전기 화학적 에칭 및 전자 충격 이온화 샤프 전계 방출 포인트의 특성
Summary
A method for electrochemically etching field emission tips is presented. Etching parameters are characterized and the operation of the tips in field emission mode is investigated.
Abstract
A new variation of the drop-off method for fabricating field emission points by electrochemically etching tungsten rods in a NaOH solution is described. The results of studies in which the etching current and the molarity of the NaOH solution used in the etching process were varied are presented. The investigation of the geometry of the tips, by imaging them with a scanning electron microscope, and by operating them in field emission mode is also described. The field emission tips produced are intended to be used as an electron beam source for ion production via electron impact ionization of background gas or vapor in Penning trap mass spectrometry applications.
Introduction
예리한 팁 또는 포인트 오랫동안 이러한 필드 이온 현미경 (FIM) (1)과, 주사 터널링 현미경 (STM)이, 다양한 재료의 예리한 팁을 제조하는 기술의 범위로 현미경 애플리케이션에서 사용 된 3가 개발되었다. 이 첨예도 그들에 고전압을인가하여 전계 전자 방출 지점 (FEPs)로서 동작하고 편리한 전자빔 원의 역할을 할 수있다. 같은 소스의 하나의 응용 프로그램은 전자 충격 이온화 (EII)를 통해 이온 생산이다. FEP를 열 방출에 의해 생성 된 온도 변화는 바람직하지 않은 응용 프로그램에서 특히 유리하다. 예를 들면, 고정밀의 배경 페닝 가스 또는 증기의 EII 통해 이온 생산 4,5- 트랩.
FEPs 제조하는 간단한 방법은 전기 화학적 수산화 나트륨 (NaOH로) 용액에 텅스텐 봉을 에칭한다. 이 방법으로 상대적으로 구현이 간단적당한 장비는 매우 신뢰성 있고, 재현성있는 것으로 밝혀졌다. 다수의 방법이 문헌에 기재되어 있으며이 기술에 관한 개선도 6을 계속 표시. 여기서 우리는 NaOH 용액에 텅스텐 팁의 전기 화학적 에칭하는 방법을 설명합니다. 우리의 방법은 라멜라 드롭 오프 기술 7,8의 변화 및 부유 계층 기술 9,10입니다. 이러한 두 가지 방법과 마찬가지로 하나의 에칭 과정에서이 팁의 생산을 가능하게한다. 팁을 에칭하기위한 실험 장치의 그림은 그림 1과 같다.
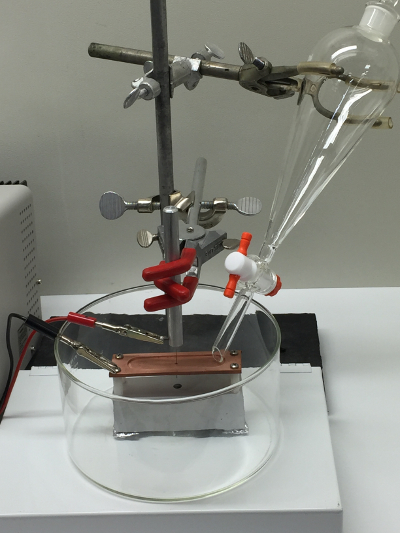
그림 1. 에칭 장치. NaOH 용액과 텅스텐 막대의 전기 화학적 에칭에 사용되는 실험 장치의 사진. 를 클릭하십시오여기이 그림의 더 큰 버전을 볼 수 있습니다.
