אלקטרוכימי תחריט ואפיון של נקודות שדה פליטה שארפ עבור יינון אלקטרונים
Summary
A method for electrochemically etching field emission tips is presented. Etching parameters are characterized and the operation of the tips in field emission mode is investigated.
Abstract
A new variation of the drop-off method for fabricating field emission points by electrochemically etching tungsten rods in a NaOH solution is described. The results of studies in which the etching current and the molarity of the NaOH solution used in the etching process were varied are presented. The investigation of the geometry of the tips, by imaging them with a scanning electron microscope, and by operating them in field emission mode is also described. The field emission tips produced are intended to be used as an electron beam source for ion production via electron impact ionization of background gas or vapor in Penning trap mass spectrometry applications.
Introduction
טיפים או נקודות שארפ כבר זמן רב בשימוש ביישומים מיקרוסקופית, כגון המיקרוסקופ יון שדה (FIM) 1 ואת מיקרוסקופ מנהור סורק (STM) 2, ומגוון של טכניקות לייצור בקצוות החדים של חומרים שונים פותחו 3. טיפים חדים אלה יכולים להיות מופעלים גם כנקודות פליטת שדה (FEPs) על ידי החלת מתח גבוה להם, ולשמש מקור אלקטרוני קורה נוח. אחד היישומים של כגון המקור הוא ייצור יון באמצעות יינון השפעה אלקטרונים (EII). FEP יתרון במיוחד ביישומים שבהם תנודות הטמפרטורה המיוצר על ידי קרינת חום אינם רצויים. לדוגמא, ייצור יון באמצעות EII גז רקע או אדי דיוק גבוה פנינג מלכודות 4,5.
שיטה פשוטה עבור בודה FEPs היא לחרוט מוטות טונגסטן אלקטרוכימי בתוך נתרן הידרוקסידי פתרון (NaOH). טכניקה זו היא פשוטה יחסית ליישם עםציוד צנוע הוכח להיות די לשחזור ואמין. מספר שיטות מתוארים בספרות ושיפורים הטכניקות הללו ממשיכים להופיע 6. כאן אנו מתארים שיטת התחריט אלקטרוכימי של טיפים טונגסטן בתמיסת NaOH. השיטה שלנו היא וריאציה של 7,8 טכניקת ירידה- off lamella ואת 9,10 טכניקת השכבה צף. כמו שתי שיטות הוא מאפשר את ייצורם של שני טיפי הליך תחריט יחיד. תמונה של המנגנון הניסיוני לתחריט הטיפים מוצגת באיור 1.
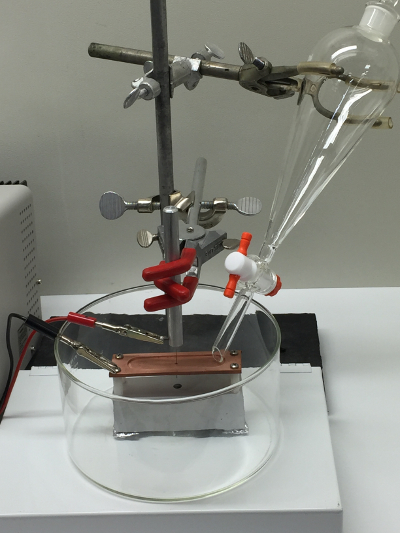
מנגנון תחריט באיור 1.. תצלום של מנגנון הניסוי נעשה שימוש חריטה אלקטרוכימי של מוטות טונגסטן עם פתרון NaOH. אנא לחץכאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.
תחריט אלקטרוכימי של טונגסטן בבסיס NaOH המימי מתרחש באמצעות תהליך דו שלבים. ראשית, תחמוצות טונגסטן ביניים נוצרות, ושנית, תחמוצות אלה שאינם אלקטרוכימי מומס כדי ליצור את אניון Tungstate המסיס. תהליך זה מתואר, בצורה פשוטה, על ידי שתי תגובות
(1) W + 6OH – → WO 3 (S) + 3H 2 O + 6E -, ו
(2) WO 3 (S) + 2OH – → WO 4 2- + H 2 O.
