גילוי גליקוגן בתאי הדם היקפי mononuclear עם תקופתי חומצה שיף מכתים
Summary
Periodic acid Schiff staining is a technique that visualizes the polysaccharide content of tissues. This article demonstrates periodic acid Schiff staining protocol adapted for use on peripheral blood mononuclear cells purified from human venous blood. Such samples are enriched for lymphocytes and other white blood cells of the immune system.
Abstract
Periodic acid Schiff (PAS) staining is an immunohistochemical technique used on muscle biopsies and as a diagnostic tool for blood samples. Polysaccharides such as glycogen, glycoproteins, and glycolipids stain bright magenta making it easy to enumerate positive and negative cells within the tissue. In muscle cells PAS staining is used to determine the glycogen content in different types of muscle cells, while in blood cell samples PAS staining has been explored as a diagnostic tool for a variety of conditions. Blood contains a proportion of white blood cells that belong to the immune system. The notion that cells of the immune system possess glycogen and use it as an energy source has not been widely explored. Here, we describe an adapted version of the PAS staining protocol that can be applied on peripheral blood mononuclear immune cells from human venous blood. Small cells with PAS-positive granules and larger cells with diffuse PAS staining were observed. Treatment of samples with amylase abrogates these patterns confirming the specificity of the stain. An alternate technique based on enzymatic digestion confirmed the presence and amount of glycogen in the samples. This protocol is useful for hematologists or immunologists studying polysaccharide content in blood-derived lymphocytes.
Introduction
שיף צביעת חומצה תקופתית (PAS) היא טכניקה immunohistochemical כי נעשתה שימוש נרחב במחקר שריר ואבחון. כמו כן הוא משמש ככלי אבחון בדגימות דם. הטכניקה עובדת על ידי יישום פתרון חומצה תקופתי למדגם, אשר מתחמצן יחידות בתוך קבוצות אלדהיד פוליסכריד יצירת המגיבות עם המגיב של שיף חסר הצבע וכך לייצר מוצר מגנטה עמוק. צעדיו של נוהל זה מוצגים באיור 1. הכתם הופך כל דבר עם מגנט רב-סוכרים, כולל גליקוגן, גליקופרוטאינים, glycolipids, mucins, או מולקולות אחרות עם moieties פוליסכריד.
צביעת PAS משמשת לעתים קרובות כדי למדוד את רמות הגליקוגן בסיבי שריר. חלקי רקמות שרירים הם אידיאליים עבור הטכניקה כמו שהם מייחסים היטב לשקופית ולעמוד שלבי כביסה וצביעה מרובים. גליקוגן הוא ההווה ביותר בעווית מהירה סוג II סיבי שריר, שבו יש ביקוש גבוהלייצור ATP מהיר הדורש גליקוגן ל1,2 ביצועים מרבי. גליקוגן הוא פולימר מסועף של גלוקוז שיכול להיות שבור לגלוקוז החופשי דרך הפעולה של אנזימי phosphorylase הגליקוגן. בימים של מנוחה ותזונה-הסתפקות, גליקוגן מתחדש בתהליך של גליקוגנזה, ואילו בתקופות של ביקוש אי ספיקה או אנרגיה גבוהה תזונתי; גליקוגן מתפרק לגלוקוז על ידי "גליקוגנוליסיס". ממוקדם ככל 1950 מדעני קלינאי בחנו צביעת PAS על דגימות דם כדי לנתח תוכן גליקוגן במחלות שונות 3-7. לדוגמא, במחלת-אחסון גליקוגן bonafide Pompe תאי דם לבנים disease- לצבור כמויות גדולות של גליקוגן ששונה באופן משמעותי מנבדקי ביקורת בריאים 8.
וידאו-מאמר זה מדגים גרסה מותאמת של מכתים PAS לשימוש בתאי הדם היקפי mononuclear (PBMC) דגימות מהדם ורידים של בני אדם בריאים. PBMCs מכיל בעיקר לימפוציטים של הלימפוציטים T ומשפחות הלימפוציטים B, כמו גם תאים חיסוניים אחרים, כגון תאי הרג טבעיים ומונוציטים. הצעד הראשון לטיהור מסיר אריתרוציטים, נויטרופילים, וגרנולוציטים אחרים. טכניקה זו מספקת נתונים על שיעור מרוכז של לימפוציטים מסוג המאפשר לספירה חזקה יותר של תאי PAS-חיובי בהשוואה לשימוש במשטחי דם כולה.
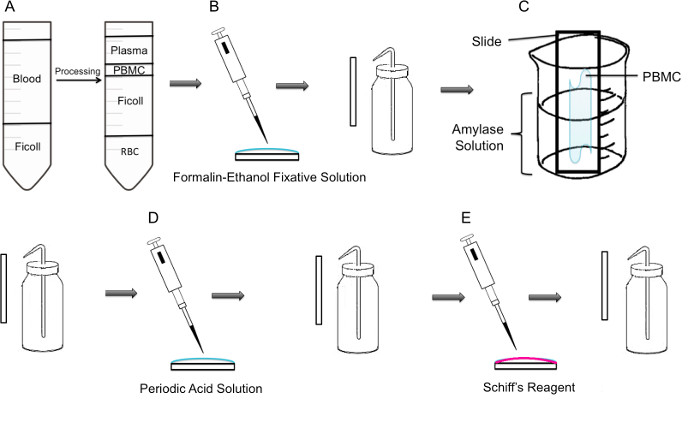
איור 1:. צעד אחר צעד המתודולוגיה של מכתים PAS על PBMC () ראשית, בידוד של PBMC מושגת באמצעות שיפוע ficoll, הלוח השמאלי מציג את ההכנה לפני צנטריפוגה, הפנל הימני מראה את זה אחרי צנטריפוגה בי המעיל באפי המכיל את PBMC הוא ציין במרכז של הצינור. PBMCs מבודדת (ב ') הם קבועים לשקופית באמצעות solu מקבע פורמלין-אתנולtion. השקופיות היא שטפו בעדינות עם מים מזוקקים מבקבוק פלסטיק לשטוף. (C) השקופית ממוקמת אז במחצית דרך 100 מיליליטר כוס מלאה פתרון עמילאז, שיתמוסס גליקוגן. השקופיות היא שטפו בעדינות. הוא טיפל (D) השקופיות עם פתרון חומצה תקופתי, שבו חמצון של סוכרים מתרחש. שקופיות הם שטופים בעדינות; זה יסיר את החומצה התקופתית העודפת ולעצור את צעד החמצון. (E) כאשר מגיב שיף מתווסף לשקופיות, זה יגיב עם אלדהידים נוצרו במהלך שלב החמצון. אז מגיב חסר צבע זה יגרום מוצר מגנטה אדום עמוק. שקופיות הם שטופים בעדינות כדי להסיר את מגיב שיף העודף.
