שימוש של assay רמזי כדי למדוד את הפרשת נוזלים ויון שטף מחירים ב<em> תסיסנית melanogaster</em> אבובית Malpighian
Summary
פרוטוקול זה מתאר את השימוש של assay רמזי למדידת שיעורי הפרשת נוזל מצינוריות Malpighian (כליות) מבודדות מmelanogaster תסיסנית. בנוסף, השימוש באלקטרודות יון ספציפי למדידת ריכוזי נתרן ואשלגן בנוזל המופרש, המאפשר חישוב של שטף יון transepithelial, מתואר.
Abstract
אפנון של תחבורת יון אפיתל כליות מאפשר אורגניזמים לשמור על הומאוסטזיס יוני והאוסמוטי בפרצוף של משתנה תנאים חיצוניים. אבובית דרוזופילה melanogaster Malpighian (כליות) מציעה הזדמנות שאין כמותו כדי לחקור את המנגנונים המולקולריים של תחבורת יון אפיתל, בשל הגנטיקה החזקה של האורגניזם הזה ואת הנגישות של tubules הכליות שלה למחקר פיסיולוגי. כאן, אנו מתארים את השימוש של assay רמזי למדידת שיעורי הפרשת נוזל מtubules הכליות לטוס מבודד, עם השימוש באלקטרודות יון ספציפי למדידת ריכוזי נתרן ואשלגן בנוזל המופרש. assay זה מאפשר לימוד והנתיבים נוזל transepithelial ויון של ~ 20 tubules בזמן, ללא הצורך להעביר את הנוזל המופרש למנגנון נפרד למדידת ריכוזי יון. מבחינה גנטית ניתן לנתח tubules השונה כדי להעריך את התפקיד של גנים ספציפיים בתהליכי הובלה. בנוסף, במלוח athing יכול להיות שונה כדי לבחון את ההשפעות של מאפייניו הכימיים, או תרופות או הורמונים הוסיפו. לסיכום, טכניקה זו מאפשרת האפיון המולקולרי של מנגנונים בסיסיים של תחבורת אפיתל יון באבובית דרוזופילה, כמו גם הסדרת מנגנוני תחבורה אלה.
Introduction
תחבורת יון אפיתל כליות בבסיס iono- האורגניזם וויסות האוסמוטי. אבובית דרוזופילה melanogaster Malpighian (כליות) מציעה הזדמנות שאין כמותו כדי לחקור את המנגנונים המולקולריים של תחבורת יון אפיתל. זאת בשל השילוב של הגנטיקה החזקה של דרוזופילה, יחד עם הנגישות של tubules הכליות שלה למחקר פיסיולוגי. Assay ראמזי, על שמו של החוקר שהיה חלוץ טכניקת 1, מודד שיעורי הפרשת נוזל מצינוריות Malpighian מבודדות, והוקם בשנת 1994 על ידי תסיסנית דאו ועמיתים 2. זה סלל את הדרך למחקרים נוספים באמצעות תסיסנית כלים גנטיים, כגון מערכת GAL4-כטב"מ 3,4, להגדיר מסלולי איתות תא ספציפי המסדירים את הפרשת נוזלים. דוגמא כוללת איתות סידן בתגובה להורמון פפטיד 5, בקרב רבים אחרים 6,7.
