多流灌注生物反应器集成了出口分馏功能,用于动态细胞培养
Summary
本文提出了一种构建和操作低成本、多通道灌注细胞培养系统的方法,用于测量细胞过程中溶质分泌和吸收速率的动态。该系统还可以使细胞暴露于动态刺激曲线中。
Abstract
某些细胞和组织功能在几分钟到几小时的动态时间尺度内运行,而传统培养系统无法很好地解决这些功能。这项工作开发了一种低成本的灌注生物反应器系统,该系统允许将培养基连续灌注到细胞培养模块中,并在下游模块中分馏以测量这种规模的动态。该系统几乎完全由市售部件构成,可以并行化以同时在常规多孔细胞培养板中进行独立实验。本视频文章演示了如何组装基础设置,该设置只需要一个多通道注射器泵和一个改进的馏分收集器即可并行灌注多达六种培养物。还提出了模块化设计的有用变体,允许受控的刺激动力学,例如溶质脉冲或药代动力学样曲线。重要的是,当溶质信号通过系统时,它们会因溶质色散而失真。此外,还描述了一种使用MATLAB用示踪剂测量灌注装置组件的停留时间分布(RTD)的方法。RTD可用于计算多室系统中的流动如何使溶质信号失真。该系统非常坚固且可重复,因此基础研究人员可以轻松采用它,而无需专门的制造设施。
Introduction
许多重要的生物过程发生在细胞和组织培养物中,时间尺度为几分钟到几小时1,2,3。虽然可以使用延时显微镜4,生物发光1或其他方法以自动方式观察和记录其中一些现象,但涉及收集用于化学分析的培养物上清液样品的实验通常在静态细胞培养物中手动进行。由于频繁或下班后采样时间点的不便,手动采样限制了某些研究的可行性。静态培养方法的进一步缺点包括涉及受控的瞬时暴露于化学刺激的实验。在静态培养物中,必须手动添加和去除刺激,并且刺激曲线仅限于随时间的步进变化,而培养基的变化也会添加和去除其他培养基成分,这可能会以不受控制的方式影响细胞5。流体系统可以克服这些挑战,但现有设备带来了其他挑战。微流体装置伴随着专业设备和培训的生产和使用成本过高,需要微分析方法来处理样品,并且灌注后细胞难以从装置中回收6。对于这里描述的实验类型,很少有大流体系统7,8,9,10,并且它们由内部制造的多个定制部件组成,需要多个泵或馏分收集器。此外,作者不知道除了用于悬浮培养的搅拌罐生物反应器之外,任何市售的大流体灌注细胞培养系统,这些系统对生物制造有用,尽管不是为建模和研究生理学而设计的。
作者之前报告了低成本灌注生物反应器系统的设计,该系统几乎完全由市售部件11组成。该系统的基本版本使孔板中的多种培养物能够保存在CO2 培养箱中,并连续灌注来自注射器泵的培养基,而来自培养物的流出培养基流随着时间的推移使用具有定制修改的馏分收集器自动分馏到样品中。因此,该系统能够自动取样培养基上清液,并随着时间的推移连续地将溶质输入到培养物中。该系统是大流体和模块化的,可以很容易地修改,以满足新型实验设计的需要。
这里介绍的方法的总体目标是构建,表征和使用灌注细胞培养系统,该系统能够进行实验,其中测量细胞随时间推移的物质分泌或吸收速率,和/或细胞暴露于精确的瞬态溶质信号。本视频文章介绍了如何组装碱基设置,该设置能够使用单个注射器泵和改进的馏分收集器同时灌注多达六种细胞培养物。还介绍了基础系统上的两个有用变体,它们利用额外的泵和部件来允许将细胞暴露于瞬态溶质浓度信号的实验,包括短暂的脉冲和药代动力学样曲线12, 如图1所示。
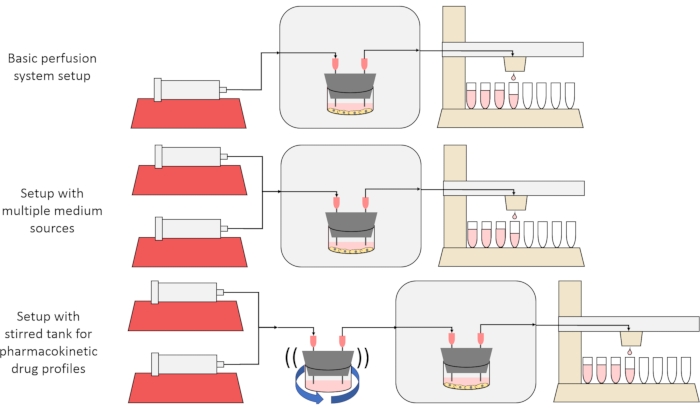
图1:灌注系统设计的三种变化 (顶部)基本灌注系统。(中)带有旋塞阀的灌注系统,用于多种介质来源。(底部)灌注系统带有搅拌罐,以模拟混合良好的分布体积。 请点击此处查看此图的大图。
由于流动中的色散和扩散,溶质信号在通过流动系统时会失真或“模糊”。这种失真可以通过使用停留时间分布(RTD)来量化13。本文介绍了如何对灌注系统的组件进行示踪剂实验(图 2),并提供 MATLAB 脚本来根据测量数据生成 RTD。关于这一分析的详细解释可以在作者之前的论文11中找到。附加的MATLAB脚本将适当的函数拟合到RTD并提取物理参数,并使用RTD执行信号卷积,以预测用户输入的溶质信号将如何通过灌注系统14传播和扭曲。
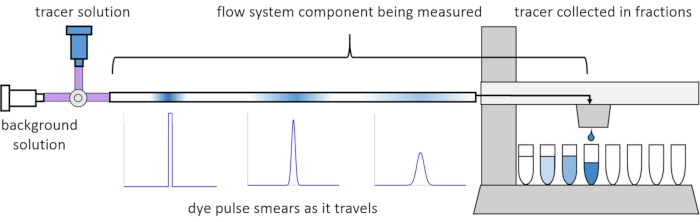
图 2:停留时间分布。 流量系统组件的RTD,例如这个长度的管道,是通过向系统输入示踪剂脉冲并测量它在退出收集的馏分时如何“涂抹”来测量的。这个数字是从埃里克森等人11修改而来的。 请点击此处查看此图的大图。
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
这项工作描述了具有多个培养基来源的灌注细胞培养系统的组装和操作,并展示了一个具体的例子,其中测量了NF-κB驱动的基因表达响应于TNF-α瞬时脉冲的动态。对灌注系统组分的RTD进行测量和建模,并使用信号卷积来预测细胞暴露于TNF-α脉冲和TNF-α在收集的流出介质中的分布。将细胞暴露于脉冲并收集分数40小时,之后在分数中测量GLuc并与预测的TNF-α信号一起绘制,以揭示刺激 – 反应动力学。<…
Divulgazioni
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
这项研究是在拨款号的支持下进行的。R01EB012521、R01EB028782 和 T32 GM008339 来自美国国立卫生研究院。
Materials
| 18 Gauge 1 1/2- in Disposable Probe Needle For Use With Syringes and Dispensing Machines | Grainger | 5FVK2 | |
