Raggiungimento di pressioni Moderate in vasi sigillati utilizzando ghiaccio secco come una fonte di solido CO2
Summary
Qui presentiamo un protocollo per l’esecuzione di reazioni in recipienti di reazione semplice sotto basse a moderate pressioni di CO2. Le reazioni possono essere eseguite in una varietà di navi semplicemente amministrando l’anidride carbonica sotto forma di ghiaccio secco, senza la necessità di attrezzature costose o elaborata o set-up.
Abstract
Qui è presentato una strategia generale per eseguire reazioni sotto lieve a moderata CO2 pressioni con ghiaccio secco. Questa tecnica previene l’esigenza di attrezzature specializzate raggiungere pressioni modeste e può essere utilizzata anche per raggiungere pressioni più elevate in attrezzature più specializzate e più robusti recipienti di reazione. Alla fine della reazione, le fiale possono essere facilmente depressurizzate aprendo a temperatura ambiente. Nell’esempio presente CO2 funge da un presunto gruppo dirigente così come un modo per passivare substrati di ammina, impedendo l’ossidazione durante la reazione organometallica. Oltre ad essere facilmente aggiunto, il gruppo dirigente viene rimosso anche sotto vuoto, prevenente l’esigenza di vasta purificazione rimuovere il gruppo dirigente. Questa strategia permette la facile arilazione γ-C(sp3)-H di ammine alifatiche e ha il potenziale per essere applicato ad una varietà di altre reazioni dell’ammina-basato.
Introduction
L’uso di composti gassosi nelle reazioni chimiche in genere richiede attrezzature specializzate e procedure1,2. A bilancia da banco, alcuni gas possono essere aggiunti direttamente da un serbatoio usando un regolatore di alta pressione3. Un metodo alternativo è quello di condensare il gas in condizioni criogeniche4,5. Anche se utile, queste strategie richiedono l’uso di reattori a pressione specializzati con valvole, che possono essere il costo proibitivo per l’esecuzione di numerose reazioni in parallelo. Di conseguenza questo può notevolmente rallentare il tasso al quale reazione procedere con lo screening. Di conseguenza, chimici hanno trovato opportuno introdurre questi composti utilizzando metodi alternativi. Ammoniaca può essere aggiunto a reazioni utilizzando sali di ammonio diversi carbossilato, approfittando del debole equilibrio tra questi sali e ammoniaca libera6. Idrogenazione di trasferimento è una strategia importante per le reazioni di riduzione di olefine, carbonilico e gruppi nitro che elude l’uso di gas di idrogeno infiammabile con composti come formiato di ammonio o idrazina come elementi portanti di H27. Un altro gas di interesse in questa zona è il monossido di carbonio8 -CO può essere generato in situ di liberazione da metallo carbonilici complessi9,10, o in alternativa può essere generato dal decarbonylation da fonti quali formiati e formamides11,12,13 o cloroformio14,15.
Un gas che non ha goduto di sviluppo significativo in questo senso è anidride carbonica16. Una ragione di questo è che molte trasformazioni che coinvolgono CO2 inoltre richiedono pressioni e temperature elevate e quindi automaticamente sono relegate a reattori specializzati17,18. I recenti sforzi per sviluppare catalizzatori più reattivi, tuttavia, hanno facilitato in esecuzione molte di queste reazioni sotto pressioni atmosferiche di CO219,20,21,22. Abbiamo recentemente scoperto una reazione in cui anidride carbonica potrebbe essere utilizzato per mediare il γ-C (sp3) – H arilazione di ammine alifatiche23. Questa strategia era previsto per combinare i vantaggi di un approccio statico gruppo dirigente cui ammide24,25,26,27,28, sulfamidico 29 , 30 , 31 , 32, tiocarbonile33,34o idrazone35-basato dirigere gruppi (robustezza chimica), con la facilità di un gruppo dirigente temporanei (passaggio in diminuzione economia)36, 37,38,39.
Anche se la reazione potrebbe verificarsi sotto pressione atmosferica di CO2, la necessità di un set-up di Schlenk alle reazioni di schermo si dimostrò eccessivamente lento. Inoltre, aumentando la pressione leggermente portata a migliorato rendimenti di reazione, ma non poteva essere raggiunti facilmente utilizzando una linea di Schlenk. Abbiamo quindi cercato una strategia alternativa, e successivamente identificato quel ghiaccio secco potrebbe essere facilmente utilizzato come una solida fonte di CO2 che può essere aggiunto a una varietà di recipienti di reazione per introdurre la quantità necessaria di biossido di carbonio per raggiungere moderato pressioni (Figura 1). Anche se sottoutilizzato in sintesi, una simile strategia è abbastanza comune come un metodo per generare liquido CO2 per estrazione e cromatografia applicazioni40,41,42,43, 44. Utilizzando questa strategia ha permesso che il nostro gruppo a rapidamente schermo tantissimi reazioni in parallelo, mentre la capacità di accesso moderato CO2 pressioni di tra 2-20 atmosfere sono stati fondamentale per migliorare i rendimenti delle reazioni. In queste condizioni, sia primario (1°) e ammine secondarie (2°) possono essere arylated con elettroni ricchi e alogenuri arilici povero elettrone.
