flow conditions and start/end the flow |
| reaction tubes 1.5/ 2.0mL | Sarstedt | 72.706/ 72.695.500 | required for antibody dilutions |
| reaction tubes with 50 mL volume | Sarstedt | 6,25,48,004 | |
| RFP-expressing pneumococci | National Collection of Type Cultures, Public Health England | 10,319 | Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 47 expressing RFP fused to ahistone-like protein integrated into the genome |
| serological pipets 5, 10 mL | Sarstedt | 86.1253.025/ 86.1254.025 | for pipeting larger volumes |
| Sodium Carbonate (Na2CO3, water free) | Sigma Aldrich | 451614-25G | for preparation of 100 mM Sodium Carbonate buffer |
| Sodium dihydrogen phosphate (NaH2PO4) | Carl Roth GmbH + Co. KG, Karlsruhe | P030.2 | used for PBS buffer |
| Spectral Photometer Libra S22 | Biochrom | 80-2115-20 | measurement of optical density (OD) of bacterial suspension at 600 nm |
| Sucrose | Sigma Aldrich | S0389-500G | for preparation of blocking buffer |
| Triton X-100 | Sigma Aldrich | T9284-500ML | Used in 0.1% end concentration diluted in dH20 for eukaryotic cell permeabilization after PFA fixation |
| Yeast extract | oxoid | LP0021 | bacteria are cultivated in THB supplement with 1% [w/w] yeast extract = complete bacterial cultivation medium THY |
References
- Weiser, J. N., Ferreira, D. M., Paton, J. C. Streptococcus pneumoniae: transmission, colonization and invasion. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 16 (6), 355-367 (2018).
- Bergmann, S., Hammerschmidt, S. Versatility of pneumococcal surface proteins. Microbiology. 152, 295-303 (2006).
- Bergmann, S., et al. Integrin-linked kinase is required for vitronectin-mediated internalization of Streptococcus pneumoniae by host cells. Journal of Cell Science. 122, 256-267 (2009).
- Bergmann, S., Schoenen, H., Hammerschmidt, S. The interaction between bacterial enolase and plasminogen promotes adherence of Streptococcus pneumoniae to epithelial and endothelial cells. International Journal of Medical Microbiology. 303, 452-462 (2013).
- Bergmann, S., Rohde, M., Chhatwal, G. S., Hammerschmidt, S. Alpha-enolase of Streptococcus pneumoniae is a plasmin(ogen)-binding protein displayed on the bacterial cell surface. Molecular Microbiology. 40, 1273-1287 (2001).
- Bergmann, S., et al. Identification of a novel plasmin(ogen)-binding motif in surface displayed alpha-enolase of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Molecular Microbiology. 49, 411-423 (2003).
- Bergmann, S., Rohde, M., Preissner, K. T., Hammerschmidt, S. The nine residue plasminogen-binding motif of the pneumococcal enolase is the major cofactor of plasmin-mediated degradation of extracellular matrix, dissolution of fibrin and transmigration. Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 94, 304-311 (2005).
- Jagau, H., et al. Von willebrand factor mediates pneumococcal aggregation and adhesion in flow. Frontiers in Microbiology. 10, 511 (2019).
- Tischer, A., et al. Enhanced local disorder in a clinically elusive von willebrand factor provokes high-affinity platelet clumping. Journal of Molecular Biology. 429, 2161-2177 (2017).
- Ruggeri, Z. M. Structure of von willebrand factor and its function in platelet adhesion and thrombus formation. Best Practice Research Clinical Haematology. 14, 257-279 (2001).
- Spiel, A. O., Gilbert, J. C., Jilma, B. Von willebrand factor in cardiovascular disease: Focus on acute coronary syndromes. Circulation. 117, 1449-1459 (2008).
- Springer, T. A. Von Willebrand factor, Jedi knight of the bloodstream. Blood. 124, 1412-1425 (2014).