זרם התחריט ואת molarity פתרון NaOH המשמש להשפיע על זמן המתח הנדרש כדי לחרוט דרך מוט טונגסטן. מחקרים על השפעות אלה הוצגו ונדונו. יתרה מכך, את הפרמטרים תחריט יש השפעה על הגיאומטריה של טיפים, וככזה, על פעולתן במצב פליטת שדה. הגיאומטריה של טיפים שהפקנו התאפיינו ומצלמת אותם עם מיקרוסקופ אלקטרונים סורק (SEM). תמונות אלה יכולים לשמש כדי להעריך, למשל, רדיוס הקצה. בנוסף, טיפים הופעלו במצב פליטת שדה ידי החלת מתח שלילי של בדרך כלל כמה מאות וולט כמה kilovolts להם וניטור הזרם פליטת אלקטרונים שהתקבל. הקשר בין נוכחי פליטת השדה, אני, ומיישם מתח הטיה, V, יכול להיות מתואר על ידי משוואת פאולר-Nordheim 11
(3) אני = AV 2 דואר EFF -Cr / V,
שם EFF r הוא הרדיוס האפקטיבי של הקצה, A הוא קבוע, ו- C הוא קבוע השני פאולר-Nordheim 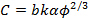 , שבו b = 6.83 eV – 3/2 V / ננומטר,030eq11.jpg "/> היא עבודת הפונקציה של טונגסטן (
, שבו b = 6.83 eV – 3/2 V / ננומטר,030eq11.jpg "/> היא עבודת הפונקציה של טונגסטן ( 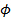 ≈ 4.5 eV), k הוא גורם זה תלוי בגיאומטריה (k ≈ 5), ו
≈ 4.5 eV), k הוא גורם זה תלוי בגיאומטריה (k ≈ 5), ו 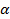 הוא המונח תיקון תמונה Nordheim (
הוא המונח תיקון תמונה Nordheim ( 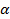 ≈ 1) 12. לפיכך, הרדיוס האפקטיבי של הקצה יכול להיקבע על ידי מדידת זרם האלקטרונים כפונקציה של מתח הטיה. באופן ספציפי, זה יכול להיות המתקבל שיפוע מגרש שנקרא פאולר-Nordheim (FN) של ln (I / V 2) לעומת 1 / V.
≈ 1) 12. לפיכך, הרדיוס האפקטיבי של הקצה יכול להיקבע על ידי מדידת זרם האלקטרונים כפונקציה של מתח הטיה. באופן ספציפי, זה יכול להיות המתקבל שיפוע מגרש שנקרא פאולר-Nordheim (FN) של ln (I / V 2) לעומת 1 / V.
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
תארנו נהלים פשוטים כדי לחרוט נקודות פליטת שדה חדות אלקטרוכימי (FEPs) בתמיסת NaOH, וכדי לבדוק את FEPs ידי ותפעולן במצב פליטת שדה. הליך התחריט תאר הוא וריאציה של טכניקות קיימות טכניקת ירידה- off lamella 7,8 ואת 9,10 טכניקת השכבה צף. עם זאת, מצאנו אותו להיות יותר נוח ואמין מא?…
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the services of Stanley Flegler, Carol Flegler, and Abigail Tirrell at the MSU Center for Advanced Microscopy. We thank Ray Clark and Mark Wilson for technical assistance with the set-up of the electrochemical etching apparatus. Earlier contributions from Anne Benjamin, Georg Bollen, Rafael Ferrer, David Lincoln, Stefan Schwarz and Adrian Valverde, and technical assistance from John Yurkon are also acknowledged. This work was partially supported by the National Science Foundation contract no. PHY-1102511 and PHY-1307233, Michigan State University and the Facility for Rare Isotope Beams, and Central Michigan University.