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
Utilizzo di van der Waals equazione di stato, la pressione approssimativa di questi sistemi può essere calcolato45
EQ. 1: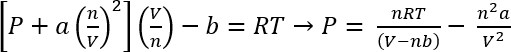
Le condizioni nel protocollo n. 1, possiamo supporre 26,3 mg di CO2 dà n = 5,98 x 10-4 moli
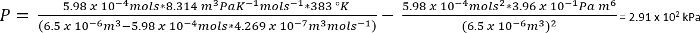
Seco…
Declarações
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
Gli autori desiderano riconoscere finanziamento di Start-up da The University of Toledo, nonché fondi dalla Herman Frasch Foundation di American Chemical Society in supporto parziale di questo lavoro. Mr. Thomas Kina è riconosciuto per la sua assistenza con lo sviluppo di un adatto manometro per la misurazione delle pressioni di reazione. Mr. Steve Modar è ringraziato per utili discussioni.
Materials
| 7.5 mL Sample Vial with Screw Cap (Thermoset) | Qorpak | GLC-00984 | Can be reused. |
| 40 mL Sample Vial with Screw Cap (Thermoset) | Qorpak | GLC-01039 | Can be reused. |
| Pressure Tube, #15 Thread, 7" Long, 25.4 mm O.D. | Ace Glass | 8648-06 | Can be reused. |
| Pie-Block for 2 Dram Vials | ChemGlass | CG-1991-P14 | Can be reused. |
| Pie-Block for 10 Dram Vials | ChemGlass | CG-1991-P12 | Can be reused. |
| 3.2 mm PTFE Disposable Stir Bars | Fisher | 14-513-93 | Can be reused. |
| C-MAG HS 7 Control Hotplate | IKA | 20002695 | |
| Analytical Weighing Balance | Sartorius | QUINTIX2241S | |
| Double-Ended Micro-Tapered Spatula | Fisher Scientific | 21-401-10 | |
| Hei-VAP Advantage – Hand Lift Model with G5 Dry Ice Condenser Rotary Evaporator | Heidolph | 561-01500-00 | |
| Bump Trap 14/20 Joint | ChemGlass | CG-1322-01 | |
| tert-Amyl amine | Alfa Aesar | B24639-14 | Used as received. |
| 2-Methyl-N-(3-methylbenzyl)butan-2-amine | N/A | N/A | Prepared from reductive amination of tert-amyl amine and 3-tolualdehyde in the presence of sodium borohydride in methanol. |
| Palladium Acetate | Chem-Impex International, Inc. | 4898 | Used as received. |
| Silver Trifluoroacetate | Oakwood Chemicals | 007271 | Used as received. |
| Phenyl Iodide | Oakwood Chemicals | 003461 | Used as received. |
| Acetic Acid | Fisher Chemical | A38 | Used as received. |
| 1,1,1,3,3,3-Hexafluoroisopropanol | Oakwood Chemicals | 003409 | Used as received. |
| Deionized Water | Obtained from in-house deionized water system. | ||
| Dry Ice | Carbonic Enterprises Dry Ice Inc. | Non-food grade dry ice. | |
| Concentrated Hydrochloric Acid | Fisher Chemical | A144SI | Diluted to a 1.2 M solution prior to use. |
| Diethyl Ether, Certified | Fisher Chemical | E138 | Used as received. |
| Hexanes, Certified ACS | Fisher Chemical | H292 | Used as received. |
| Saturated Ammonium Hydroxide | Fisher Chemical | A669 | Used as received. |
| Dichloromethane | Fisher Chemical | D37 | Used as received. |
| Sodium Sulfate, Anhydrous | Oakwood Chemicals | 044702 | Used as received. |
| 250 mL Separatory Funnel | Prepared in-house by staff glassblower. | ||
| 100 mL Round Bottom Flask | Prepared in-house by staff glassblower. | ||
| Scientific Disposable Funnel | Caplugs | 2085136030 | |
| Borosilicate Glass Scintillation Vials, 20 mL | Fisher Scientific | 03-337-15 | |
| 5 mm O.D. Thin Walled Precision NMR Tubes | Wilmad | 666000575 | |
| Chloroform-d | Cambridge Isotope Laboratories, Inc. | DLM-7 | Used as received. |
Referências
- Verboom, W. Selected Examples of High-Pressure Reactions in Glass Microreactors. Chemical Engineering and Technology. 32 (11), 1695-1701 (2009).
