Studie van endoplasmatisch reticulum en mitochondriën interacties door<em> In Situ</em> Proximity Ligatie Assay in gefixeerde cellen
Summary
Hier beschrijven we een werkwijze voor het visualiseren en kwantificeren gevoeligheid een endogene interacties tussen het endoplasmatisch reticulum en mitochondria in gefixeerde cellen. Het protocol is voorzien van een geoptimaliseerde in situ nabijheid ligation assay gericht op de inositol 1,4,5-trifosfaat receptor / glucose-gereguleerd eiwit 75 / voltage-afhankelijke anion kanaal / cyclofiline D-complex aan de mitochondria bijbehorende membraan interface.
Abstract
Structural interactions between the endoplasmic reticular (ER) and mitochondrial membranes, in domains known as mitochondria-associated membranes (MAM), are crucial hubs for cellular signaling and cell fate. Particularly, these inter-organelle contact sites allow the transfer of calcium from the ER to mitochondria through the voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC)/glucose-regulated protein 75 (GRP75)/inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor (IP3R) calcium channeling complex. While this subcellular compartment is under intense investigation in both physiological and pathological conditions, no simple and sensitive method exists to quantify the endogenous amount of ER-mitochondria contact in cells. Similarly, MAMs are highly dynamic structures, and there is no suitable approach to follow modifications of ER-mitochondria interactions without protein overexpression. Here, we report an optimized protocol based on the use of an in situ proximity ligation assay to visualize and quantify endogenous ER-mitochondria interactions in fixed cells by using the close proximity between proteins of the outer mitochondrial membrane (VDAC1) and of the ER membrane (IP3R1) at the MAM interface. Similar in situ proximity ligation experiments can also be performed with the GRP75/IP3R1 and cyclophilin D/IP3R1 pairs of antibodies. This assay provides several advantages over other imaging procedures, as it is highly specific, sensitive, and suitable to multiple-condition testing. Therefore, the use of this in situ proximity ligation assay should be helpful to better understand the physiological regulations of ER-mitochondria interactions, as well as their role in pathological contexts.
Introduction
Mitochondria en het endoplasmatisch reticulum (ER) zijn niet onafhankelijk organellen in de cel, maar ze omgaan structureel en functioneel in contact plaatsen gedefinieerd als mitochondriën verbonden endoplasmatisch reticulum membranen (MAM). In feite, MTM overeen met gebieden waar de membranen van het ER en mitochondria nauw apposed, zodat interacties tussen eiwitten van beide kanten. Toch weet de membranen van deze organellen niet fuseren binnen deze regio's, zodat ze behouden hun afzonderlijke entiteiten. De MTM spelen een cruciale rol in de calcium (Ca 2+) en fosfolipiden transfer van ER naar mitochondriën, invloed energiemetabolisme en celoverleving 1-3.
De associatie tussen het ER en mitochondria werd eerst gevisualiseerd in de jaren 1970 met elektronenmicroscopie. Sindsdien, transmissie-elektronenmicroscopie 4,5, electron tomography 6,7 of immuno-lokalisatie van ER en mitochondriën-specifieke fluorofoors / fluorescente proteïnen werden 8 klassiek gebruikt om ER-mitochondriën interacties te bestuderen. Een ander bruikbaar middel voor de analyse van MAM is gebaseerd op het gebruik van subcellulaire fractionering. Het laat de isolatie van MAM fracties door differentiële ultracentrifugatie gekoppeld met een Percoll gradiënt 9. De eindproduct bevat MAM verrijkte fracties, dan zuivere fracties. In totaal hebben deze strategieën niet bijzonder gevoelig en / of kwantitatieve en zijn lastig om grote screening. Alternatief genetische benadering en de geneesmiddel-geïnduceerd fluorescent inter-organel linkers zijn ontstaan, maar niet de analyse van organel interacties zodat het endogene expressieniveaus van eiwitten 10.