Materials
| Tungsten Rod 0.020" x 12" | ESPI Metals | http://www.espimetals.com/index.php/online-catalog/467-Tungsten | 3N8 Purity |
| NaOH salt | Cole-Parmer | Item # WU-88404-71 | 100 g |
| Separatory funnel | Cole-Parmer | Item# WU-34506-03 | 250 mL |
| DC Power supply | BK Precision | 1672 | Triple Output 0 – 32 V, 0 – 3 A DC Power Supply |
| Acetone | Cole-Parmer | Item# WU-88000-68 | 500 mL |
| Data Acquisition Card | National Instruments | NI PXI-6221 | 16 AI, 24 DIO, 2 AO |
| Relay | Magnecraft | 276 XAXH-5D | 7 A, 30 V DC Reed Relay |
| 6-way 6" conflat flange cross | Kurt J Lesker | C6-0600 | |
| 6" to 2-3/4" conflat zero length reducer flange (x3) | Kurt J Lesker | RF600X275 | |
| 2-3/4" conflat flange SHV feedthrough | Kurt J Lesker | IFTSG041033 | |
| 2-3/4" conflat flange BNC feedthrough | Kurt J Lesker | IFTBG042033 | |
| 2-3/4" conflat flange linear feedthrough | MDC | 660006, REF# BLM-275-2 | |
| 6" conflat flange blankoff | Kurt J Lesker | F0600X000N | |
| 6" conflat flange window | Kurt J Lesker | VPZL-600 | |
| HV Power supply | Keithley Instruments | Keithley Model #2290-5 | 0 – 5 kV DC HV Power Supply |
| Picoammeter | Keithley Instruments | Keithley Model #6485 | |
| Faraday Cup | Beam Imaging Solutions | Model FC-1 Faraday Cup |
References
- Muller, E. W., Bahadur, K. Field Ionization of Gases at a Metal Surface and the Resolution of the Field Ion Microscope. Phys. Rev. 102, 624 (1956).
- Binnig, G., Rohrer, H. Scanning Tunneling Microscopy. Helv. Phys. Acta. 55, 726-735 (1982).
- Melmed, A. J. The art and science and other aspects of making sharp tips. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B. 9, 601-608 (1990).
- Shi, W., Redshaw, M., Myers, E. G. Atomic masses of 32,33S, 84,86Kr, and 129,132Xe with uncertainties 0.1 ppb. Phys. Rev. A. 72, 022510 (2005).
- Van Dyck, R. S., Zafonte, S. L., Van Liew, S., Pinegar, D. B., Schwinberg, D. B. Ultraprecise Atomic Mass Measurement of the α particle and 4He. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 220802 (2004).
- Hobara, R., Yoshimoto, S., Hasegawa, S., Sakamoto, K. Dynamic electrochemical-etching technique for tungsten tips suitable for multi-tip scanning tunneling microscopes. e-J. Surf. Sci. Nanotechnol. 5, 94-98 (2007).
- Klein, M., Schwitzgebel, G. An improved lamellae drop-off technique for sharp tip preparation in scanning tunneling microscopy. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 68, 3099-3103 (1997).
- Kerfriden, S., Nahlé, A. H., Campbell, S. A., Walsh, F. C., Smith, J. R. The electrochemical etching of tungsten STM tips. Electrochim. Acta. 43, 1939-1944 (1998).
- Lemke, H., Göddenhenrich, T., Bochem, H. P., Hartmann, U., Heiden, C. Improved microtips for scanning probe microscopy. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 61, 2538-2538 (1990).
- Song, J. P., Pryds, N. H., Glejbøl, K., Mørch, K. A., Thölén, A. R., Christensen, L. N. A development in the preparation of sharp scanning tunneling microscopy tips. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 64, 900-903 (1993).
- Fowler, R. H., Nordheim, L. Electron Emission in Intense Electric Fields. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A. , 119-173 (1928).
- Kim, Y. -. G., Choi, E. -. H., Kang, S. -. O., Cho, G. Computer-controlled fabrication of ultra-sharp tungsten tips. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B. 16, 2079 (1998).
- Brown, K. L., Tautfest, G. W. Faraday-Cup Monitors for High-Energy Electron Beams. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 27, 696 (1956).
- Redshaw, M., et al. Fabrication and characterization of field emission points for ion production in Penning trap applications. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 379, 187-193 (2015).
- Ibe, J. P., et al. On the electrochemical etching of tips for scanning tunneling microscopy. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A. 8, 3570 (1990).
- Ekvall, I., Wahlström, E., Claesson, D., Olin, H., Olsson, E. Preparation and characterization of electrochemically etched W tips for STM. Meas. Sci. Technol. 10, 11-18 (1999).
- Schiller, C., Koomans, A. A., van Rooy, T. L., Schönenberger, C., Elswijk, H. B. Decapitation of tungsten field emitter tips during sputter sharpening. Surf. Sci. 339, L925-L930 (1995).