ve_content "> שילוב של טכניקות גנטיות ומחקר פיסיולוגי קלאסי הוכיח כי דור שתן בזבוב מתרחש באמצעות ההפרשה של נוזל כלוריד-עשיר אשלגן מהמגזר העיקרי של אבובית. זו מתרחשת באמצעות הפרשת transepithelial המקבילה של קטיונים, בעיקר K + אלא גם Na +, דרך התא העיקרי, וCl -. ההפרשה דרך תא stellate 8-12 היכולת למדוד בנפרד והנתיבים transepithelial K + וNa + מאפשרת אפיון מפורט יותר של מנגנוני תחבורה מאשר המדידה של הפרשת נוזל יש לבד. לדוגמא, בtubules תסיסנית unstimulated, + Na / K + -ATPase מעכב ouabain אין כל השפעה על הפרשת נוזל 2, גם כאשר ספיגתו לתוך תאים עיקריים היא מעוכבת על ידי taurocholate מעכב טרנספורטר אניון האורגני 13. עם זאת, לינטון ו אודונל הראה כי ouabain depolarizesפוטנציאל הממברנה basolateral, ומגביר Na + שטף 9. כפי שניתן לראות בנציגי התוצאות, אנו משוכפלים ממצאים אלה, והראו כי K + שטף הוא במקביל ירד 14; שטף Na + המוגבר וירידת K + שטף יש השפעות מנוגדות על הפרשת נוזל, וכתוצאה מכך אין שינוי נטו בהפרשה. לפיכך, יש שתי החלטות ל" פרדוקס ouabain, "כלומר, ההתבוננות הראשונית שouabain אין כל השפעה על הפרשת נוזלים באבובית תסיסנית:. ראשונה, בtubules המגורה, ההשפעה של ouabain על הפרשת נוזל אינה נראית לעין עקב הספיגה שלה על ידי טרנספורטר אניון האורגני 13; ושנייה, בtubules unstimulated, ouabain יש השפעות מנוגדות על transepithelial Na + K + ושטף, וכתוצאה מכך אין שינוי נטו בהפרשת נוזל (ראה תוצאות ונ"צ נציג. 9). לכן, התפקיד העיקרי של + Na / K + -ATPASE בtubules unstimulated הוא להוריד תאיים ריכוז Na + ליצור שיפוע ריכוז נוח לNa + -coupled תהליכי הובלה על פני קרום basolateral. ואכן, על ידי מדידה בנפרד Na + K + ונתיבים, שהוכחנו כי tubules חסר cotransporter נתרן, אשלגן-2-כלוריד זבוב (NKCC) ירד K + שטף transepithelial, ללא ירידה נוספת לאחר תוספת ouabain, ולא חלו שינוי בtransepithelial Na + שטף 14. ממצאים אלה נתמכים מסקנתנו כי Na + כניסה לתא דרך NKCC ממוחזרת דרך Na + / K + -ATPase. בדוגמא אחרת, Ianowski נצפה et al. כי הורדת K אמבטיה + ריכוז מ -10 מ"מ ועד 6 מ"מ ירד K transepithelial + שטף וtransepithelial המוגבר שטף Na + בצינוריות מprolixus Rhodnius, ללא שינוי נטו בהפרשת נוזל <sup> 15. אפקטי ההפרש בשטף Na + K + ושטף על פני tubules זחל גם נצפו בtubules דרוזופילה בתגובה לדיאטות מלח שונה 16 ובשני מיני יתושים בתגובה לגידול מליחות 17.האתגר הגדול ביותר במדידת שטף יון transepithelial בהכנת assay רמזי הוא קביעת ריכוזי יון בתוך הנוזל המופרש. אתגר זה כבר נפגש עם פתרונות שונים, כולל photometery להבה 18, שימוש ביונים רדיואקטיביים 19, וגל אלקטרון הבדיקה ספקטרוסקופיה נפיצה 20. טכניקות אלה דורשות העברה של ירידת הנוזל המופרשת למכשיר למדידת ריכוזי יון. מאז את נפח הנוזל המופרש על ידי אבובית תסיסנית unstimulated הוא קטן, בדרך כלל ~ 0.5 NL / דקה, זה מציב אתגר טכני וגם מציגה שגיאה אם חלק מהנוזל המופרש הואאיבד על העברה. לעומת זאת, השימוש באלקטרודות יון ספציפי מאפשרת המדידה של פעילות יון (שממנו ניתן לחשב ריכוז יון) באתרו. הפרוטוקול הנוכחי הותאם מזה בשימוש על ידי Maddrell ועמיתים למדידת K transepithelial + שטף על פני אבובית Rhodnius באמצעות valinomycin כK + ionophore 21, ומתאר גם את השימוש ב-butylcalix 4 טרט [4] חומצת arene-tetraacetic Na מבוסס אסתר tetraethyl + אלקטרודה יון ספציפי -specific המאופיינת Messerli et. אל. 22. אלקטרודות יון ספציפיות יש גם שימשו למדידת ריכוזי יון בנוזל המופרש על ידי צינוריות Malpighian בassay רמזי ב9,23 מבוגרים ו -16 זחל תסיסנית melanogaster, ניו זילנד Alpine Weta (Hemideina מאורי) 24 וביתושים 17.