| 293T Cells | ATCC | CRL-3216 | HEK 293T cells used in the Representative Results experiment. |
| 96-Well Clear Bottom Plates, Corning | VWR | 89091-010 | Plates for measuring dye concentrations in RTD experiments and GLuc in representative results experiment. |
| BD Disposable Syringes with Luer-Lok Tips, 5 mL | Fisher Scientific | 14-829-45 | |
| BioFrac Fraction Collector | Bio-Rad | 7410002 | Fraction collector that can be used for a single stream, or modified using our method to enable collection from multiple streams. |
| Clear High-Strength UV-Resistant Acrylic 12" x 12" x 1/8" | McMaster-Carr | 4615T93 | This sheet is cut using a laser cutter according to the DXF file in the supplemental materials to produce the multi-head dispenser that can be attached to the BioFrac fraction collector. |
| Coelenterazine native | NanoLight Technology | 303 | Substrate used in Gaussia luciferase bioluminescence assay in representative results. |
| Corning Costar TC-Treated Multiple Well Plates, size 48 wells, polystyrene plate, flat bottom wells | Millipore Sigma | CLS3548 | Used to grow and perfuse 293T cells in representative results. |
| Corning Costar Flat Bottom Cell Culture Plates, size 12 wells | Fisher Scientific | 720081 | Can be plugged and used as a stirred tank to produce pharmacokinetic profiles in perfusion. Can also contain cells for perfusion. |
| DMEM, high glucose | ThermoFisher Scientific | 11965126 | |
| Epilog Zing 24 Laser | Cutting Edge Systems | Epilog Zing 24 | Laser cutter used to produce multi-head dispenser from acrylic sheet. Other laser cutters may be used. |
| Fisherbrand Sterile Syringes for Single Use, Luer-Lock, 20 mL | Fisher Scientific | 14-955-460 | |
| Fisherbrand Sterile Syringes for Single Use, Luer-Lock, 60 mL | Fisher Scientific | 14-955-461 | |
| Fisherbrand Premium Microcentrifuge Tubes: 1.5mL | Fisher Scientific | 05-408-129 | Microcentrifuge tubes for collecting fractions. |
| Fisherbrand Round Bottom Disposable Borosilicate Glass Tubes with Plain End | Fisher Scientific | 14-961-26 | Glass tubes for collecting fractions. |
| Fisherbrand SureOne Micropoint Pipette Tips, Universal Fit, Non-Filtered | Fisher Scientific | 2707410 | 300 ul pipette tips that best fit the multi-head dispenser and tubing to act as dispensing tips. |
| Gibco DPBS, powder, no calcium, no magnesium | Fisher Scientific | 21600010 | Phosphate buffered saline. |