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
השלבים הקריטיים של מאמר זה וידאו היו במהלך טיפול כביסה ועמילאז של התאים. בזמן שטיפת השקופיות, צעד מפתח השתמש בבקבוק שטיפת סָחִיט פלסטיק ולתת את המים בעדינות להפעיל באמצעות המדגם בשקופית ולא מכוון ישירות על הדגימות. אפילו לחץ המים ישיר הקל היה לגרום לתאים לרדת שקופיו?…
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a grant from the NSERC Discovery program grant number RGPIN 418522-2013. We thank R. Kilgour for helpful discussions, and Katelin Gresty and Dr. A. Berghdal for providing the mouse muscle sections.
Materials
| Periodic Acid Shiff Kit | Sigma-Aldrich | 395B | Bring to room temperature prior to use. Materials in this kit are toxic and harmful. Use caution http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/sigma/395b?lang=en®ion=CA |
| α-Amylase from porcine pancreas | Sigma-Aldrich | A3176 | http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/sigma/a3176?lang=en®ion=CA |
| Binocular Microscope | Carl Zeiss Microscopy | Axio Lab A0 | |
| Glycogen Assay Kit | Sigma-Aldrich | MAK016 | http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/sigma/mak016?lang=en®ion=CA |
| Ficoll-Paque PLUS | VWR, GE Healthcare | 17-1440-02 | Nonionic synthetic polymer of sucrose https://us.vwr.com/store/catalog/product.jsp?product_id=4779441 |
| Centrifuge | For PBMC isolation, swing buckets were used |
References
- Rich, P. R. The molecular machinery of keilin’s respiratory chain. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 31 (Pt 6), 1095-1105 (2003).
- Peter, J. B., Barnard, R. J., Edgerton, V. R., Gillespie, C. A., Stempel, K. E. Metabolic profiles of three fiber types of skeletal muscle in guinea pigs and rabbits). Biochemistry. 11 (14), 2627-2633 (1972).
- Jones, R. V., Goffi, G. P., Hutt, M. S. R. Lymphocyte glycogen content in various disease. J. Clin. Pathol. 15 (1), 36-39 (1962).
- Scott, R. B. Glycogen in human peripheral blood leukocytes. I. characteristics of the synthesis and turnover of glycogen in vitro. J. Clin. Invest. 47 (2), 344-352 (1968).
- Fedele, D., et al. positive index of lymphocytes and metabolic control in insulin-treated and type II diabetes mellitus. Diabete Metab. 9 (3), 188-192 (1983).
- Brelińska-Peczalska, R., Mackiewicz, S. Cytochemical studies of peripheral blood granulocytes and lymphocytes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Pol.Med.Sci.Hist.Bull. 15 (2), 231-234 (1976).
- Yunis, A. A., Arimura, G. K. Enzymes of glycogen metabolism in white blood cells. I. glycogen phosphorylase in normal and leukemic human leukocytes. Cancer, Res. 24, 489-492 (1964).
- Hagemans, M. L., et al. PAS-positive lymphocyte vacuoles can be used as diagnostic screening test for pompe disease. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 33 (2), 133-139 (2010).
- Totsuka, Y., et al. Physical performance and soleus muscle fiber composition in wild-derived and laboratory inbred mouse strains. 95 (2), 720-727 (2003).
- Murat, J. C., Serfaty, A. Simple enzymatic determination of polysaccharide (glycogen) content of animal tissues. Clin. Chem. 20 (12), 1576-1577 (1974).
- Arrizabalaga, O., Lacerda, H. M., Zubiaga, A. M., Zugaza, J. L. Rac1 protein regulates glycogen phosphorylase activation and controls interleukin (IL)-2-dependent T cell proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 287 (15), 11878-11890 (2012).
- Pelletier, J., G, J., Mazure, N. M. Biochemical titration of glycogen in vitro. J.Vis.Exp. (81), (2013).
- Roach, P. J., Depaoli-Roach, A. A., Hurley, T. D. Tagliabracci V.S. Glycogen and its metabolism: Some new developments and old themes. Biochem.J. 441 (3), 763-787 (2012).
- Salmoral, E. M., Tolmasky, D. S., Krisman, C. R. Evidence for the presence of glycogen in rat thymus. Cell Mol.Biol. 36 (2), 163-174 (1990).
- Darlington, P. J., et al. Diminished Th17 (not Th1) responses underlie multiple sclerosis disease abrogation after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Ann.Neurol. 73 (3), 341-354 (2013).