כאן, אנו מתארים בפירוט את השימוש ברמזים כאומר למדוד שיעורי הפרשת נוזל בtubules Malpighian מדרוזופילה melanogaster, כמו גם שימוש באלקטרודות יון ספציפי כדי לקבוע את הריכוזים של K + וNa + בתוך הנוזל המופרש ולכן החישוב של נתיבי יון transepithelial. סקירה של assay מסופקת באיור 1.
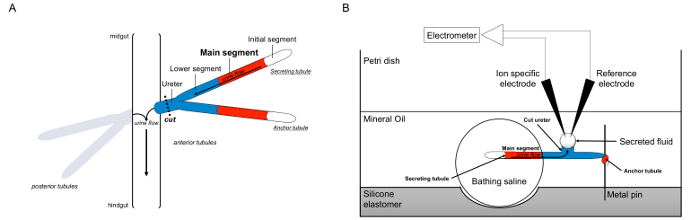
איור 1. סכמטי של קשיות Malpighian וAssay רמזי עם שימוש ביון ספציפי אלקטרודות למדידת ריכוזי יון. נתון זה ממחיש את ההתקנה לassay רמזי. (א) לכל זבוב ארבעה tubules, זוג הצינוריות קדמית וזוג הצינוריות אחורית, לצוף שבחלל הבטן המוקף hemolymph. בכל זוג, שתי הצינוריות להצטרף בשופכן, אשר לאחר מכן מרוקן את השתן בצומת של midgut וhindguלא. Tubules הם הסתיים עיוור. שתן נוצר על ידי המגזר העיקרי מפרישי הנוזל (באדום), וזורם לכיוון השופכן והחוצה אל הבטן. לאחר נתיחה, זוג אבובית הוא ניתק מהבטן על ידי חוצה את השופכן. (ב) זוג הצינוריות מועבר לאחר מכן לטיפה של ים מלוח בתוך היטב של צלחת assay. אחד משתי הצינוריות, המכונה כאן "אבובית העוגן," עטוף סביב סיכת מתכת והוא אינרטי. אבובית האחרות היא אבובית הסתרתו. הקטע הראשוני (שאינו מפריש נוזל) והקטע העיקרי של אבובית מפרישות להישאר בתוך הטיפה של ים מלוח. יונים ומהלך מים מתמיסת מלח הים ולתוך לום אבובית של המגזר העיקרי, ולאחר מכן לנוע לכיוון השופכן, כפי שהיו קורים בvivo. הקטע התחתון (הכחולה) הוא מחוץ למלוח רחצה ולכן אדיש. מאז שופכן הוא לחתוך, הנוזל המופרש מתגלה כטיפה מסוף החתך של השופכן. Tהוא מופרש טיפת נוזל מגדילה לאורך הזמן כהפרשה ממשיכה, וקוטרה נמדד באמצעות מיקרומטר עיני. שכבה של שמן מינרלים מונעת אידוי של הנוזל המופרש. אלקטרודות ספציפיות ההתייחסות והיון למדוד את ריכוז היון של הנוזל המופרש. אנא לחץ כאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
השימוש של assay ראמזי, יחד עם אלקטרודות יון ספציפי, מאפשר המדידה של שיעורי הפרשת נוזל והנתיבים יון בMalpighian tubules חרקים מבודדים (כליות). ניתן assayed עשרים או יותר tubules בזמן, המאפשר תפוקה גבוהה יותר בהשוואה לassay של פרט בtubules המבחנה microperfused. בנוסף, אלקטרודות יון ספציפי תאפשר ק…
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Drs. Sung-wan An and Mike O’Donnell for practical advice on establishing this assay, Dr. Chih-Jen Cheng for helpful discussions on the use of ion-specific electrodes, and Dr. Chou-Long Huang for his mentorship and support. This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (K08DK091316 to ARR) and the American Society of Nephrology Gottschalk Award to ARR.
