دراسة اندوبلازمية شبكية والميتوكوندريا التفاعلات التي كتبها<em> في الموقع</em> القرب من ربط الفحص في خلايا ثابتة
Summary
هنا، نحن تصف الإجراء لتصور وقياس مع حساسية عالية التفاعلات الذاتية بين الشبكة الإندوبلازمية والميتوكوندريا في الخلايا الثابتة. يتميز البروتوكول والأمثل في الموقع قرب ربط فحص استهداف إينوزيتول 1،4،5-ثلاثي مستقبلات / التنظيم الجلوكوز البروتين 75 / قناة أنيون / cyclophilin مجمع تعتمد على الجهد D في واجهة غشاء المرتبطة الميتوكوندريا.
Abstract
Structural interactions between the endoplasmic reticular (ER) and mitochondrial membranes, in domains known as mitochondria-associated membranes (MAM), are crucial hubs for cellular signaling and cell fate. Particularly, these inter-organelle contact sites allow the transfer of calcium from the ER to mitochondria through the voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC)/glucose-regulated protein 75 (GRP75)/inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor (IP3R) calcium channeling complex. While this subcellular compartment is under intense investigation in both physiological and pathological conditions, no simple and sensitive method exists to quantify the endogenous amount of ER-mitochondria contact in cells. Similarly, MAMs are highly dynamic structures, and there is no suitable approach to follow modifications of ER-mitochondria interactions without protein overexpression. Here, we report an optimized protocol based on the use of an in situ proximity ligation assay to visualize and quantify endogenous ER-mitochondria interactions in fixed cells by using the close proximity between proteins of the outer mitochondrial membrane (VDAC1) and of the ER membrane (IP3R1) at the MAM interface. Similar in situ proximity ligation experiments can also be performed with the GRP75/IP3R1 and cyclophilin D/IP3R1 pairs of antibodies. This assay provides several advantages over other imaging procedures, as it is highly specific, sensitive, and suitable to multiple-condition testing. Therefore, the use of this in situ proximity ligation assay should be helpful to better understand the physiological regulations of ER-mitochondria interactions, as well as their role in pathological contexts.
Introduction
الميتوكوندريا والشبكة الإندوبلازمية (أوروبا) ليست العضيات مستقلة في الخلية، لكنها تتفاعل هيكليا ووظيفيا في مواقع الاتصال الذي يعرف بأنه أغشية الشبكة الإندوبلازمية المرتبط الميتوكوندريا (MAM). في الواقع، MAMs تتوافق مع المناطق التي الرئيسي يعارضها أغشية ER والميتوكوندريا عن كثب، والسماح التفاعلات بين البروتينات من كلا الجانبين. ومع ذلك، فإن أغشية هذه العضيات لا تلتحم في هذه المناطق، حتى أنها تحافظ على كياناتها المنفصلة. وMAMs تلعب دورا حاسما في الكالسيوم (الكالسيوم 2+) ونقل فوسفورية من ER إلى الميتوكوندريا، مما يؤثر استقلاب الطاقة وبقاء الخلية 1-3.
وتصور العلاقة بين لائحة والميتوكوندريا الأول في 1970s مع المجهر الإلكتروني. ومنذ ذلك الحين، انتقال المجهر الإلكتروني 4،5، والإلكترون التصوير المقطعي 6،7 أو المناعية توطين ER والميتوكوندريا الخاصة fluorophoreق / البروتينات الفلورية 8 استخدمت تقليديا لدراسة التفاعلات-ER الميتوكوندريا. ويستند أداة أخرى مفيدة لتحليل MAM على استخدام تجزئة التحت خلوية. وهو يتيح للعزل كسور MAM بواسطة تنبيذ فائق الفرق بالإضافة إلى التدرج Percoll 9. ومع ذلك، فإن المنتج النهائي يحتوي على كسور MAM المخصب، بدلا من كسور نقية. وإجمالا، فإن هذه الاستراتيجيات ليست حساسة بشكل خاص و / أو الكمية، وأنها ليست قابلة بسهولة إلى غربلة واسعة. بدلا من ذلك، برزت طرق الوراثية باستخدام linkers محرض المخدرات الفلورسنت بين عضية، لكنها لا تسمح لتحليل التفاعلات عضية في مستويات التعبير الذاتية للبروتينات 10.
