ザ·<em>アフリカツメガエル</em蛍光測定で>卵母細胞のカットオープンワセリンギャップ電圧クランプ法
Summary
カットオープンワセリンギャップアプローチは、高速チャネル動態の高解像度で、アフリカツメガエル卵母細胞で発現電位依存性イオンチャネルからのイオンおよびゲート電流の低ノイズの録音を得るために使用される。マイナーな変更を加えて、電圧クランプ蛍光法は、カットオープン卵母プロトコルに結合することができる。
Abstract
カットオープン卵母ワセリンギャップ(COVG)電圧クランプ技術は、卵母細胞における異種イオンチャネルの電気生理学的および動力学的特性の分析を可能にする。カットオープンセットアップからの記録は、低振幅ゲート電流、急速なイオン電流の活性化、および非アクティブ化を解決するために特に有用である。 2電極電圧クランプ(TEVC)技術上の主な利点は、増加したクランプ速度、改善された信号対雑音比、および細胞内および細胞外環境を調節する能力が挙げられる。
ここでは、人間の心臓のナトリウムチャネル(HNA V 1.5)を採用し、切り開い設定やプロトコルだけでなく、電圧クランプ蛍光測定機能を追加するために必要な変更を示すために、 アフリカツメガエル卵母細胞で発現。
このようなHNA V 1.5の速度で活性化イオンチャネルの特性は、完全にwhicで、TEVCを用いて室温付近では解決できないhは、卵母細胞膜の全体が電圧制御を困難にクランプされる。しかしながら、カットオープン技術では、細胞膜の小部分のみの単離は、パッチクランプ技術に関連するチャネルランダウンを防止しつつ、正確に速い反応速度を記録するために必要な迅速な締付けを可能にする。
COVG法、イオンチャネル動態及び電気生理学的特性に関連してさらにタンパク質の動きが細胞外に適用さフルオロフォア、遺伝的にコード化された蛍光タンパク質の挿入、または非天然アミノ酸の組込みのシステインコンジュゲーションを介して追跡される電圧クランプ蛍光法を用いてアッセイすることができる関心1の領域へ。この追加データは、蛍光分子を取り巻く微小環境の変化を介してタンパク質の電位依存性のコンホメーションの再編成についての速度論的な情報が得られます。
Introduction
特殊な電圧クランプ技法を制御膜電位におけるイオン電流の記録を可能にする。広く使用される2つの電極電圧クランプ(TEVC)およびパッチクランプ技術は、多くのイオンチャネルの電気生理学的特性に関する信頼できる情報を提供する。しかしながら、これらの方法の両方は、高速電位依存性ナトリウムチャネルおよびアフリカツメガエル卵母細胞のもののような膜における他の高速活性化チャネルに対する信頼性のあるデータの取得を妨げる欠点を有する。 Bezanillaとステファニー·ラボラトリーズは、結果的に卵母細胞2のカットのオープンワセリンギャップ電圧クランプ法(COVG)を開発しました。技術をNa +、K +、およびCa 2 +チャネル3-8を記録するために広く適用されている。
COVG記録中に、異種タンパク質を発現する卵母細胞膜は、3つの領域に分割されている。イオン電流のデータは次のように卵母細胞の上部領域から記録されている上部領域を取り囲む浴を容易かつ迅速に変更することができるコマンド電位にクランプされる。中間領域の頂部領域9と同電位にクランプされることにより、リーク電流を保護します。卵母細胞開度(カットオープン)サポニン溶液またはカニューレの使用を介して発生する場所底部領域である。化学的または底部領域での膜のマニュアル開はグランドにクランプされた内部電位の制御を可能にし、下部チャンバ溶液で細胞内部の連続をレンダリングする。上部チャンバー内の溶液交換は、外部環境を変えるのに対して、下室への解決策の灌流は、内部環境の特性を調整することができます。 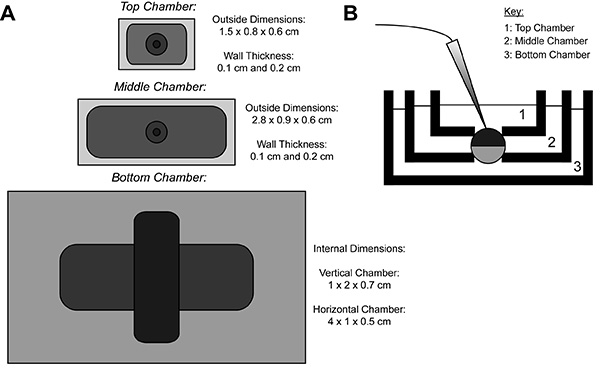
図1。卵母細胞のカット開放電圧クランプバースセットアップ図(A)トップ互いから分離された3つの浴のダウン図である。 COVG用チャンバーの寸法は、図に表示されます。 (B)試験位置にある風呂セットアップの側面図。 拡大画像を表示するには、ここをクリックしてください 。
COVG技術の利点は、低電流ノイズ(3 kHzでは1nA)、外部媒体のイオン組成、内部メディア、高速時間分解能(の減衰20-100秒の時定数を調節する能力の制御を含む容量過渡)、数時間9安定した録音。欠点は、それが特殊な装置を必要とし、2つの電極電圧クランプ(TEVC)10と比較して行うことはより困難であることである。
COVGアプローチは非常に特殊な装置や複雑な手順要素が必要ですが、それは貴重の取得を可能にすることができることができ、電気生理学的データ。このような高速の動態およびテール電流4に電流をゲートするように、このデータは、チャネルランダウンを含め、他の電圧クランププロトコルに関連する問題のいくつかがなく記録することができます。 COVGのセットアップへの軽微な変更は、温度コントローラと電圧クランプ蛍光法(VCF)の使用を可能にすることができる。 COVGアセンブリ内の電圧クランプ蛍光測定要素を含めることは、同時に、現在の11-13を記録しながら、タンパク質コンホメーション変化を監視する機能を付与することによりデータ出力を増大させることができる。
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
カットオープン卵母細胞ワセリンギャップ電圧クランプ法は、データの迅速な解決を可能にし、低ノイズで、比較的長いプロトコル19に係る内部液と外液組成を制御し、安定した録画を増加させた。これらの利点は別として標準の2電極電圧クランプおよびパッチクランプ技術から、この手法を設定してください。特殊な装置が必要であり、プロトコルが比較的困難であるされていま?…
