<em> Xenopus의</em형광 측정으로> 난자 절개 바셀린 갭 전압 클램프 기술
Summary
절개 바셀린 갭 접근 방식은 빠른 채널 반응 속도의 높은 해상도와 Xenopus의 난자에서 발현 전압 – 의존성 이온 채널에서 이온 및 게이팅 전류의 낮은 잡음 녹음을 얻는 데 사용됩니다. 사소한 변형에, 전압 클램프 형광 측정은 절개 난자 프로토콜에 연결될 수있다.
Abstract
절개 난자 바셀린 갭 (COVG) 전압 클램프 기술은 난자의 이종 이온 채널의 전기 생리학과 운동 특성을 분석 할 수 있습니다. 절개 설정에서 녹음 낮은 크기의 게이트 전류, 빠른 이온 전류의 활성화 및 비활성화를 해결하는 데 특히 유용합니다. 두 전극 전압 클램프 (TEVC) 기법을 통해 주요 장점은 증가 된 클램프 속도, 개선 된 신호대 잡음비, 및 세포 내 및 세포 외 환경을 조절하는 능력을 포함한다.
여기서는 절개 설정 및 프로토콜뿐만 아니라 전압 클램프 형광 측정 기능을 추가하는 데 필요한 변형을 설명하기 위해, (HNA V 1.5), 아프리카 손톱 개구리의 난모 세포에서 발현 인간 심장 나트륨 채널을 이용한다.
이러한 HNA V 1.5 빨리 활성화 이온 채널의 특성은 완전히 whic에서 TEVC를 사용하여 상온 근처에 해결 될 수없는난자의 세포막의 시간 전체가 전압 제어가 어려워 고정된다. 그러나 절개 기술에서 세포막의 단지 작은 부분의 절연은 패치 클램프 기술과 연관된 채널 황폐 방지하면서 정확하게 빠른 반응 속도를 기록 할 필요 급속한 클램핑을 허용한다.
COVG 기술, 이온 채널 속도론 및 전기 생리 특성과 함께 추가로 단백질 움직임이 세포 외로 적용 형광체, 유전자에 의해 코딩 형광 단백질의 삽입 또는 부자연 아미노산의 혼입 시스테인 공액 통해 추적되는 전압 클램프 형광 측정을 사용하여 정량 할 수있다 관심 1의 영역으로. 이러한 추가적인 데이터는 형광 분자를 둘러싸는 미세 변화를 통한 단백질의 전압 의존성 구조적 재 배열 대해 운동 정보를 산출한다.
Introduction
특수 전압 클램핑 기술은 제어 된 막 전위에서 이온 전류의 기록을 허용한다. 널리 두 전극 전압 클램프 (TEVC)를 사용하고 패치 클램프 기술은 많은 이온 채널의 특성에 대한 신뢰성있는 전기 생리 정보를 제공한다. 그러나, 이러한 방법은 모두 빠른 전압 문 나트륨 채널과 같은 Xenopus의 난자의 세포막에있는 것과 같은 다른 빠른 활성화 채널에 대한 신뢰할 수있는 데이터의 취득을 방지 단점이 있습니다. Bezanilla과 스테파니 연구소는 따라서 난자 2의 절개 바셀린 갭 전압 클램프 기술 (COVG)를 개발했다. 기법은, 나 +, K +, 및 칼슘 2 + 채널 3-8을 기록 널리 적용되어왔다.