- Schettino, V., Bini, R. Constraining Molecules at the Closest Approach: Chemistry at High Pressure. Chemical Society Reviews. 36, 869-880 (2007).
- Hemminger, O., Marteel, A., Mason, M. R., Davies, J. A., Tadd, A. R., Abraham, M. A. Hydroformylation of 1-Hexene in Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Using a Heterogeneous Rhodium Catalyst. 3. Evaluation of Solvent Effects. Green Chemistry. 4, 507-512 (2002).
- Mo, F., Dong, G. Regioselective Ketone α-Alkylation with Simple Olefins via Dual Activation. Science. 345 (6192), 68-72 (2014).
- Schultz, A. G., Kirincich, S. J., Rahm, R. Asymmetric Organic Synthesis. Preparation and Birch Reduction-Alkylation of 2-Methyl-3,4-Dihydroisoquinolin-1-ones. Tetrahedron Letters. 36 (26), 4551-4554 (1995).
- Dong, L., Aleem, S., Fink, C. A. Microwave-Accelerated Reductive Amination Between Ketones and Ammonium Acetate. Tetrahedron Letters. 51 (39), 5210-5212 (2010).
- Wang, D., Astruc, D. The Golden Age of Transfer Hydrogenation. Chemical Reviews. 115 (13), 6621-6686 (2015).
- Morimoto, T., Kakiuchi, K. Evolution of Carbonylation Catalysis: No Need for Carbon Monoxide. Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 43 (42), 5580-5588 (2004).
- Iranpoor, N., Firouzabadi, H., Motevalli, S., Talebi, M. Palladium-Free Aminocarbonylation of Aryl, Benzyl, and Styryl Iodides and Bromides by Amines Using Mo(CO)6 and Norbornadiene. Tetrahedron. 69 (1), 418-426 (2013).
- Ren, W., Yamane, M. Mo(CO)6-Mediated Carbamoylation of Aryl Halides. Journal of Organic Chemistry. 75 (24), 8410-8415 (2010).
- Wang, H., Dong, B., Wang, Y., Li, J., Shi, Y. A Palladium-Catalyzed Regioselective Hydroesterification of Alkenylphenols to Lactones with Phenyl Formate as CO Source. Organic Letters. 16 (1), 186-189 (2014).
- Zhang, Y., Chen, J. -. L., Chen, Z. -. B., Zhu, Y. -. M., Ji, S. -. J. Palladium-Catalyzed Carbonylative Annulation Reactions Using Aryl Formate as a CO Source: Synthesis of 2-Substituted Indene-1,3(2H)-Dione Derivatives. Journal of Organic Chemistry. 80 (21), 10643-10650 (2015).
- Wan, Y., Alterman, M., Larhed, M., Hallberg, A. Dimethylformamide as a Carbon Monoxide Source in Fast Palladium-Catalyzed Aminocarbonylations of Aryl Bromides. Journal of Organic Chemistry. 67 (17), 6232-6235 (2002).
- Gockel, S. N., Hull, K. L. Chloroform as a Carbon Monoxide Precursor: In or Ex Situ Generation of CO for Pd-Catalyzed Aminocarbonylations. Organic Letters. 17 (13), 3236-3239 (2015).
- Zhao, H., Du, H., Yuan, X., Wang, T., Han, W. Iron-Catalyzed Carbonylation of Aryl Halides with Arylborons Using Stoichiometric Chloroform as the Carbon Monoxide Source. Green Chemistry. 18, 5782-5787 (2016).
- Chen, P., Xu, C., Yin, H., Gao, X., Qu, L. Shock Induced Conversion of Carbon Dioxide to Few Layer Graphene. Carbon. , 471-476 (2017).
- Iijima, T., Yamaguchi, T. Efficient Regioselective Carboxylation of Phenol to Salicylic Acid with Supercritical CO2 in the Presence of Alumnium Bromide. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical. 295 (1-2), 52-56 (2008).
- Jevtovikj, I., Manzini, S., Hanauer, M., Rominger, F., Schaub, T. Investigations on the Catalytic Carboxylation of Olefins with CO2 Towards α, β-Unsaturated Carboxylic Acid Salts: Characterization of Intermediates and Ligands as well as Substrate Effects. Dalton Transactions. 44, 11083-11094 (2015).