Declarações
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
セントルイス心臓分子工学研究所のワシントン大学のすべてのメンバー。 (JSに)1010299 – バロウズは科学的なインターフェイスで、基金のキャリア賞を歓迎します。
Materials
| External Solution | Brand | Catalog Number | [Final], weight, or volume |
| N-methyl-D-glucamine (NMDG) | Sigma-Aldrich | M2004 | 25mM |
| MES Sodium Salt | Sigma-Aldrich | M5057 | 90mM |
| HEPES | Research Products International | H75030 | 20mM |
| Calcium hydroxide | Sigma-Aldrich | 239232 | 2mM |
| MES Hydrate | Sigma-Aldrich | M8250 | variable (pH to 7.4) |
| Internal Solution | |||
| N-methyl-D-glucamine (NMDG) | Sigma-Aldrich | M2004 | 105mM |
| MES Sodium Salt | Sigma-Aldrich | M5057 | 10mM |
| HEPES | Research Products International | H75030 | 20mM |
| Ethylene glycol-bis(2-aminoethylether)-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid (EGTA) | Sigma-Aldrich | E4378 | 2mM |
| MES Hydrate | Sigma-Aldrich | M8250 | variable (pH to 7.4) |
| Depolarizing Solution | |||
| KCl | Sigma-Aldrich | 221473 | 110mM |
| Magnesium chloride | Sigma-Aldrich | M8266 | 1.5mM |
| Calcium Chloride | Caisson | C021 | 0.8mM |
| HEPES | Research Products International | H75030 | 10mM |
| Pipet Solution | |||
| KCl | Sigma-Aldrich | 221473 | 3M |
| Saponin Solution | |||
| Saponin | Sigma-Aldrich | 47036 | 0.125g |
| Internal Solution | See above | 50mL | |
| Agar Bridge Solution | |||
| N-methyl-D-glucamine (NMDG) | Sigma-Aldrich | M2004 | 100ml of 1M |
| HEPES | Research Products International | H75030 | 1.2g |
| MES Hydrate | Sigma-Aldrich | M8250 | variable (pH to 7.4) |
| Granulated Agar | Research Products International | A20250 | 3% |
| NMDG Storage Solution | |||
| NMDG, HEPES, MES Hydrate solution | see above | 40ml | |
| Water | 60ml | ||
| Name of Material/ Equipment | Company | Catalog Number | Comments/Description |
| High Performance Oocyte Clamp | Dagan | CA-1B | |
| Data Acquisition System | Axon CNS | Digidata 1440A | |
| Oscilloscope | Tektronix | TDS 210 | |
| Rack Power Filter | APC | G5 | |
| Heating/Cooling Bath Temperature Controller | Dagan | HCC-100A | |
| PC | Dell | Optiplex 990 | |
| pCLAMP 10.3 Voltage Clamp Software | Molecular Devices, LLC | pCLAMP10.3 | |
| TMC Vibration Control TableTop Platform | TMC | 64 SERIES | |
| TMC Vibration Control Air Table | TMC | 20 Series | |
| V1/I Electrode Data Collector | Dagan | part of CA-1B | |
| MX10L Micromanipulator | Siskiyou | MX10L | |
| Bath/Guard (I/V) Headstage (with appropriate connectors) | Dagan | part of CA-1B | |
| Microscope | Omano | OM2300S-JW11 | |