COVG 기록하는 동안, 이종 단백질 발현 난자의 막을 세 지역으로 나누어 져 있습니다. 이온 전류 데이터로서 난자의 상부 영역으로부터 기록된다정상 영역을 둘러싸 욕을 용이하고 신속하게 변경 될 수있는 명령 전위에 클램프된다. 중간 영역의 상부 영역 (9)과 동일한 전위에 클램프 됨으로써 누설 전류에 대하여 가드. 난자 개구 (절개) 사포닌 용액 또는 정맥의 사용을 통해 발생하는 위치를 하단 영역입니다. 화학적 또는 저부 영역에서 멤브레인의 수동 개방은 접지에 클램프 내부 전위의 제어를 허용하고, 하부 챔버 용액과 인접 셀 내부를 렌더링한다. 상부 챔버의 솔루션 교환이 외부 환경을 변경하는 반면 하부 챔버에 솔루션을 살포는 내부 환경의 특성을 조정할 수 있습니다. 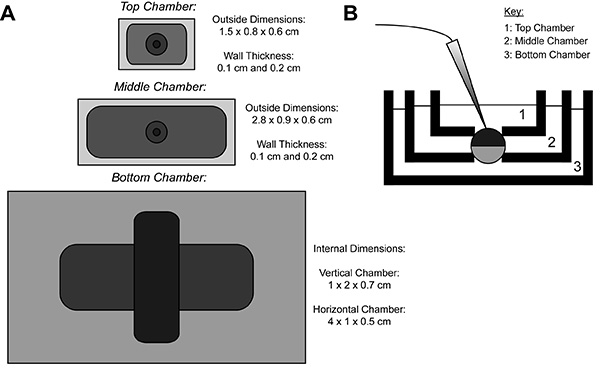
그림 1. 난자 절개 전압 클램프 욕실 설치 다이어그램. (A) 최고서로 분리 된 세 개의 화장실의 아래로보기. COVG의 챔버의 치수는 그림에 표시됩니다. (B) 테스트 위치에 화장실 설치의 측면보기. 더 큰 이미지를 보려면 여기를 클릭하십시오 .
COVG 기법의 이점은 낮은 전류 노이즈 (3 kHz에서 1 NA), 외부 미디어의 이온 조성, 내부 용지, 빠른 시간 해상도 (의 붕괴 20-100 마이크로 초 시간 상수를 조절하는 능력의 제어를 포함 용량이 과도), 몇 시간 9 안정 녹음. 단점은 특수 장비를 필요로하며 두 전극 전압 클램프 (TEVC) (10)에 비해 수행하기 더 어려운 것이있다.
COVG 접근 방식은 고도의 전문 장비와 복잡한 절차 적 요소가 필요하지만, 그것은 VALU의 인수를 허용 할 수 있습니다수 전기 생리학 데이터. 같은 빠른 반응 속도와 꼬리 전류 4 전류를 게이팅 등이 데이터는, 채널 런 다운 등 다른 전압 클램핑 프로토콜과 관련된 몇 가지 문제없이 녹음 할 수 있습니다. COVG 설정에 약간의 수정은 온도 조절기와 전압 클램프 형광 측정 (VCF)의 사용을 허용 할 수있다. COVG 조립체 내의 전압 클램프 형광 측정 요소의 포함은 동시에 현재 11-13을 촬영하면서 단백질 형태 적 변화를 모니터링하는 기능을 부여하여 데이터 출력을 증강 할 수있다.
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
절개 난자 바셀린 갭 전압 클램프 기술은 데이터의 신속한 해결이 가능, 낮은 노이즈, 상대적으로 긴 프로토콜 19을 통해 내부 솔루션 및 외부 용액 조성물을 제어하고, 안정된 레코딩을 증가했다. 이러한 장점 떨어져 표준 두 전극 전압 클램프 및 패치 클램프 기술에서이 기술을 설정합니다. 전문 장비가 필요하고 프로토콜이 상대적으로 어려운 있지만 시스템이 최적화되면, 아주 몇 가지…
Declarações
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
모든 세인트 루이스 심장 분자 공학 연구실에있는 워싱턴 대학의 구성원. 버로우즈는 과학 인터페이스에서 기금 경력 상을 오신 것을 환영합니다 – 1010299을 (JS에).
