대장균 및 다른 박테리아로부터의 세포외 소포의 확장 가능한 분리 및 정제
Summary
박테리아는 생리 활성 생물학적 분자를 운반하는 나노 미터 크기의 세포 외 소포 (EV)를 분비합니다. EV 연구는 생물 발생, 미생물-미생물 및 숙주-미생물 상호 작용 및 질병에서의 역할, 잠재적 인 치료 응용 프로그램을 이해하는 데 중점을 둡니다. EV 연구의 표준화를 촉진하기 위해 다양한 박테리아로부터 EV를 확장 가능한 분리를 위한 워크플로우가 제시됩니다.
Abstract
다양한 박테리아 종은 지질, 단백질, 핵산, 글리칸 및 모 세포에서 파생된 기타 분자로 구성된 ~20-300nm의 세포외 소포(EV)를 분비합니다. EV는 종내 및 종간 통신 벡터로 기능하는 동시에 감염 및 식민지화의 맥락에서 박테리아와 숙주 유기체 간의 상호 작용에 기여합니다. 건강 및 질병에서 EV에 기인하는 다양한 기능을 감안할 때 체외 및 생체 내 연구를 위해 EV를 분리하는 데 대한 관심이 증가하고 있습니다. 물리적 특성, 즉 크기에 기반한 EV의 분리는 다양한 박테리아 배양에서 소포의 분리를 용이하게 할 것이라는 가설이 세워졌습니다.
분리 워크플로우는 박테리아 배양에서 EV를 분리하기 위한 원심분리, 여과, 한외여과 및 크기 배제 크로마토그래피(SEC)로 구성됩니다. 펌프 구동 접선 유동 여과(TFF) 단계를 통합하여 확장성을 향상시켜 시작 세포 배양 리터에서 물질을 분리할 수 있습니다. 대장균 은 EV 관련 나노루시퍼라제 및 비EV 관련 mCherry를 리포터 단백질로 발현하는 모델 시스템으로 사용되었습니다. 나노루시페라아제는 N-말단을 사이토리신 A와 융합하여 EV를 표적으로 삼았습니다. 관련 사이토리신 A-나노루크와 함께 20-100nm EV를 포함하는 초기 크로마토그래피 분획은 유리 단백질을 포함하는 후기 분획과 구별되었습니다. EV-관련 나노루시퍼라제의 존재는 면역금 표지 및 투과 전자 현미경에 의해 확인되었다. 이 EV 분리 워크플로우는 다른 인간 장 관련 그람 음성 및 그람 양성 박테리아 종에 적용할 수 있습니다. 결론적으로, 원심분리, 여과, 한외여과/TFF 및 SEC를 결합하면 다양한 박테리아 종에서 EV를 확장 가능한 분리할 수 있습니다. 표준화된 분리 워크플로우를 사용하면 종 간 미생물 EV의 비교 연구가 용이해질 것입니다.
Introduction
세포외 소포(EV)는 원핵 세포 및 진핵 세포 모두에서 분비되는 지질, 단백질, 글리칸 및 핵산으로 구성된 나노미터 크기의 리포솜 유사 구조입니다1. 그람 음성 박테리아2에서 EV의 방출을 시각화하는 초기 연구 이후, 박테리아 EV (직경 20-300 nm)에 기인 한 생물학적 기능의 수는 지난 수십 년 동안 지속적으로 증가하고 있습니다. 이들의 기능에는 항생제 내성전달3, 생물막 형성4, 쿼럼 감지5 및 독소 전달6이 포함됩니다. 또한 박테리아 EV를 치료제로 사용하는 것, 특히 백신학7 및 암 치료8에 대한 관심이 증가하고 있습니다.
EV 연구에 대한 관심이 높아지고 있음에도 불구하고 격리 방법에 대한 기술적 과제는 여전히 남아 있습니다. 특히, 재현 가능하고 확장 가능하며 다양한 EV 생산 유기체와 호환되는 분리 방법이 필요합니다. EV 분리 및 연구 방법을 계획하고 보고하기 위한 통일된 원칙을 만들기 위해 국제 세포외 소포 학회는 MISEV 입장 논문9를 발행하고 업데이트합니다. 또한 EV-TRACK 컨소시엄은 투명성을 높이기 위해 출판된 원고에 사용된 EV 격리에 대한 세부 방법론을 보고할 수 있는 개방형 플랫폼을 제공합니다10.