수성 NaOH를베이스에 텅스텐의 전기 화학적 에칭은 두 단계 과정을 통해 발생한다. 우선, 중간 텅스텐 산화물이 형성되며, 둘째,이 산화물은 비 전기 화학적 가용성 텅스텐 음이온을 형성하도록 용해된다. 이 프로세스는 두 반응에 의해, 단순화 된 형태로 기술되어
(1) W + 6OH – WO → 3 (S) + 3H 2 O + (e) – 및
(2) (3) (S) + WO 2OH – → 4 + 2 H 2 O WO
에칭 현재 사용 된 NaOH 용액의 몰 농도는 텅스텐 봉을 에칭하는데 필요한 시간 및 전압에 영향을 미친다. 이러한 효과에 대한 연구가 제시되고 논의된다. 더 중요한 것은, 에칭 파라미터는 전계 방출 모드에서의 동작에 같은 선단의 형상과,에 영향을 갖는다. 의 기하 우리가 생성 팁을 주 사형 전자 현미경 (SEM)로 촬상 특징 하였다. 이러한 이미지는, 예를 들어, 팁 반경을 추정하기 위해 사용될 수있다. 또한, 팁은 그들 몇 킬로 볼트에 일반적으로 몇 백 볼트의 음의 전압을인가하고, 생성 된 전자 방출 전류를 모니터링함으로써 전계 방출 모드에서 작동되었다. 전계 방출 전류의 관계는, I, 및이 바이어스 전압, V, 파울러 노드 하임 식 (11)에 의해 설명 될 수 적용된
(3) I = AV 2 전자 -Cr의 EFF / V,
R의 EFF는 팁의 유효 반경이고, A는 상수이며, C는 제 파울러 – 노드 하임 일정 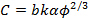 , 어떤에서 B = eV의 6.83 – 3/2 V / 나노,030eq11.jpg "/> 텅스텐의 일 함수 (인
, 어떤에서 B = eV의 6.83 – 3/2 V / 나노,030eq11.jpg "/> 텅스텐의 일 함수 (인 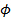 ≈ 4.5 eV의가), k는 형상에 의존하는 요인 (K ≈ 5), 및
≈ 4.5 eV의가), k는 형상에 의존하는 요인 (K ≈ 5), 및 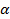 노드 하임 화상 보정 항은 (인
노드 하임 화상 보정 항은 (인 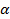 ≈ 1) 12. 따라서, 팁의 유효 반경은 바이어스 전압의 함수로서 전자 전류를 측정함으로써 결정될 수있다. 구체적으로는 LN의 소위 파울러 노드 하임 (FN) 플롯 (I / V 2) 대 1 / V의 기울기로부터 구할 수있다.
≈ 1) 12. 따라서, 팁의 유효 반경은 바이어스 전압의 함수로서 전자 전류를 측정함으로써 결정될 수있다. 구체적으로는 LN의 소위 파울러 노드 하임 (FN) 플롯 (I / V 2) 대 1 / V의 기울기로부터 구할 수있다.
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
우리는 전기 화학적 NaOH 용액 날카로운 전계 방출 지점 (FEPs)을 에칭하고, 전계 방출 모드들을 조작함으로써 FEPs을 테스트하는 간단한 절차를 설명 하였다. 기재된 에칭 방법은 기존 기술 – 라멜라 이탈 기법 -7,8- 플로팅 층 기법 9,10의 변형이다. 그러나, 우리는 상기 한 방법보다 구현하는 것이 더 편리하고 신뢰할 수를 발견했다.
도 2에 도시 된 바…
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the services of Stanley Flegler, Carol Flegler, and Abigail Tirrell at the MSU Center for Advanced Microscopy. We thank Ray Clark and Mark Wilson for technical assistance with the set-up of the electrochemical etching apparatus. Earlier contributions from Anne Benjamin, Georg Bollen, Rafael Ferrer, David Lincoln, Stefan Schwarz and Adrian Valverde, and technical assistance from John Yurkon are also acknowledged. This work was partially supported by the National Science Foundation contract no. PHY-1102511 and PHY-1307233, Michigan State University and the Facility for Rare Isotope Beams, and Central Michigan University.