- Juliá-Hernández, F., Moragas, T., Cornella, J., Martin, R. Remote Carboxylation of Halogenated Aliphatic Hydrocarbons with Carbon Dioxide. Nature. 545, 84-88 (2017).
- North, M., Pasquale, R. Mechanism of Cyclic Carbonate Synthesis from Epoxides and CO2. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 48 (16), 2946-2948 (2009).
- Yeung, C. S., Dong, V. M. Beyond Aresta’s Complex: Ni- and Pd-Catalyzed Organozinc Coupling to CO2. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 130 (25), 7826-7827 (2008).
- Zhu, D. -. Y., Fang, L., Han, H., Wang, Y., Xia, J. -. B. Reductive CO2 Fixation via Tandem C-C and C-N Bond Formation: Synthesis of Spiro-Indopyrrolidines. Organic Letters. 19 (16), 4259-4262 (2017).
- Kapoor, M., Liu, D., Young, M. C. Carbon Dioxide Mediated C(sp3)–H Arylation of Amine Substrates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. , (2018).
- Zhang, Y. -. F., Zhao, H. -. W., Wang, H., Wei, J. -. B., Shi, Z. -. J. Readily Removable Directing Group Assisted Chemo- and Regioselective C(sp3)-H Activation by Palladium Catalysis. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 54 (46), 13686-13690 (2015).
- He, G., Chen, G. A Practical Strategy for the Structural Diversification of Aliphatic Scaffolds Through the Palladium-Catalyzed Picolinamide-Directed Remote Functionalization of Unactivated C(sp3)-H Bonds. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 50 (22), 5192-5196 (2011).
- Nack, W. A., Wang, X., Wang, B., He, G., Cheng, G. Palladium-Catalyzed Picolinamide-Directed Iodination of Remote ortho-C-H Bonds of Arenes: Synthesis of Tetrahydroquinolines. Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry. 12, 1243-1249 (2016).
- Feng, P., Li, M., Ge, H. Room Temperature Palladium-Catalyzed Decarboxylative ortho-Acylation of Acetanilides with α-Oxocarboxylic Acids. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 132 (34), 11898-11899 (2010).
- Coomber, C. E., Benhamou, L., Bučar, D. -. K., Smith, P. D., Porter, M. J., Sheppard, T. D. Silver-Free Palladium-Catalyzed C(sp3)-H Arylation of Saturated Bicyclic Amine Scaffolds. Journal of Organic Chemistry. 83 (5), 2495-2503 (2018).
- Mei, T. -. S., Wang, X., Yu, J. -. Q. Pd(II)-Catalyzed Amination of C-H Bonds Using Single-Electron or Two-Electron Oxidants. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 131 (31), 10806-10807 (2009).
- Xie, W., Yang, J., Wang, B., Li, B. Regioselective Ortho Olefination of Aryl Sulfonamide via Rhodium-Catalyzed Direct C-H Bond Activation. Journal of Organic Chemistry. 79 (17), 8278-8287 (2014).
- Rodriguez, N., Romero-Revilla, J. A., Fernández-Ibáñez, M. &. #. 1. 9. 3. ;., Carretero, J. C. Palladium-Catalyzed N-(2-pyridyl)sulfonyl-Directed C(sp3)-H γ-Arylation of Amino Acid Derivatives. Chemical Science. 4, 175-179 (2013).
- Zheng, Y., Song, W., Zhu, Y., Wei, B., Xuan, L. Pd-Catalyzed Acetoxylation of γ-C(sp3)-H Bonds of Amines Directed by a Removable Bts-Protecting Group. Journal of Organic Chemistry. 83 (4), 2448-2454 (2018).
- Jain, P., Verma, P., Xia, G., Yu, J. -. Q. Enantioselective Amine α-Functionalization Via Palladium-Catalysed C-H Arylation of Thioamides. Nature Chemistry. 9, 140-144 (2017).
- Tran, A. T. Practical Alkoxythiocarbonyl Auxiliaries for Ir(I)-Catalyzed C-H Alkylation of Azacycles. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 56 (35), 10530-10534 (2017).
- Huang, Z., Wang, C., Dong, G. A Hydrazone-Based exo-Directing Group Strategy for β-C-H Oxidation of Aliphatic Amines. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 55 (17), 5299-5303 (2016).
- Xu, Y., Young, M. C., Wang, C., Magness, D. M., Dong, G. Catalytic C(sp3)-H Arylation of Free Primary Amines via an in situ Generated Exo-Directing Group. Chemie International Edition. 55 (31), 9084-9087 (2016).