Materials
| External Solution | Brand | Catalog Number | [Final], weight, or volume |
| N-methyl-D-glucamine (NMDG) | Sigma-Aldrich | M2004 | 25mM |
| MES Sodium Salt | Sigma-Aldrich | M5057 | 90mM |
| HEPES | Research Products International | H75030 | 20mM |
| Calcium hydroxide | Sigma-Aldrich | 239232 | 2mM |
| MES Hydrate | Sigma-Aldrich | M8250 | variable (pH to 7.4) |
| Internal Solution | |||
| N-methyl-D-glucamine (NMDG) | Sigma-Aldrich | M2004 | 105mM |
| MES Sodium Salt | Sigma-Aldrich | M5057 | 10mM |
| HEPES | Research Products International | H75030 | 20mM |
| Ethylene glycol-bis(2-aminoethylether)-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid (EGTA) | Sigma-Aldrich | E4378 | 2mM |
| MES Hydrate | Sigma-Aldrich | M8250 | variable (pH to 7.4) |
| Depolarizing Solution | |||
| KCl | Sigma-Aldrich | 221473 | 110mM |
| Magnesium chloride | Sigma-Aldrich | M8266 | 1.5mM |
| Calcium Chloride | Caisson | C021 | 0.8mM |
| HEPES | Research Products International | H75030 | 10mM |
| Pipet Solution | |||
| KCl | Sigma-Aldrich | 221473 | 3M |
| Saponin Solution | |||
| Saponin | Sigma-Aldrich | 47036 | 0.125g |
| Internal Solution | See above | 50mL | |
| Agar Bridge Solution | |||
| N-methyl-D-glucamine (NMDG) | Sigma-Aldrich | M2004 | 100ml of 1M |
| HEPES | Research Products International | H75030 | 1.2g |
| MES Hydrate | Sigma-Aldrich | M8250 | variable (pH to 7.4) |
| Granulated Agar | Research Products International | A20250 | 3% |
| NMDG Storage Solution | |||
| NMDG, HEPES, MES Hydrate solution | see above | 40ml | |
| Water | 60ml | ||
| Name of Material/ Equipment | Company | Catalog Number | Comments/Description |
| High Performance Oocyte Clamp | Dagan | CA-1B | |
| Data Acquisition System | Axon CNS | Digidata 1440A | |
| Oscilloscope | Tektronix | TDS 210 | |
| Rack Power Filter | APC | G5 | |
| Heating/Cooling Bath Temperature Controller | Dagan | HCC-100A | |
| PC | Dell | Optiplex 990 | |
| pCLAMP 10.3 Voltage Clamp Software | Molecular Devices, LLC | pCLAMP10.3 | |
| TMC Vibration Control TableTop Platform | TMC | 64 SERIES | |
| TMC Vibration Control Air Table | TMC | 20 Series | |
| V1/I Electrode Data Collector | Dagan | part of CA-1B | |
| MX10L Micromanipulator | Siskiyou | MX10L | |
| Bath/Guard (I/V) Headstage (with appropriate connectors) | Dagan | part of CA-1B | |
| Microscope | Omano | OM2300S-JW11 | |
| Temperature Control Bath | Custom or Dagan | Custom or HE-204C | Custom chamber made from materials from Cool Polymers (D-series). Dagan also provides a prefeabricated stage (HE-204C). |
| Custom AgCl Pellet Container | Custom | Custom | Custom machined |
| Ag/AgCl electrode, pellet, 2.0 mm | Warner | E-206 | |
| External Oocyte Bath | Custom or Dagan | Custom or CC-1-T-LB | Custom machined or purchased from Dagan |
| Internal Oocyte Bath | Custom or Dagan | Custom or CC-TG-ND | Custom machined or purchased from Dagan |
| Capillaries for Agar Bridges and Pulled Electrodes | Warner | G150T-4 | |
| Rotatable Mounts for the Microscope, Micromanipulator, and Bath | Siskiyou | SD-1280P | |
| Fiber-Lite | Dolan-Jenner | LMI-600 | |
| Regular Bleach | Clorox | 470174-764 | |
| Xenopus laevis Oocytes | Nasco | LM535M (sexually mature females) | |
| 90 Na+ External Solution | See Solutions sheet | ||
| 10 Na+ Internal Solution | See Solutions sheet | ||
| 3 M KCL | See Solutions sheet | ||
| Saponin | Sigma-Aldrich | 47036 | |
| NMDG Storage Solution | See Solutions sheet | ||
| 5mL transfer pipets | SciMart | GS-52 | |
| Modified KCl electrode injector | BD | 309659 | Plastic syringe tip melted to allow for injection of solution into electrodes. Alternatively, a Microfil by WPI can be purchased. |
| Microvaccum | Custom | Custom | |
| Forceps | VWR | 63040-458 | |
| Oocyte Handling Tools (Pipette Pump) | VWR | 53502-222 | |
| Deionized Water Squirt Bottle | VWR | 16649-911 | |
| Vaseline Petroleum Jelly | Fisher Scientific | 19-086-291 | |
| Additional Materials Required for VCF Recordings: | |||
| VCF Microscope | Nikon | Eclipse FN1 | |
| Nikon CFI APO 40XW NIR Objective | Nikon | N40X-NIR | |
| X-Y Translator System for Fixed-Stage Upright Microscopes | Sutter Instruments | MT500-586 | |
| External VCF Oocyte Bath | Custom | Custom machined. The chamber dimensions are 2.7 x 1.9 x 0.4 cm. | |
| Internal VCF Oocyte Bath | Custom | Custom machined. The chamber dimensions are 1.6 x 1.6 x 0.4 cm. | |
| Modified Temperature Control Bath | Custom | Custom chamber made from materials from Cool Polymers (D-series). The chamber dimensions of the modified temperature controller bath are 2.7 x 1.9 x 0.3 cm for the horizontal chamber, and 1 x 2.5 x 0.5 cm for the vertical chamber. |
Referências
- Kalstrup, T., Blunck, R. Dynamics of internal pore opening in KV channels probed by a fluorescent unnatural amino acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110, 8272-8277 (2013).