Materials
| Tungsten Rod 0.020" x 12" | ESPI Metals | http://www.espimetals.com/index.php/online-catalog/467-Tungsten | 3N8 Purity |
| NaOH salt | Cole-Parmer | Item # WU-88404-71 | 100 g |
| Separatory funnel | Cole-Parmer | Item# WU-34506-03 | 250 mL |
| DC Power supply | BK Precision | 1672 | Triple Output 0 – 32 V, 0 – 3 A DC Power Supply |
| Acetone | Cole-Parmer | Item# WU-88000-68 | 500 mL |
| Data Acquisition Card | National Instruments | NI PXI-6221 | 16 AI, 24 DIO, 2 AO |
| Relay | Magnecraft | 276 XAXH-5D | 7 A, 30 V DC Reed Relay |
| 6-way 6" conflat flange cross | Kurt J Lesker | C6-0600 | |
| 6" to 2-3/4" conflat zero length reducer flange (x3) | Kurt J Lesker | RF600X275 | |
| 2-3/4" conflat flange SHV feedthrough | Kurt J Lesker | IFTSG041033 | |
| 2-3/4" conflat flange BNC feedthrough | Kurt J Lesker | IFTBG042033 | |
| 2-3/4" conflat flange linear feedthrough | MDC | 660006, REF# BLM-275-2 | |
| 6" conflat flange blankoff | Kurt J Lesker | F0600X000N | |
| 6" conflat flange window | Kurt J Lesker | VPZL-600 | |
| HV Power supply | Keithley Instruments | Keithley Model #2290-5 | 0 – 5 kV DC HV Power Supply |
| Picoammeter | Keithley Instruments | Keithley Model #6485 | |
| Faraday Cup | Beam Imaging Solutions | Model FC-1 Faraday Cup |
References
- Muller, E. W., Bahadur, K. Field Ionization of Gases at a Metal Surface and the Resolution of the Field Ion Microscope. Phys. Rev. 102, 624 (1956).
- Binnig, G., Rohrer, H. Scanning Tunneling Microscopy. Helv. Phys. Acta. 55, 726-735 (1982).
- Melmed, A. J. The art and science and other aspects of making sharp tips. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B. 9, 601-608 (1990).
- Shi, W., Redshaw, M., Myers, E. G. Atomic masses of 32,33S, 84,86Kr, and 129,132Xe with uncertainties 0.1 ppb. Phys. Rev. A. 72, 022510 (2005).
- Van Dyck, R. S., Zafonte, S. L., Van Liew, S., Pinegar, D. B., Schwinberg, D. B. Ultraprecise Atomic Mass Measurement of the α particle and 4He. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 220802 (2004).
- Hobara, R., Yoshimoto, S., Hasegawa, S., Sakamoto, K. Dynamic electrochemical-etching technique for tungsten tips suitable for multi-tip scanning tunneling microscopes. e-J. Surf. Sci. Nanotechnol. 5, 94-98 (2007).
- Klein, M., Schwitzgebel, G. An improved lamellae drop-off technique for sharp tip preparation in scanning tunneling microscopy. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 68, 3099-3103 (1997).
- Kerfriden, S., Nahlé, A. H., Campbell, S. A., Walsh, F. C., Smith, J. R. The electrochemical etching of tungsten STM tips. Electrochim. Acta. 43, 1939-1944 (1998).
- Lemke, H., Göddenhenrich, T., Bochem, H. P., Hartmann, U., Heiden, C. Improved microtips for scanning probe microscopy. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 61, 2538-2538 (1990).
- Song, J. P., Pryds, N. H., Glejbøl, K., Mørch, K. A., Thölén, A. R., Christensen, L. N. A development in the preparation of sharp scanning tunneling microscopy tips. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 64, 900-903 (1993).
- Fowler, R. H., Nordheim, L. Electron Emission in Intense Electric Fields. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A. , 119-173 (1928).
- Kim, Y. -. G., Choi, E. -. H., Kang, S. -. O., Cho, G. Computer-controlled fabrication of ultra-sharp tungsten tips. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B. 16, 2079 (1998).
- Brown, K. L., Tautfest, G. W. Faraday-Cup Monitors for High-Energy Electron Beams. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 27, 696 (1956).
- Redshaw, M., et al. Fabrication and characterization of field emission points for ion production in Penning trap applications. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 379, 187-193 (2015).
- Ibe, J. P., et al. On the electrochemical etching of tips for scanning tunneling microscopy. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A. 8, 3570 (1990).
- Ekvall, I., Wahlström, E., Claesson, D., Olin, H., Olsson, E. Preparation and characterization of electrochemically etched W tips for STM. Meas. Sci. Technol. 10, 11-18 (1999).
- Schiller, C., Koomans, A. A., van Rooy, T. L., Schönenberger, C., Elswijk, H. B. Decapitation of tungsten field emitter tips during sputter sharpening. Surf. Sci. 339, L925-L930 (1995).