وبناء على اكتشاف Szabadkai للمجمع IP3R / GRP75 / VDAC في MAM 11، قمنا بتطوير الأسلوب الكمي لتحليل التفاعلات-ER الميتوكوندريا. استخدمنا في ligati قرب الموقععلى الفحص لكشف وتحديد التفاعلات بين VDAC1 وIP3R1، اثنين من البروتينات عضية سطح تشارك في كا 2+ -channeling مجمع في واجهة MAM في الخلايا الثابتة 12. باختصار، نحن سبر VDAC1 في الغشاء الخارجي الميتوكوندريا (الماوس مكافحة VDAC1 الأجسام المضادة الأولية) وIP3R1 في غشاء ER (أرنب مكافحة IP3R1 الأجسام المضادة الأولية) (الشكل 1، لوحة أ). ثم، وأضاف نحن على حد سواء لمكافحة فأر ومفتش المضادة للأرنب (تحقيقات الماوس والقرب أرنب ربط الفحص)، والتي يتم تصريفها إلى ملحقات النوكليوتيد التكميلية وفقا للفحص. إذا اثنين من البروتينات المستهدفة هي على مسافة أقل من 40 نانومتر، يمكن للأليغنوكليوتيد هجن مع oligos موصل وأضاف في وقت لاحق للسماح بتشكيل قالب دائري الحمض النووي (الشكل 1، لوحة ب). هو ligated هذا الجزيء DNA دائري وتضخيمها، وخلق منتج الحمض النووي المفرد الذين تقطعت بهم السبل تعلق تساهمي إلى واحدة من تحقيقات القرب (الشكل 1، لوحة ج) </stroنانوغرام>. منذ المسافة بين لائحة والميتوكوندريا في واجهة MAM تتراوح من 10 نانومتر إلى 25 نانومتر 6، ربط القرب والتضخيم يمكن القيام به، مما أدى إلى كشف لاحقا بسبب التهجين تكساس [أليغنوكليوتيد الحمراء المسمى المسابير (الشكل 1، لوحة د ). وتمثل كل نقطة الفلورسنت التفاعلات بين VDAC1 / IP3R1، مما يسمح للالكمي لفي الموقع التفاعلات ER-الميتوكوندريا في الخلايا الفردية.
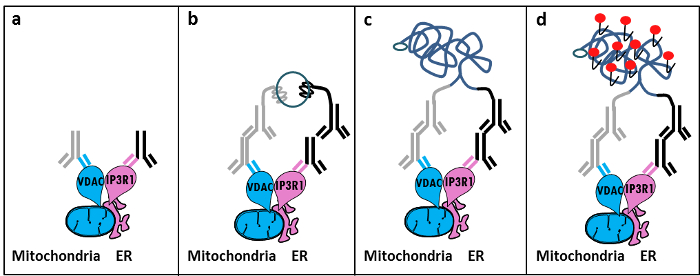
الشكل 1: رسم توضيحي تخطيطي للكشف عن التفاعلات اندوبلازمية شبكية-الميتوكوندريا من قبل في الموقع القرب من ربط الفحص. أ) الأجسام المضادة الماوس الأولية الموجهة ضد VDAC1 والأجسام المضادة أرنب الأولية الموجهة ضد IP3R1 يمكن ربط الحواتم في القرب في واجهة MAM، ب) إضافة زوج من تحقيقات ربط القربالموجهة ضد الماوس ومفتش أرنب. وتعلق هذه التحقيقات جدائل الحمض النووي التي يمكن أن تشكل نماذج لربط من oligos الموصل. ج) حبلا الحمض النووي دائرية شكلت بعد ربط يمكن تضخيمها ود) تصور بواسطة المجهر بمثابة نقطة الفلورسنت باستخدام تكساس أليغنوكليوتيد] وصفت الأحمر. الرجاء انقر هنا لعرض نسخة أكبر من هذا الرقم.
تشبه في التجارب فحص الموقع قرب ربط يمكن القيام بها مع الزوج GRP75 / IP3R1 من الأجسام المضادة، وكذلك cyclophilin D (CypD) / الأجسام المضادة IP3R1، معتبرا أن تبين CypD للتفاعل مع مجمع IP3R / GRP75 / VDAC في واجهة MAM 12-14.
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
Collectively, our studies indicate that the in situ proximity ligation assay is truly a relevant strategy to follow and quantify endogenous ER-mitochondria interactions in fixed cells, without the need for using organelle-specific fluorophores or fluorescent proteins. The specific use of VDAC1/IP3R1 antibodies has been adapted to study ER-mitochondria interactions in HuH7 cells. However, alternative isoforms of VDAC and IP3R may be used, depending on the cell type. In this case, antibodies need to be validated b…
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
نشكر جميع الناس في مختبرنا الذي ساهم في تحسين والتحقق من صحة البروتوكول. وأيد هذا العمل من قبل INSERM وكالة أبحاث وطنية (وكالة الاستخبارات الوطنية-09-JCJC-0116 وكالة الاستخبارات الوطنية-11-BSV1-033-02). وأيد ET خلال شهادة الدكتوراه من قبل زمالة بحثية من الوزارة الفرنسية للتعليم العالي والبحوث.