- Stefani, E., Bezanilla, F. Cut-open oocyte voltage-clamp technique. Methods Enzymol. 293, 300-318 (1998).
- Muroi, Y., Chanda, B. Local anesthetics disrupt energetic coupling between the voltage-sensing segments of a sodium channel. J. Gen. Physiol. 133, 1-15 (2009).
- Stefani, E., Toro, L., Perozo, E., Bezanilla, F. Gating of Shaker K+ channels: I. Ionic and gating currents. Biophys. J. 66, 996-1010 (1994).
- Wang, S., Liu, S., Morales, M. J., Strauss, H. C., Rasmusson, R. L. A quantitative analysis of the activation and inactivation kinetics of HERG expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J. Physiolt. 502 (Pt 1), 45-60 (1997).
- Neely, A., Garcia-Olivares, J., Voswinkel, S., Horstkott, H., Hidalgo, P. Folding of active calcium channel beta(1b) -subunit by size-exclusion chromatography and its role on channel function. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 21689-21694 (2004).
- Silva, J. R., Goldstein, S. A. Voltage-sensor movements describe slow inactivation of voltage-gated sodium channels I: wild-type skeletal muscle. Na(V)1.4. J. Gen. Physiol. 141, 309-321 (2013).
- Silva, J. R., Goldstein, S. A. Voltage-sensor movements describe slow inactivation of voltage-gated sodium channels II: a periodic paralysis mutation in Na(V)1.4 (L689I). J. Gen. Physiol. 141, 323-334 (2013).
- Taglialatela, M., Toro, L., Stefani, E. Novel voltage clamp to record small, fast currents from ion channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Biophys. J. 61, 78-82 (1992).
- Clare, J. J., Trezise, D. J. . Expression and analysis of recombinant ion channels : from structural studies to pharmacological screening. , (2006).
- Cha, A., Zerangue, N., Kavanaugh, M., Bezanilla, F., Susan, G. A. . Methods in enzymology. 296, 566-578 (1998).
- Lakowicz, J. R. . Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy. 3rd edn. , (2006).
- Cha, A., Bezanilla, F. Characterizing voltage-dependent conformational changes in the Shaker K+ channel with fluorescence. Neuron. 19, 1127-1140 (1997).
- Richards, R., Dempski, R. E. Examining the conformational dynamics of membrane proteins in situ with site-directed fluorescence labeling. J. Vis. Exp. , (2011).
- Cohen, S., Au, S., Pante, N. Microinjection of Xenopus laevis oocytes. J. Vis. Exp. , (2009).
- Raynauld, J. P., Laviolette, J. R. The silver-silver chloride electrode: a possible generator of offset voltages and currents. J. Neurosci. Methods. 19, 249-255 (1987).
- Gagnon, D. G., Bissonnette, P., Lapointe, J. Y. Identification of a disulfide bridge linking the fourth and the seventh extracellular loops of the Na+/glucose cotransporter. J. Gen. Physiol. 127, 145-158 (2006).
- Pantazis, A., Olcese, R., Roberts, G. . Cut-Open Oocyte Voltage-Clamp Technique. In: Roberts G. (Ed.) Encyclopedia of Biophysics: SpringerReference. , (2013).