Op basis van de ontdekking Szabadkai's van de IP3R / GRP75 / VDAC complex in het MAM 11, ontwikkelden we een kwantitatieve methode om de ER-mitochondria interacties te analyseren. We gebruikten de in situ omgeving ligatiOp assay voor het detecteren en kwantificeren van interacties tussen VDAC1 en IP3R1 twee organel-oppervlakte-eiwitten betrokken zijn bij de Ca2 + -channeling complex in het MAM interface gefixeerde cellen 12. Samengevat, zijn we gehybridiseerd VDAC1 het buitenste mitochondriale membraan (muis anti-VDAC1 primair antilichaam) en IP3R1 het ER membraan (konijn anti-IP3R1 primaire antilichaam) (Figuur 1, panel a). Vervolgens wordt aan de test, voegden we zowel anti-muis en anti-konijn IgG (muis en konijn nabijheid ligatie assay probes) die zijn geconjugeerd met complementaire oligonucleotide extensies. Als de twee eiwitten gericht zijn op een afstand onder 40 nm, kunnen de oligonucleotiden hybridiseren met de later toegevoegde connector oligo om de vorming van een circulair DNA-matrijs (Figuur 1, paneel b) toestaan. Deze circulaire DNA molecuul wordt geligeerd en geamplificeerd, waardoor een enkelstrengs DNA product covalent aan één van de probes nabijheid (Figuur 1, panel c) </strong>. Aangezien de afstand tussen het ER en mitochondriën bij de MAM-interface varieert van 10 nm tot 25 nm 6, nabijheid ligatie en amplificatie kan leiden tot daaropvolgende detectie door hybridisatie van Texas rood gemerkte oligonucleotiden probes (Figuur 1, panel d ). Elke fluorescerende stip staat wisselwerkingen tussen VDAC1 / IP3R1, waardoor de kwantificering van in situ ER-mitochondriën interacties in individuele cellen.
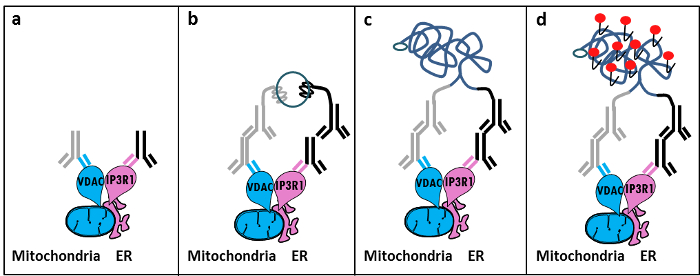
Figuur 1: Schematische weergave van de Opsporing van het endoplasmatisch reticulum-mitochondria interacties van In Situ Proximity Ligatie Assay. a) Een muis primair antilichaam gericht tegen VDAC1 en een konijn primair antilichaam tegen IP3R1 kan binden aan hun epitopen in de nabijheid van het MAM-interface, b) de toevoeging van een paar proximity ligatieprobesgericht tegen muizen en konijnen IgG. Deze sondes DNA strengen die sjablonen voor de ligatie van oligonucleotiden connector kan vormen verbonden. c) De circulaire DNA-streng gevormd na ligatie kunnen worden geamplificeerd en d) gevisualiseerd door microscopie als fluorescerend dot met Texas-rood gemerkte oligonucleotiden. Klik hier om een grotere versie van deze figuur te bekijken.
Vertaald in situ nabijheid ligatie assay experimenten kunnen worden uitgevoerd met de GRP75 / IP3R1 paar antilichamen, evenals cyclofiline D (CypD) / IP3R1 antilichamen, aangezien CypD bleek interactie met de IP3R / GRP75 / VDAC complex in het MAM-interface 12-14.
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
Collectively, our studies indicate that the in situ proximity ligation assay is truly a relevant strategy to follow and quantify endogenous ER-mitochondria interactions in fixed cells, without the need for using organelle-specific fluorophores or fluorescent proteins. The specific use of VDAC1/IP3R1 antibodies has been adapted to study ER-mitochondria interactions in HuH7 cells. However, alternative isoforms of VDAC and IP3R may be used, depending on the cell type. In this case, antibodies need to be validated b…
Declarações
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
Wij danken alle mensen in ons laboratorium die hebben bijgedragen aan het optimaliseren en valideren van het protocol. Dit werk werd ondersteund door INSERM en de nationale onderzoeksbureau (ANR-09-JCJC-0116 EN ANR-11-BSV1-033-02). ET werd gesteund tijdens haar promotieonderzoek door een onderzoeksbeurs van het Franse ministerie van hoger onderwijs en onderzoek.
