Hochstereoselektive Synthese von 1,6-Ketoester durch Ionische Flüssigkeiten vermittelte: Ein Dreikomponentenreaktion zur raschen Zugang zu einer neuen Klasse von niedermolekularen Gelbildner
Summary
Ionic liquids (ILs) mediate fast, simple and cheap access to 1,6-ketoesters in high diastereoselectivities and good yields. The reaction protocol is robust and the 1,6-ketoesters can be obtained in gram scale after a simple filtration protocol. Moreover, the 1,6-ketoesters are potent gelators in hydrocarbon solvents.
Abstract
In organic chemistry ionic liquids (ILs) have emerged as safe and recyclable reaction solvents. In the presence of a base ILs can be deprotonated to form catalytically active N-Heterocyclic Carbenes (NHCs). Here we have used ILs as precatalysts in the addition of α,β-unsaturated aldehydes to chalcones to form 1,6-ketoesters, incorporating an anti-diphenyl moiety in a highly stereoselective fashion. The reaction has a broad substrate scope and several functional groups and heteroaromatics can be integrated into the ketoester backbone in generally good yields with maintained stereoselectivity. The reaction protocol is robust and scalable. The starting materials are inexpensive and the products can be obtained after simple filtration, avoiding solvent-demanding chromatography. Furthermore, the IL can be recycled up to 5 times without any loss of reactivity. Moreover, the 1,6-ketoester end product is a potent gelator in several hydrocarbon based solvents. The method enables rapid access to and evaluation of a new class of low molecular weight gelators (LMWGs) from recyclable and inexpensive starting materials.
Introduction
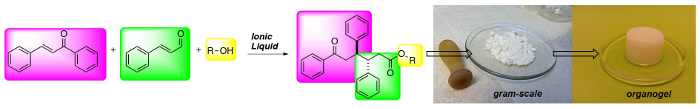
(Oben) Drei-Komponenten-Synthese von 1,6-Ketoestern: eine neue Klasse von Gewichts Gelatoren niedrigem Molekulargewicht.
Ionische Flüssigkeiten (ILs) eine hohe Stabilität, geringe Volatilität, nicht-entflammbar und daher als sicher Reaktionsmedien und ideale Lösungsmittel für Recycling gemacht Aufmerksamkeit. 1-3 Dialkyl imidazoliums sind eine bestimmte Art von ionischen Flüssigkeiten, die, in der Gegenwart einer Base kann deprotoniert, um ein N-heterocyclisches Carben (NHC). 4 Auf dem Gebiet der Organokatalyse übertragen werden, NHCs, die unter verschiedenen Reaktionswegen, haben eine weit verbreitete Nutzung in einer breiten Palette von generischen Reaktionen gefunden. 5-11
Trotz dieser, die Verbindung zwischen ILs und CC-Bindung forming NHC-Katalyse ist relativ unerforscht. Dennoch NHC von ILs abgeleitet wurde berichtet, dass CC-Bindung bildenden Reaktionen wie der Benzoinkondensation und die Stetter-Reaktion katalysieren. 12-22 beispielsweise Davis et al. Haben gezeigt, dass IL aus N-Alkyl Thiazoliumgruppen abgeleitet dienen als Präkatalysatoren in der Bildung Benzoin aus Benzaldehyd. 12
In jüngerer Zeit, Chen et al erweitert dieses Konzept unter Verwendung eines Imidazolium basierend IL, 1-Ethyl-3-methyl-imidazolium-acetat (EMIMAc), um die Benzoinkondensation von 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) durch, um zu generieren 5,5 '-di (hydroxymethyl) Furoin (DHMF). 23 Da ILs sind kommerziell erhältlich und bieten eine kostengünstige Möglichkeit der Erzeugung von NHCs, waren wir an die Untersuchung, was andere Arten von Reaktionen ILs durchführen könnte. Zu diesem Zweck haben wir festgestellt, daß Dialkylcarbonate imidazoliums könnte effizient wie Präkatalysatoren in der formalen Konjugat additi verwendet werdenon von ungesättigten Aldehyden Chalkone (Abbildung 1), was 1,6-Ketoester. Die effizienteste IL, EMIMAc, fördert eine hoch stereoselektive Reaktion von Zimtaldehyd und Chalkon. Die Umsetzung erfolgt mit hoher Präferenz für das anti-Diastereomer und die 1,6-Ketoester in Ausbeuten bis zu 92% isoliert werden. 24,25,26
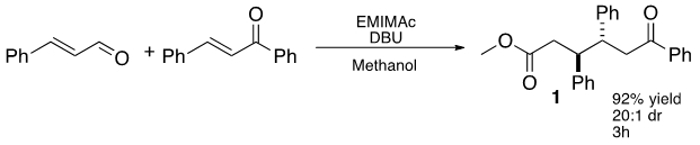
Abbildung 1: IL-vermittelte dreikomponentigen, stereoselektive Addition von Zimtaldehyd zu Chalkon.