| Temperature Control Bath | Custom or Dagan | Custom or HE-204C | Custom chamber made from materials from Cool Polymers (D-series). Dagan also provides a prefeabricated stage (HE-204C). |
| Custom AgCl Pellet Container | Custom | Custom | Custom machined |
| Ag/AgCl electrode, pellet, 2.0 mm | Warner | E-206 | |
| External Oocyte Bath | Custom or Dagan | Custom or CC-1-T-LB | Custom machined or purchased from Dagan |
| Internal Oocyte Bath | Custom or Dagan | Custom or CC-TG-ND | Custom machined or purchased from Dagan |
| Capillaries for Agar Bridges and Pulled Electrodes | Warner | G150T-4 | |
| Rotatable Mounts for the Microscope, Micromanipulator, and Bath | Siskiyou | SD-1280P | |
| Fiber-Lite | Dolan-Jenner | LMI-600 | |
| Regular Bleach | Clorox | 470174-764 | |
| Xenopus laevis Oocytes | Nasco | LM535M (sexually mature females) | |
| 90 Na+ External Solution | See Solutions sheet | ||
| 10 Na+ Internal Solution | See Solutions sheet | ||
| 3 M KCL | See Solutions sheet | ||
| Saponin | Sigma-Aldrich | 47036 | |
| NMDG Storage Solution | See Solutions sheet | ||
| 5mL transfer pipets | SciMart | GS-52 | |
| Modified KCl electrode injector | BD | 309659 | Plastic syringe tip melted to allow for injection of solution into electrodes. Alternatively, a Microfil by WPI can be purchased. |
| Microvaccum | Custom | Custom | |
| Forceps | VWR | 63040-458 | |
| Oocyte Handling Tools (Pipette Pump) | VWR | 53502-222 | |
| Deionized Water Squirt Bottle | VWR | 16649-911 | |
| Vaseline Petroleum Jelly | Fisher Scientific | 19-086-291 | |
| Additional Materials Required for VCF Recordings: | |||
| VCF Microscope | Nikon | Eclipse FN1 | |
| Nikon CFI APO 40XW NIR Objective | Nikon | N40X-NIR | |
| X-Y Translator System for Fixed-Stage Upright Microscopes | Sutter Instruments | MT500-586 | |
| External VCF Oocyte Bath | Custom | Custom machined. The chamber dimensions are 2.7 x 1.9 x 0.4 cm. | |
| Internal VCF Oocyte Bath | Custom | Custom machined. The chamber dimensions are 1.6 x 1.6 x 0.4 cm. | |
| Modified Temperature Control Bath | Custom | Custom chamber made from materials from Cool Polymers (D-series). The chamber dimensions of the modified temperature controller bath are 2.7 x 1.9 x 0.3 cm for the horizontal chamber, and 1 x 2.5 x 0.5 cm for the vertical chamber. |
Referências
- Kalstrup, T., Blunck, R. Dynamics of internal pore opening in KV channels probed by a fluorescent unnatural amino acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110, 8272-8277 (2013).