| Labline 4625 Titer Shaker | Marshall Scientific | Labline 4625 Titer Shaker | Orbital shaker used to keep stirred tanks mixed. |
| Masterflex Fitting, Polycarbonate, Four-Way Stopcock, Male Luer Lock, Non-Sterile; 10/PK | Cole-Parmer | EW-30600-04 | Used to join multiple inlet streams for RTD experiments and cell culture experiments. |
| Masterflex Fitting, Polycarbonate, Straight, Female Luer x Cap; 25/PK | Masterflex | UX-45501-28 | |
| Masterflex Fitting, Polypropylene, Straight, Female Luer to Hosebarb Adapters, 1/16" | Cole-Parmer | EW-45508-00 | |
| Masterflex Fitting, Polypropylene, Straight, Male Luer Lock to Hosebarb Adapter, 1/16" ID | Cole-Parmer | EW-45518-00 | |
| Masterflex Fitting, Polypropylene, Straight, Male Luer Lock to Plug Adapter; 25/PK | Masterflex | EW-30800-30 | |
| Masterflex L/S Precision Pump Tubing, Platinum-Cured Silicone, L/S 14; 25 ft | Masterflex | EW-96410-14 | |
| MATLAB | MathWorks | R2019b | Version R2019b. Newer versions may also be used. Some older versions may work. |
| NE-1600 Six Channel Programmable Syringe Pump | New Era Pump Systems | NE-1600 | |
| Rack Set F1 | Bio-Rad | 7410010 | Racks to hold collecting tubes in the fraction collector. |
| Recombinant Human TNF-alpha (HEK293-expressed) Protein, CF | Bio-Techne | 10291-TA-020 | Cytokine used to stimulate 293T cells in representative results. |
| Saint Gobain Solid Stoppers, Versilic Silicone, Size: 00, Bottom 10.5mm | Saint Gobain | DX263015-50 | Fits 48-well plates. |
| Saint Gobain Solid Stoppers, Versilic Silicone, Size: 4 Bottom 21mm | Saint Gobain | DX263027-10 | Fits 12-well plates. |
| Sodium Hydroxide, 10.0 N Aqueous Solution APHA; 1 L | Spectrum Chemicals | S-395-1LT | |
| SolidWorks | Dassault Systems | SolidWorks | CAD software used to create the multi-head dispenser DXF file. |
| Varioskan LUX multimode microplate reader | ThermoFisher Scientific | VL0000D0 | Plate reader. |
| Wilton Color Right Performance Color System Base Refill, Blue | Michaels | 10404779 | Blue food dye containing Brilliant Blue FCF, used as a tracer in RTD experiments. Absorbance spectrum peaks at 628 nm. |
Riferimenti
- Welsh, D. K., Yoo, S. H., Liu, A. C., Takahashi, J. S., Kay, S. A. Bioluminescence imaging of individual fibroblasts reveals persistent, independently phased circadian rhythms of clock gene expression. Current Biology. 14 (24), 2289-2295 (2004).