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
Bezogen auf die anti-Konfiguration durch Röntgenanalyse -Ketoester 3 und auf der Untersuchung des Reaktionsmechanismus von Bode et al vorgeschlagenen 30 bestimmt die folgenden Reaktionspfad vorgeschlagen (Figur 5). Deprotonierung des IL erzeugt NHC Arten; das NHC reagiert mit dem ungesättigten Aldehyds der Breslow-Intermediat I. Der Breslow-Intermediat zu bilden, und die Chalcon reagieren in einer Quer Benzoin Reaktion auf Dien II bilden. Mittelstufe II durchläuft eine Oxy-Cope-Um…
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the Swedish Research Council Formas for generous financial support.
Materials
| 1-ethyl-3-methyl imidazolium acetate | Aldrich | 51053-100G-F | Produced by BASF ≥90%, dried on a rotary evaporated before use (10 mBar, 40 °C, 1h) CAS NUMBER: 143314-17-4 |
| 1,3-diphenyl-2-propen-1-one | Aldrich | 11970-100G | 98.0% CAS NUMBER: 94-41-7 |
| trans-cinnamaldehyde | Aldrich | C80687-25G | 99%, stored under nitrogen prior to use CAS NUMBER: 14371-10-9 |
| 1,8-Diazobicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene | Aldrich | 139009-25G | 98% CAS NUMBER: 6674-22-2 |
| Methanol | Sigma-Aldrich | 32213N-2.5L | puriss. P.a., ACS reagent, reag. ISO, reag. Ph. Eur. ≥99.8% (GC) CAS NUMBER: 67-56-1 |
| Dichloromethane | Fischer Chemical | D/1852/17X | Analytic reagent grade, stabilized with amylene CAS NUMBER:9/2/1975 |
| n-Heptane | Fischer Chemical | H/0160/17X | Analytic reagent grade CAS NUMBER: 142-82-5 |
References
- Hallett, J. P., Welton, T. Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids: Solvents for Synthesis and Catalysis. 2. Chem. Rev. 111, 3508-3576 (2011).
- Welton, T. Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids. Solvents for Synthesis and Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 99, 2071-2084 (1999).
- Vora, H. U., Wheeler, P., Rovis, T. Exploiting acyl and enol azolium intermediates via N-hetero- cyclic carbene-catalyzed reactions of α-reducible aldehydes. Adv. Synth. Catal. 354, 1617-1639 (2012).
- Holloczki, O., et al. Carbenes in ionic liquids. New J. Chem. 34, 3004-3009 (2010).
- Enders, D., Balensiefer, T. Nucleophilic Carbenes in Asymmetric Organocatalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 37, 534-541 (2004).
- Enders, D., Niemeier, O., Henseler, A. Organocatalysis by N-Heterocyclic Carbenes. Chem. Rev. 107, 5606-5655 (2007).
- List, B. Enamine Catalysis Is a Powerful Strategy for the Catalytic Generation and Use of Carbanion Equivalents. Acc. Chem. Res. 37, 548-557 (2004).
- Nair, V., Bindu, S., Sreekumar, V. N-Heterocyclic carbenes: Reagents, not just ligands!. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 43, 5130-5135 (2004).
- Marion, N., Dìez-González, S., Nolan, S. P. N-Heterocyclic Carbenes as Organocatalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46, 2988-3000 (2007).
- Biju, A. T., Kuhl, N., Glorius, F. Extending NHC-Catalysis: Coupling Aldehydes with Unconventional Reaction Partners. Acc. Chem. Res. 44, 1182-1195 (2011).
- Bugaut, X., Glorius, F. Organocatalytic umpolung: N-heterocyclic carbenes and beyond. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 3511-3522 (2012).
- Davis, h. j., Forrester, K. J. Thiazolium-ion based organic ionic liquids (OILs).1,2 Novel OILs which promote the benzoin condensation. Tetrahedron Lett. 40, 1621-1622 (1999).