Materials
| Formaldehyde | Sigma | F-8775 | |
| Glycine | Sigma | G-8898 | |
| Triton | Sigma | T8532 | |
| 35mm Glass bottom culture dishes | MatTeK corporation | P35G-0-14-C | |
| Blocking solution | Sigma | DUO-92004 or DUO-92002 | provided in the Duolink PLA probes, Sigma |
| VDAC1 antibody | Abcam | ab14734 | |
| IP3R1-H80 antibody | Santa Cruz | sc28614 | |
| CypD antibody | Abcam | ab110324 | |
| Grp75 antibody | Santa Cruz | sc13967 | |
| TBS 10X | euromedex | ET220 | Dilute to obtain 1X |
| Tween 100X | euromedex | 2001-B | dilute in TBS to obtain 0,01% |
| PLA Probes Mouse MINUS | Sigma | DUO-92004 | Duolink, Sigma |
| PLA Probes Rabbit PLUS | Sigma | DUO-92002 | Duolink, Sigma |
| Duolink detection reagents red | Sigma | DUO-92008 | Duolink, Sigma |
| Ligation solution | Sigma | DUO-92008 | Part of the Duolink detection reagents red, Sigma |
| Ligase | Sigma | DUO-92008 | Part of the Duolink detection reagents red, Sigma |
| Amplification solution | Sigma | DUO-92008 | Part of the Duolink detection reagents red, Sigma |
| Polymerase | Sigma | DUO-92008 | Part of the Duolink detection reagents red, Sigma |
| Duolink Mounting Medium | Sigma | DUO80102 | Duolink, Sigma |
| Softwares: | |||
| Blob-finder software | BlobFinder is a freely distributed software that can perform calculations on cells from fluorescence microscopy images. This software can be downloaded for free from The Centre for Image Analysis at Uppsala University who have developed the software and the work was supported by the EU FP6 Project ENLIGHT and Olink Bioscience. http://www.cb.uu.se/~amin/BlobFinder/index_files/Page430.htm | ||
| ImageJ software | Can be downloaded for free from: http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij/download.html |
References
- Bravo-Sagua, R., et al. Organelle communication: signaling crossroads between homeostasis and disease. The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology. 50, 55-59 (2014).
- Giorgi, C., et al. Mitochondria-associated membranes: composition, molecular mechanisms, and physiopathological implications. Antioxidants & redox signaling. 22, 995-1019 (2015).
- Phillips, M. J., Voeltz, G. K. Structure and function of ER membrane contact sites with other organelles. Nature reviews. Molecular cell biology. 17, 69-82 (2016).
- Cosson, P., et al. The RTM resistance to potyviruses in Arabidopsis thaliana: natural variation of the RTM genes and evidence for the implication of additional genes. PLoS One. 7, 39169 (2012).
- Mannella, C. A. Structure and dynamics of the mitochondrial inner membrane cristae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1763, 542-548 (2006).
- Csordas, G., et al. Structural and functional features and significance of the physical linkage between ER and mitochondria. The Journal of cell biology. 174, 915-921 (2006).
- Mannella, C. A., Buttle, K., Rath, B. K., Marko, M. Electron microscopic tomography of rat-liver mitochondria and their interaction with the endoplasmic reticulum. Biofactors. 8, 225-228 (1998).
- Rizzuto, R., et al. Close contacts with the endoplasmic reticulum as determinants of mitochondrial Ca2+ responses. Science. 280, 1763-1766 (1998).
- Wieckowski, M. R., Giorgi, C., Lebiedzinska, M., Duszynski, J., Pinton, P. Isolation of mitochondria-associated membranes and mitochondria from animal tissues and cells. Nat Protoc. 4, 1582-1590 (2009).
- Csordas, G., et al. Imaging interorganelle contacts and local calcium dynamics at the ER-mitochondrial interface. Mol Cell. 39, 121-132 (2010).
- Szabadkai, G., et al. Chaperone-mediated coupling of endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondrial Ca2+ channels. J Cell Biol. 175, 901-911 (2006).
- Tubbs, E., et al. Mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane (MAM) integrity is required for insulin signaling and is implicated in hepatic insulin resistance. Diabetes. 63, 3279-3294 (2014).
- Paillard, M., et al. Depressing Mitochondria-Reticulum Interactions Protects Cardiomyocytes From Lethal Hypoxia-Reoxygenation Injury. Circulation. 128, 1555-1565 (2013).
- Rieusset, J., et al. Disruption of calcium transfer from ER to mitochondria links alterations of mitochondria-associated ER membrane integrity to hepatic insulin resistance. Diabetologia. 59, 614-623 (2016).
- Allalou, A., Wahlby, C. BlobFinder, a tool for fluorescence microscopy image cytometry. Computer methods and programs in biomedicine. 94, 58-65 (2009).
- Theurey, P., et al. Mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes allow adaptation of mitochondrial metabolism to glucose availability in the liver. Journal of molecular cell biology. , (2016).
- de Brito, O. M., Scorrano, L. Mitofusin 2 tethers endoplasmic reticulum to mitochondria. Nature. 456, 605-610 (2008).
- Soderberg, O., et al. Direct observation of individual endogenous protein complexes in situ by proximity ligation. Nature methods. 3, 995-1000 (2006).
- De Pinto, V., Messina, A., Lane, D. J., Lawen, A. Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel (VDAC) in the plasma membrane. FEBS letters. 584, 1793-1799 (2010).
- Kaul, S. C., Taira, K., Pereira-Smith, O. M., Wadhwa, R. Mortalin: present and prospective. Experimental gerontology. 37, 1157-1164 (2002).