- Talaei, K., et al. A mathematical model of the dynamics of cytokine expression and human immune cell activation in response to the pathogen Staphylococcus aureus. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology. 11, 711153 (2021).
- Kemas, A. M., Youhanna, S., Zandi Shafagh, R., Lauschke, V. M. Insulin-dependent glucose consumption dynamics in 3D primary human liver cultures measured by a sensitive and specific glucose sensor with nanoliter input volume. FASEB Journal. 35 (3), 21305 (2021).
- Muzzey, D., van Oudenaarden, A. Quantitative time-lapse fluorescence microscopy in single cells. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology. 25, 301-327 (2009).
- Calligaro, H., Kinane, C., Bennis, M., Coutanson, C., Dkhissi-Benyahya, O. A standardized method to assess the endogenous activity and the light-response of the retinal clock in mammals. Molecular Vision. 26, 106-116 (2020).
- Battat, S., Weitz, D. A., Whitesides, G. M. An outlook on microfluidics: the promise and the challenge. Lab on a Chip. 22 (3), 530-536 (2022).
- Petrenko, V., Saini, C., Perrin, L., Dibner, C. Parallel measurement of circadian clock gene expression and hormone secretion in human primary cell cultures. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (117), e54673 (2016).
- Yamagishi, K., Enomoto, T., Ohmiya, Y. Perfusion-culture-based secreted bioluminescence reporter assay in living cells. Analytical Biochemistry. 354 (1), 15-21 (2006).
- Watanabe, T., et al. Multichannel perfusion culture bioluminescence reporter system for long-term detection in living cells. Analytical Biochemistry. 402 (1), 107-109 (2010).
- Murakami, N., Nakamura, H., Nishi, R., Marumoto, N., Nasu, T. Comparison of circadian oscillation of melatonin release in pineal cells of house sparrow, pigeon and Japanese quail, using cell perfusion systems. Brain Research. 651 (1-2), 209-214 (1994).
- Erickson, P., Houwayek, T., Burr, A., Teryek, M., Parekkadan, B. A continuous flow cell culture system for precision cell stimulation and time-resolved profiling of cell secretion. Analytical Biochemistry. 625, 114213 (2021).
- Saltzman, W. M. . Drug Delivery: Engineering Principles for Drug Therapy. , (2001).
- Fogler, H. S. . Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering. 4th edn. , (2006).
- Conesa, J. A. . Chemical Reactor Design: Mathematical Modeling and Applications. , (2019).
- Toson, P., Doshi, P., Jajcevic, D. Explicit residence time distribution of a generalised cascade of continuous stirred tank reactors for a description of short recirculation time (bypassing). Processes. 7 (9), 615 (2019).
- Tamayo, A. G., Shukor, S., Burr, A., Erickson, P., Parekkadan, B. Tracking leukemic T-cell transcriptional dynamics in vivo with a blood-based reporter assay. FEBS Open Biology. 10 (9), 1868-1879 (2020).
- Newell, B., Bailey, J., Islam, A., Hopkins, L., Lant, P. Characterising bioreactor mixing with residence time distribution (RTD) tests. Water Science and Technology. 37 (12), 43-47 (1998).
- Dubois, J., Tremblay, L., Lepage, M., Vermette, P. Flow dynamics within a bioreactor for tissue engineering by residence time distribution analysis combined with fluorescence and magnetic resonance imaging to investigate forced permeability and apparent diffusion coefficient in a perfusion cell culture chamber. Biotechnology and Bioengineering. 108 (10), 2488-2498 (2011).
- Gaida, L. B., et al. Liquid and gas residence time distribution in a two-stage bioreactor with cell recycle. HAL Open Science. , (2008).
- Rodrigues, M. E., Costa, A. R., Henriques, M., Azeredo, J., Oliveira, R. Wave characterization for mammalian cell culture: residence time distribution. New Biotechnology. 29 (3), 402-408 (2012).
- Olivet, D., Valls, J., Gordillo, M. A., Freixó, A., Sánchez, A. Application of residence time distribution technique to the study of the hydrodynamic behaviour of a full-scale wastewater treatment plant plug-flow bioreactor. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology. 80 (4), 425-432 (2005).