- Xu, L. -. W., Gao, Y., Yin, J. -. J., Li, L., Xia, C. -. G. Efficient and mild benzoin condensation reaction catalyzed by simple 1-N-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium salts. Tetrahedron Lett. 46, 5317-5320 (2005).
- Jiang, F. S., Yu, H., Gao, G., Xie, R. G. Benzoin condensation in imidazolium based room-temperature ionic liquids. Chin. Chem. Lett. 16, 321-324 (2005).
- Estager, J., Lévêque, J. M., Turgis, R., Draye, M. Solventless and swift benzoin condensation catalyzed by 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium ionic liquids under microwave irradiation. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 256, 261-264 (2006).
- Estager, J., Lévêque, J. -. M., Turgis, R., Draye, M. Neat benzoin condensation in recyclable room-temperature ionic liquids under ultrasonic activation. Tetrahedron Lett. 48, 755-759 (2007).
- Orsini, M., Chiarotto, I., Elinson, M. N., Sotgiu, G., Inesi, A. Benzoin condensation in 1,3-dialkylimidazolium ionic liquids via electrochemical generation of N-heterocyclic carbene. Electrochem. Commun. 11, 1013-1017 (2009).
- Dunn, M. H., Cole, M. L., Harper, J. B. Effects of an ionic liquid solvent on the synthesis of [gamma]-butyrolactones by conjugate addition using NHC organocatalysts. RSC Advances. 2, 10160-10162 (2012).
- Kelemen, Z., Holloczki, O., Nagy, J., Nyulaszi, L. An organocatalytic ionic liquid. Org. Biomol. Chem. 9, 5362-5364 (2011).
- Yu, F. -. L., Zhang, R. -. L., Xie, C. -. X., Yu, S. -. T. Synthesis of thermoregulated phase-separable triazolium ionic liquids catalysts and application for Stetter reaction. Tetrahedron. 66, 9145-9150 (2010).
- Aupoix, A., Vo-Thanh, G. Solvent-free synthesis of alkylthiazolium-based ionic liquids and their use as catalysts in the intramolecular Stetter reaction. Synlett. , 1915-1920 (2009).
- Yu, F. -. L., Jiang, J. -. J., Zhao, D. -. M., Xie, C. -. X., Yu, S. -. T. Imidazolium chiral ionic liquid derived carbene-catalyzed conjugate umpolung for synthesis of [gamma]-butyrolactones. RSC Advances. 3, 3996-4000 (2013).
- Liu, D., Zhang, Y., Chen, E. Y. X. Organocatalytic upgrading of the key biorefining building block by a catalytic ionic liquid and N-heterocyclic carbenes. Green Chem. 14, 2738-2746 (2012).
- Ta, L., Axelsson, A., Bijl, J., Haukka, M., Sundén, H. Ionic Liquids as Precatalysts in the Highly Stereoselective Conjugate Addition of α,β-Unsaturated Aldehydes to Chalcones. Chem. Eur. J. 20, 13889-13893 (2014).
- Nair, V., et al. Nucleophilic Heterocyclic Carbene Catalyzed Annulation of Enals to Chalcones in Methanol: A Stereoselective Synthesis of Highly Functionalized Cyclopentanes. Org. Lett. 11, 2507-2510 (2009).
- Ma, J., Huang, Y., Chen, R. N-Heterocyclic carbene-catalyzed (NHC) three-component domino reactions: highly stereoselective synthesis of functionalized acyclic ϵ-ketoesters. Org. Biomol. Chem. 9, 1791-1798 (2011).
- Domingo, L. R., Saez, J. A., Arno, M. A DFT study on the NHC catalysed Michael addition of enols to α,β-unsaturated acyl-azoliums. A base catalysed C-C bond-formation step. Org. Biomol. Chem. 12, 895-904 (2014).
- Kaeobamrung, J., Mahatthananchai, J., Zheng, P., Bode, J. W. An Enantioselective Claisen Rearrangement Catalyzed by N-Heterocyclic Carbenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 8810-8812 (2010).
- Zweep, N., van Esch, J. H. . Functional Molecular Gels. , 1-29 (2014).
- Chiang, P. -. C., Kaeobamrung, J., Bode, J. W. Enantioselective, Cyclopentene-Forming Annulations via NHC-Catalyzed Benzoin−Oxy-Cope Reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 3520-3521 (2007).