- Liu, Y., Ge, H. Site-Selective C-H Arylation of Primary Aliphatic Amines Enabled by a Catalytic Transient Directing Group. Nature Chemistry. 9, 26-32 (2017).
- Wu, Y., Chen, Y. -. Q., Liu, T., Eastgate, M. D., Yu, J. -. Q. Pd-Catalyzed γ-C(sp3)-H Arylation of Free Amines Using a Transient Directing Group. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 138 (44), 14554-14557 (2016).
- Yada, A., Liao, W., Sato, Y., Murakami, M. Buttressing Salicylaldehydes: A Multipurpose Directing Group for C(sp3)-H Bond Activation. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 56 (4), 1073-1076 (2017).
- Baldwin, B. W., Kuntzleman, T. S. Liquid CO2 in Centrifuge Tubes: Separation of Chamazulene from Blue Tansy (Tanacetum annum) Oil via Extraction and Thin-Layer Chromatography. Journal of Chemical Education. 95 (4), 620-624 (2018).
- McKenzie, L. C., Thompson, J. E., Sullivan, R., Hutchison, J. E. Green Chemical Processing in the Teaching Laboratory: A Convenient Liquid CO2 Extraction of Natural Products. Green Chemistry. 6, 355-358 (2004).
- Hudson, R., Ackerman, H. M., Gallo, L. K., Gwinner, A. S., Krauss, A., Sears, J. D., Bishop, A., Esdale, K. N., Katz, J. L. CO2 Dry Cleaning: A Benign Solvent Demonstration Accessible to K-8 Audiences. Journal of Chemical Education. 94, 480-482 (2017).
- Barcena, H., Chen, P. An Anesthetic Drug Demonstration and an Introductory Antioxidant Activity Experiment with "Eugene, the Sleepy Fish.". Journal of Chemical Education. 93, 202-205 (2016).
- Bodsgard, B. R., Lien, N. R., Waulters, Q. T. Liquid CO2 Extraction and NMR Characterization of Anethole from Fennel Seed: A General Chemistry Laboratory. Journal of Chemical Education. 93, 397-400 (2016).
- Fishbane, P. M., Gasiorowicz, S. G., Thornton, S. T. . Physics for Scientists and Engineers. , (2005).
- Rumpf, B., Xia, J., Maurer, G. Solubility of Carbon Dioxide in Aqueous Solutions Containing Acetic Acid or Sodium Hydroxide in the Temperature Range from 313 to 433 K and at Total Pressures up to 10 MPa. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research. 37, 2012-2019 (1998).
- Luo, J., Larrosa, I. C-H Carboxylation of Aromatic Compounds Through CO2 Fixation. ChemSusChem: Chemistry & Sustainability, Energy & Materials. 10, 3317-3332 (2017).
- Manjolinho, F., Arndt, M., Gooßen, K., Gooßen, L. J. Catalytic C-H Carboxylation of Terminal Alkynes with Carbon Dioxide. ACS Catalysis. 2, 2014-2021 (2012).
- Banerjee, A., Dick., G. R., Yoshino, T., Kanan, M. W. Carbon Dioxide Utilization via Carbonate-Promoted C-H Carboxylation. Nature. 531, 215-219 (2016).
- Fei, H., Sampson, M. D., Lee, Y., Kubiak, C. P., Cohen, S. M. Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction to Formate Using a Mn(I) Molecular Catalyst in a Robust Metal-Organic Framework. Inorganic Chemistry. 54, 6821-6828 (2015).
- Chabolla, S. A., Yang, J. Y. For CO2 Reduction, Hydrogen-Bond Donors Do the Trick. ACS Central Science. 4, 315-317 (2018).
- Kim, D., Kley, C. S., Li, Y., Yang, P. Copper Nanoparticle Ensembles for Selective Electroreduction of CO2 to C2-C3 Products. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. , C2-C3 (2017).
- Liu, Q., Wu, L., Jackstell, R., Beller, M. Using carbon dioxide as a building block in organic synthesis. Nature Communications. 6, 5933-5945 (2015).
- Hâncu, D., Green, J., Beckman, E. J. H2O2 in CO2 Sustainable Production and Green Reactions. Accounts of Chemical Research. 35, 757-764 (2002).
- Ballivet-Tkatchenko, D., Camy, S., Condoret, J. S., Lichtofouse, E., Scwarzbauer, J., Robert, D. Carbon Dioxide, a Solvent and Synthon for Green Chemistry. Environmental Chemistry. , 541-552 (2005).
- Hyatt, J. A. Liquid and Supercritical Carbon Dioxide as Organic Solvents. Journal of Organic Chemistry. 49, 5097-5101 (1984).