Materials
| Sylgard 184 Silicone Elastomer Kit | Ellsworth Adhesives | http://www.ellsworth.com/dow-corning-sylgard-184-silicone-encapsulant-0-5kg-kit-clear/ | May be purchased from multiple distributors |
| Petri dish, polystyrene, 100 mm x 15 mm | Fisher | FB0875712 | Specific brand is not important |
| Petri dish, polystyrene, 35 mm x 10 mm | Corning Life Sciences | Fisher 08-757-100A | Specific brand is not important |
| Scalpel Handle #3 | Fine Science Tools | 10003-12 | Specific brand is not important |
| Scalpel Blades #1 | Fine Science Tools | 10011-00 | Specific brand is not important; use appropriate sharps precautions |
| Needle, 30G x 1/2 | Becton Dickinson | 305106 | Use appropriate sharps precautions |
| Minutien pins, black anodized, 0.15 mm | Fine Science Tools | 26002-15 | |
| Stereomicroscope with ocular micrometer | Nikon | SMZ800 | Specific brand is not important; this is given as an example |
| Sheet of black stained glass, 3 mm (1/8 inch) thick | Hobby shop | Example includes Spectrum Black Opal by Spectrum Glass (http://www.delphiglass.com/spectrum-glass/opalescent/spectrum-black-opal) | |
| Glass cutting tools (glass cutter, glass cutting pliers) | Hobby shop | Examples include the Studio Pro Lightweight Running Pliers by Diamond Tech (http://www.delphiglass.com/glass-cutters-tools/pliers-nippers/studio-pro-lightweight-running-pliers) and the Studio Pro Brass Glass Cutter by Diamond Tech (http://www.delphiglass.com/glass-cutters-tools/glass-cutters/studio-pro-brass-glass-cutter). Use appropriate safety precautions when cutting glass | |
| Borosilicate glass capillary tube, unfilamented, GC120-10, OD 1.2 mm, ID 0.69 mm, length 10 cm | Warner Instruments | 30-0042 | |
| Borosilicate glass capillary tube, filamented, GC120F-10, OD 1.2 mm, ID 0.69 mm, length 10 cm | Warner Instruments | 30-0044 | |
| Nitric acid, 70% | Sigma | 438073 | CAUTION: see Material Data Safety Sheet for appropriate storage and handling guidelines. Specific brand is not important |
| Cimarec 7 in x 7 in hotplate | Fisher | 11675911Q | Specific brand is not important; caution when heated |
| Selectophore dichlorodimethylsilane | Sigma | 40136-1ML | CAUTION: see Material Data Safety Sheet for appropriate storage and handling guidelines |
| Two-step vertical pipet puller | Narishige | PC-10 | Other pipet pullers can be used; this is given as an example |
| Glass petri dish, 150 mm diameter x 15 mm height | Fisher | 08-748E | Specific brand is not important; only one dish needed |
| World Precision Instruments E210 1 mm micropipette storage jar | Fisher | 50-821-852 | May be available from other distributors. Useful to have two jars. Note that although this jar is specified for 1 mm pipets, and the pipets used here are 1.2 mm, in our experience the 1 mm jar works best for the 1.2 mm pipets. |
| Silica Gel, Tel-Tale Desiccant, indicating, 10-18 mesh | Fisher | S161-500 | Indicating silica useful for determining whether silica gel retains desiccating ability |
| World Precision Instruments MicroFil, 34G | Fisher | 50-821-914 | May be available from other distributors. |
| 1 ml syringe with luer lock | Becton Dickinson | 309659 | May be available from other distributors. |
| 3 ml syringe with luer lock | Becton Dickinson | 309657 | May be available from other distributors. |
| D300 3-way stopcock with female luer lock inlet port, male luer outlet port with rotating collar and guard | Cole-Parmer | UX-30600-02 | Specific brand is not important |
| Female Luer Locking Connector | 4 Medical Solutions | ADC 9873-10 | Specific brand is not important; barbed end is ~4 mm at narrowest point and ~7 mm at widest point. |
| Silicone Tubing I.D. x O.D. x Wall: 1/16 x 1/8 x 1/32 in. (1.59 x 3.18 x 0.79 mm) | Fisher | 14-179-110 | Specific brand is not important |
| E-3603 tubing, I.D. x O.D.: 1/32 x 3/32 in | Fisher | 14171208 | Specific brand is not important |
| Modeling clay | Specific brand is not important | ||