- Luttge, M., et al. Streptococcus pneumoniae induces exocytosis of weibel-palade bodies in pulmonary endothelial cells. Cellular Microbiology. 14, 210-225 (2012).
- Cornish, R. J. Flow in a Pipe of Rectangular Cross-Section. Proceedings of the Royal Society A. 786, 691-700 (1928).
- Michels, A., Swystun, L. L., Mewburn, J., Albánez, S., Lillicrap, D. Investigating von Willebrand Factor Pathophysiology Using a Flow Chamber Model of von Willebrand Factor-platelet String Formation. Journal of Visualized Experiments. 14 (126), (2017).
- Kjos, M., et al. fluorescent Streptococcus pneumoniae for live-cell imaging of host-pathogen interactions. Journal of Bacteriology. 197, 807-818 (2015).
- Bergmann, S., Steinert, M. From single cells to engineered and explanted tissues: New perspectives in bacterial infection biology. International Reviews of Cell and Molecular Biology. 319, 1-44 (2015).
- Harrison, D. J., et al. Micromachining a miniaturized capillary electrophoresis-based chemical analysis system on a chip. Science. 261 (5123), 895-897 (1993).
- Magnusson, M. K., Mosher, D. F. Fibronectin: Structure, assembly, and cardiovascular implications. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 18, 1363-1370 (1998).
- Zerlauth, G., Wolf, G. Plasma fibronectin as a marker for cancer and other diseases. The American Journal of Medicine. 77 (4), 685-689 (1984).
- Li, X. J., Valadez, A. V., Zuo, P., Nie, Z. 2012. Microfluidic 3D cell culture: potential application for tissue-based bioassays. Bioanalysis. 4, 1509-1525 (2019).
- Fiddes, L. K., et al. A circular cross-section PDMS microfluidics system for replication of cardiovascular flow conditions. Biomaterials. 31, 3459-3464 (2010).
- Schimek, K., et al. Integrating biological vasculature into a multi-organ-chip microsystem. Lab on a Chip. 13, 3588-3598 (2013).
- Pappelbaum, K. I., et al. Ultralarge von willebrand factor fibers mediate luminal Staphylococcus aureus adhesion to an intact endothelial cell layer under shear stress. Circulation. 128, 50-59 (2013).
- Schneider, S. W., et al. Shear-induced unfolding triggers adhesion of von willebrand factor fibers. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 104, 7899-7903 (2007).
- Reneman, R. S., Hoek, A. P. G. Wall shear stress as measured in vivo: consequences for the design of the arterial system. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing. 46 (5), 499-507 (2008).
- Valentijn, K. M., Sadler, J. E., Valentijn, J. A., Voorberg, J., Eikenboom, J. Functional architecture of Weibel- Palade bodies. Blood. 117, 5033-5043 (2011).
- Freshney, R. I. . Culture of animal cells: A manual of basic Technique, 5th edition. , (2005).
- Shaw, J. A., Shaw, A. J. . Epithelial cell culture- a practical approach. , 218 (1996).
- Elm, C., et al. Ectodomains 3 and 4 of human polymeric Immunoglobulin receptor (hpIgR) mediate invasion of Streptococcus pneumoniae into the epithelium. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 279 (8), 6296-6304 (2004).
- Nerlich, A., et al. Invasion of endothelial cells by tissue-invasive M3 type group A streptococci requires Src kinase and activation of Rac1 by a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-independent mechanism. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 284 (30), 20319-20328 (2009).
- Ho, C. T., et al. Liver-cell patterning lab chip: mimicking the morphology of liver lobule tissue. Lab on a Chip. 13, 3578-3587 (2013).
- Huh, D., et al. Reconstituting organ-level lung functions on a chip. Science. 328, 1662-1668 (2010).
- Harink, B., Le Gac, S., Truckenmuller, R., van Blitterswijk, C., Habibovic, P. Regeneration-on-a-chip? The perspectives on use of microfluidics in regenerative medicine. Lab on a Chip. 13, 3512-3528 (2013).