Materials
| Formaldehyde | Sigma | F-8775 | |
| Glycine | Sigma | G-8898 | |
| Triton | Sigma | T8532 | |
| 35mm Glass bottom culture dishes | MatTeK corporation | P35G-0-14-C | |
| Blocking solution | Sigma | DUO-92004 or DUO-92002 | provided in the Duolink PLA probes, Sigma |
| VDAC1 antibody | Abcam | ab14734 | |
| IP3R1-H80 antibody | Santa Cruz | sc28614 | |
| CypD antibody | Abcam | ab110324 | |
| Grp75 antibody | Santa Cruz | sc13967 | |
| TBS 10X | euromedex | ET220 | Dilute to obtain 1X |
| Tween 100X | euromedex | 2001-B | dilute in TBS to obtain 0,01% |
| PLA Probes Mouse MINUS | Sigma | DUO-92004 | Duolink, Sigma |
| PLA Probes Rabbit PLUS | Sigma | DUO-92002 | Duolink, Sigma |
| Duolink detection reagents red | Sigma | DUO-92008 | Duolink, Sigma |
| Ligation solution | Sigma | DUO-92008 | Part of the Duolink detection reagents red, Sigma |
| Ligase | Sigma | DUO-92008 | Part of the Duolink detection reagents red, Sigma |
| Amplification solution | Sigma | DUO-92008 | Part of the Duolink detection reagents red, Sigma |
| Polymerase | Sigma | DUO-92008 | Part of the Duolink detection reagents red, Sigma |
| Duolink Mounting Medium | Sigma | DUO80102 | Duolink, Sigma |
| Softwares: | |||
| Blob-finder software | BlobFinder is a freely distributed software that can perform calculations on cells from fluorescence microscopy images. This software can be downloaded for free from The Centre for Image Analysis at Uppsala University who have developed the software and the work was supported by the EU FP6 Project ENLIGHT and Olink Bioscience. http://www.cb.uu.se/~amin/BlobFinder/index_files/Page430.htm | ||
| ImageJ software | Can be downloaded for free from: http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij/download.html |
Referências
- Bravo-Sagua, R., et al. Organelle communication: signaling crossroads between homeostasis and disease. The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology. 50, 55-59 (2014).
- Giorgi, C., et al. Mitochondria-associated membranes: composition, molecular mechanisms, and physiopathological implications. Antioxidants & redox signaling. 22, 995-1019 (2015).
- Phillips, M. J., Voeltz, G. K. Structure and function of ER membrane contact sites with other organelles. Nature reviews. Molecular cell biology. 17, 69-82 (2016).
- Cosson, P., et al. The RTM resistance to potyviruses in Arabidopsis thaliana: natural variation of the RTM genes and evidence for the implication of additional genes. PLoS One. 7, 39169 (2012).
- Mannella, C. A. Structure and dynamics of the mitochondrial inner membrane cristae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1763, 542-548 (2006).
- Csordas, G., et al. Structural and functional features and significance of the physical linkage between ER and mitochondria. The Journal of cell biology. 174, 915-921 (2006).
- Mannella, C. A., Buttle, K., Rath, B. K., Marko, M. Electron microscopic tomography of rat-liver mitochondria and their interaction with the endoplasmic reticulum. Biofactors. 8, 225-228 (1998).
- Rizzuto, R., et al. Close contacts with the endoplasmic reticulum as determinants of mitochondrial Ca2+ responses. Science. 280, 1763-1766 (1998).
- Wieckowski, M. R., Giorgi, C., Lebiedzinska, M., Duszynski, J., Pinton, P. Isolation of mitochondria-associated membranes and mitochondria from animal tissues and cells. Nat Protoc. 4, 1582-1590 (2009).
- Csordas, G., et al. Imaging interorganelle contacts and local calcium dynamics at the ER-mitochondrial interface. Mol Cell. 39, 121-132 (2010).
- Szabadkai, G., et al. Chaperone-mediated coupling of endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondrial Ca2+ channels. J Cell Biol. 175, 901-911 (2006).
- Tubbs, E., et al. Mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane (MAM) integrity is required for insulin signaling and is implicated in hepatic insulin resistance. Diabetes. 63, 3279-3294 (2014).
- Paillard, M., et al. Depressing Mitochondria-Reticulum Interactions Protects Cardiomyocytes From Lethal Hypoxia-Reoxygenation Injury. Circulation. 128, 1555-1565 (2013).
- Rieusset, J., et al. Disruption of calcium transfer from ER to mitochondria links alterations of mitochondria-associated ER membrane integrity to hepatic insulin resistance. Diabetologia. 59, 614-623 (2016).
- Allalou, A., Wahlby, C. BlobFinder, a tool for fluorescence microscopy image cytometry. Computer methods and programs in biomedicine. 94, 58-65 (2009).
- Theurey, P., et al. Mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes allow adaptation of mitochondrial metabolism to glucose availability in the liver. Journal of molecular cell biology. , (2016).
- de Brito, O. M., Scorrano, L. Mitofusin 2 tethers endoplasmic reticulum to mitochondria. Nature. 456, 605-610 (2008).
- Soderberg, O., et al. Direct observation of individual endogenous protein complexes in situ by proximity ligation. Nature methods. 3, 995-1000 (2006).
- De Pinto, V., Messina, A., Lane, D. J., Lawen, A. Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel (VDAC) in the plasma membrane. FEBS letters. 584, 1793-1799 (2010).
- Kaul, S. C., Taira, K., Pereira-Smith, O. M., Wadhwa, R. Mortalin: present and prospective. Experimental gerontology. 37, 1157-1164 (2002).