- Stefani, E., Bezanilla, F. Cut-open oocyte voltage-clamp technique. Methods Enzymol. 293, 300-318 (1998).
- Muroi, Y., Chanda, B. Local anesthetics disrupt energetic coupling between the voltage-sensing segments of a sodium channel. J. Gen. Physiol. 133, 1-15 (2009).
- Stefani, E., Toro, L., Perozo, E., Bezanilla, F. Gating of Shaker K+ channels: I. Ionic and gating currents. Biophys. J. 66, 996-1010 (1994).
- Wang, S., Liu, S., Morales, M. J., Strauss, H. C., Rasmusson, R. L. A quantitative analysis of the activation and inactivation kinetics of HERG expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J. Physiolt. 502 (Pt 1), 45-60 (1997).
- Neely, A., Garcia-Olivares, J., Voswinkel, S., Horstkott, H., Hidalgo, P. Folding of active calcium channel beta(1b) -subunit by size-exclusion chromatography and its role on channel function. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 21689-21694 (2004).
- Silva, J. R., Goldstein, S. A. Voltage-sensor movements describe slow inactivation of voltage-gated sodium channels I: wild-type skeletal muscle. Na(V)1.4. J. Gen. Physiol. 141, 309-321 (2013).
- Silva, J. R., Goldstein, S. A. Voltage-sensor movements describe slow inactivation of voltage-gated sodium channels II: a periodic paralysis mutation in Na(V)1.4 (L689I). J. Gen. Physiol. 141, 323-334 (2013).
- Taglialatela, M., Toro, L., Stefani, E. Novel voltage clamp to record small, fast currents from ion channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Biophys. J. 61, 78-82 (1992).
- Clare, J. J., Trezise, D. J. . Expression and analysis of recombinant ion channels : from structural studies to pharmacological screening. , (2006).
- Cha, A., Zerangue, N., Kavanaugh, M., Bezanilla, F., Susan, G. A. . Methods in enzymology. 296, 566-578 (1998).
- Lakowicz, J. R. . Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy. 3rd edn. , (2006).
- Cha, A., Bezanilla, F. Characterizing voltage-dependent conformational changes in the Shaker K+ channel with fluorescence. Neuron. 19, 1127-1140 (1997).
- Richards, R., Dempski, R. E. Examining the conformational dynamics of membrane proteins in situ with site-directed fluorescence labeling. J. Vis. Exp. , (2011).
- Cohen, S., Au, S., Pante, N. Microinjection of Xenopus laevis oocytes. J. Vis. Exp. , (2009).
- Raynauld, J. P., Laviolette, J. R. The silver-silver chloride electrode: a possible generator of offset voltages and currents. J. Neurosci. Methods. 19, 249-255 (1987).
- Gagnon, D. G., Bissonnette, P., Lapointe, J. Y. Identification of a disulfide bridge linking the fourth and the seventh extracellular loops of the Na+/glucose cotransporter. J. Gen. Physiol. 127, 145-158 (2006).
- Pantazis, A., Olcese, R., Roberts, G. . Cut-Open Oocyte Voltage-Clamp Technique. In: Roberts G. (Ed.) Encyclopedia of Biophysics: SpringerReference. , (2013).