| Selectophore potassium ionophore I, cocktail B | Sigma | 99373 | CAUTION: see Material Data Safety Sheet for appropriate storage and handling guidelines |
| Selectophore sodium ionophore X | Sigma | 71747 | Sodium ionphore X = 4-tert-butylcalix[4]arene-tetraacetic acid tetraethylester |
| Selectophore 2-nitrophenyl octyl ether | Sigma | 73732 | |
| Selectophore sodium tetraphenylborate | Sigma | 72018 | |
| Schneider's Drosophila medium | Life Technologies | 21720024 | |
| High impedance electrometer | World Precision Instruments | FD223a | |
| Microelectrode holder 1 mm with 45° body, vented, with handle | Warner Instruments | 64-1051 | |
| Microelectrode holder 1 mm with straight body, vented | Warner Instruments | 64-1007 | |
| Silver wire | Warner Instruments | 64-1318 | |
| Micromanipulators, pair | Leitz | Various brands/models will work; this is an example | |
| Faraday cage | Technical Manufacturing Corporation | 81-334-03 | This is an example; any Faraday cage will work |
| Single gooseneck fiberoptic light | Nikon | Specific brand is not important | |
| mineral oil | Fisher | BP-2629 | Specific brand is not important |
| forceps, Dumont #5 with Biologie tip | Fine Science Tool | 11295-10 | May be available from other distributors. |
References
- Ramsay, J. A. Active Transport of Water by the Malpighian Tubules of the Stick Insect, Dixippus-Morosus (Orthoptera, Phasmidae). J Exp Biol. 31, 104-113 (1954).
- Dow, J. A., et al. The malpighian tubules of Drosophila melanogaster: a novel phenotype for studies of fluid secretion and its control. J Exp Biol. 197, 421-428 (1994).
- Brand, A. H., Perrimon, N. Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development. 118, 401-415 (1993).
- Sozen, M. A., Armstrong, J. D., Yang, M., Kaiser, K., Dow, J. A. Functional domains are specified to single-cell resolution in a Drosophila epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 94, 5207-5212 (1997).
- Rosay, P., et al. Cell-type specific calcium signalling in a Drosophila epithelium. J Cell Sci. 110 (15), 1683-1692 (1997).
- Dow, J. T., Davies, S. A. Integrative physiology and functional genomics of epithelial function in a genetic model organism. Physiol Rev. 83, 687-729 (2003).
- Beyenbach, K. W., Skaer, H., Dow, J. A. The developmental, molecular, and transport biology of Malpighian tubules. Annu Rev Entomol. 55, 351-374 (2010).
- Donnell, M. J., et al. Hormonally controlled chloride movement across Drosophila tubules is via ion channels in stellate cells. Am J Physiol. 274, 1039-1049 (1998).
- Linton, S. M., O’Donnell, M. J. Contributions of K+:Cl- cotransport and Na+/K+-ATPase to basolateral ion transport in malpighian tubules of Drosophila melanogaster. J Exp Biol. 202, 1561-1570 (1999).
- Rheault, M. R., O’Donnell, M. J. Analysis of epithelial K(+) transport in Malpighian tubules of Drosophila melanogaster: evidence for spatial and temporal heterogeneity. J Exp Biol. 204, 2289-2299 (2001).
- Donnell, M. J., Dow, J. A., Huesmann, G. R., Tublitz, N. J., Maddrell, S. H. Separate control of anion and cation transport in malpighian tubules of Drosophila Melanogaster. J Exp Biol. 199, 1163-1175 (1996).
- Cabrero, P., et al. Chloride channels in stellate cells are essential for uniquely high secretion rates in neuropeptide-stimulated Drosophila diuresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 111, 14301-14306 (2014).
- Torrie, L. S., et al. Resolution of the insect ouabain paradox. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 101, 13689-13693 (2004).
- Rodan, A. R., Baum, M., Huang, C. L. The Drosophila NKCC Ncc69 is required for normal renal tubule function. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 303, 883-894 (2012).
- Ianowski, J. P., Christensen, R. J., O’Donnell, M. J. Na+ competes with K+ in bumetanide-sensitive transport by Malpighian tubules of Rhodnius prolixus. J Exp Biol. 207, 3707-3716 (2004).
- Naikkhwah, W., O’Donnell, M. J. Salt stress alters fluid and ion transport by Malpighian tubules of Drosophila melanogaster: evidence for phenotypic plasticity. J Exp Biol. 214, 3443-3454 (2011).
- Donini, A., et al. Secretion of water and ions by malpighian tubules of larval mosquitoes: effects of diuretic factors, second messengers, and salinity. Physiol Biochem Zool. 79, 645-655 (2006).
- Maddrell, S. H. Secretion by Malpighian Tubules of Rhodnius movements of Ions and Water. J Exp Biol. 51, 71-97 (1969).
- Maddrell, S. H., Overton, J. A. Stimulation of sodium transport and fluid secretion by ouabain in an insect malpighian tubule. J Exp Biol. 137, 265-276 (1988).
- Williams, J. C., Beyenbach, K. W. Differential effects of secretagogues on Na and K secretion in the Malpighian tubules of Aedes Aegypti (L). J Comp Physiol. 149, 511-517 (1983).
- Maddrell, S. H., O’Donnell, M. J., Caffrey, R. The regulation of haemolymph potassium activity during initiation and maintenance of diuresis in fed Rhodnius prolixus. J Exp Biol. 177, 273-285 (1993).
- Messerli, M. A., Kurtz, I., Smith, P. J. Characterization of optimized Na+ and Cl- liquid membranes for use with extracellular, self-referencing microelectrodes. Anal Bioanal Chem. 390, 1355-1359 (2008).
- Ianowski, J. P., O’Donnell, M. J. Basolateral ion transport mechanisms during fluid secretion by Drosophila Malpighian tubules: Na+ recycling, Na+:K+:2Cl- cotransport and Cl- conductance. J Exp Biol. 207, 2599-2609 (2004).
- Neufeld, D. S., Leader, J. P. Electrochemical characteristics of ion secretion in malpighian tubules of the New Zealand alpine weta (Hemideina maori). J Insect Physiol. 44, 39-48 (1997).
- Greenspan, R. J. . Fly Pushing: The Theory and Practice of Drosophila Genetics. , (1997).
- Jayakannan, M., Babourina, O., Rengel, Z. Improved measurements of Na+ fluxes in plants using calixarene-based microelectrodes. J Plant Physiol. 168, 1045-1051 (2011).
- Wu, Y., Schellinger, J. N., Huang, C. L., Rodan, A. R. Hypotonicity Stimulates Potassium Flux through the WNK-SPAK/OSR1 Kinase Cascade and the Ncc69 Sodium-Potassium-2-Chloride Cotransporter in the Drosophila Renal Tubule. J Biol Chem. 289, 26131-26142 (2014).
- Blumenthal, E. M. Modulation of tyramine signaling by osmolality in an insect secretory epithelium. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 289, 1261-1267 (2005).
- Dow, J. A., Maddrell, S. H., Davies, S. A., Skaer, N. J., Kaiser, K. A novel role for the nitric oxide-cGMP signaling pathway: the control of epithelial function in Drosophila. Am J Physiol. 266, 1716-1719 (1994).
- Dube, K., McDonald, D. G., O’Donnell, M. J. Calcium transport by isolated anterior and posterior Malpighian tubules of Drosophila melanogaster: roles of sequestration and secretion. J Insect Physiol. 46, 1449-1460 (2000).
- Efetova, M., et al. Separate roles of PKA and EPAC in renal function unraveled by the optogenetic control of cAMP levels in vivo. J Cell Sci. 126, 778-788 (2013).
- Rheault, M. R., O’Donnell, M. J. Organic cation transport by Malpighian tubules of Drosophila melanogaster: application of two novel electrophysiological methods. J Exp Biol. 207, 2173-2184 (2004).
- Donnell, M. J. Too much of a good thing: how insects cope with excess ions or toxins in the diet. J Exp Biol. 212, 363-372 (2009).
- Cheng, C. J., Truong, T., Baum, M., Huang, C. L. Kidney-specific WNK1 inhibits sodium reabsorption in the cortical thick ascending limb. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 303, 667-673 (2012).
- Cheng, C. J., Yoon, J., Baum, M., Huang, C. L. STE20/SPS1-related Proline/alanine-rich Kinase (SPAK) is Critical for Sodium Reabsorption in Isolated Perfused Thick Ascending Limb. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. , (2014).