이 프로토콜에서, 포유류 세포 배양으로부터 EV의 분리에 사용된 이전의 방법론은 박테리아 세포 배양으로부터 EV의 분리를 가능하게 하기 위해11,12 조정되었다. 우리는 확장 가능한 다양한 미생물로부터 EV를 분리하고 EV 순도와 수율의 균형을 맞추는 방법을 사용하려고 했습니다(MISEV 입장논문 9에서 논의됨). 원심분리 및 여과로 박테리아 세포 및 파편을 제거한 후, 배양 배지는 원심 장치 한외여과(최대 ~100mL의 부피) 또는 펌프 구동 TFF(더 큰 부피의 경우)에 의해 농축됩니다. 그런 다음 EV는 소형 EV의 정제에 최적화된 컬럼을 사용하여 SEC에 의해 분리됩니다.
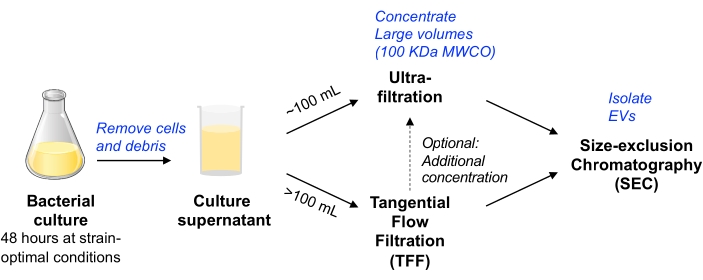
그림 1: 박테리아 EV 격리 워크플로 회로도 개요. 약어 : EV = 세포 외 소포; TFF = 접선 유동 여과; SEC = 크기 배제 크로마토그래피; MWCO = 분자량 컷오프. 이 그림의 더 큰 버전을 보려면 여기를 클릭하십시오.
Escherichia coli (즉, E. coli MP113)의 마우스-공생 균주를 모델 유기체로서 사용하였고, 이전에 보고된 바와 같이, 세포리신 A에의 융합에 의해 EV-관련 나노루시퍼라제를 발현하도록 변형시켰다14. 여기에 사용 된 방법은 적어도 몇 리터의 박테리아 배양을 처리하고 EV 관련 단백질과 비 EV 관련 단백질을 효과적으로 분리 할 수 있습니다. 마지막으로,이 방법은 다른 그람 양성 및 그람 음성 박테리아 종에도 사용할 수 있습니다. 보고된 실험의 모든 관련 데이터는 EV-TRACK 지식 베이스(EV-TRACK ID: EV210211)10에 제출되었습니다.
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
위의 프로토콜에서는 확장 가능하고 다양한 그람 음성/양성 및 호기성/혐기성 박테리아로부터 EV를 안정적으로 분리하는 방법이 설명되어 있습니다. 절차 전반에 걸쳐 몇 가지 잠재적인 정지 지점이 있지만 컨디셔닝된 박테리아 배양 배지에서 EV를 분리하는 데 48시간 이상 걸리지 않는 것이 좋습니다.
첫째, 컨디셔닝 된 박테리아 배양 배지를 생성하기 위해 박테리아를 배양?…
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
위에서 설명한 연구는 NIH TL1 TR002549-03 교육 보조금의 지원을 받았습니다. 입자 크기 분석기 기기에 쉽게 접근할 수 있도록 해주신 John C. Tilton 박사와 Zachary Troyer 박사(케이스 웨스턴 리저브 대학교)에게 감사드립니다. 입자 크기 분포 데이터의 분석에 대한 기술 지원을 위한 루라다인(Spectradyne); 코넬 대학교의 데이비드 퍼트넘 박사가 pClyA-GFP 플라스미드14를 제공한 공로; 펜실베니아 대학의 Mark Goulian 박사는 대장균 MP113을 제공했습니다.
Materials
| 0.5 mL flat cap, thin-walled PCR tubes | Thermo Scientific | 3430 | it is important to use thin-walled PCR tubes to obtain accurate readings with Qubit |
| 16% Paraformaldehyde (formaldehyde) aqueous solution | Electron microscopy sciences | 15700 | |
| 250 mL Fiberlite polypropylene centrifuge bottles | ThermoFisher | 010-1495 | |
| 500 mL Fiberlite polypropylene centrifuge bottles | ThermoFisher | 010-1493 | |
| 65 mm Polypropylene Round-Bottom/Conical Bottle Adapter | Beckman Coulter | 392077 | Allows Vivacell to fit in rotor |
| Akkermansia mucinophila | ATCC | BAA-835 | |
| Amicon-15 (100 kDa MWCO) | MilliporeSigma | UFC910024 | |
| Avanti J-20 XPI centrifuge | Beckman Coulter | No longer sold by Beckman. Avanti J-26XP is closest contemporary model. | |
| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI 5482 | ATCC | 29148 | |
| Bifidobacterium breve | NCIMB | B8807 | |
| Bifidobacterium dentium | ATCC | 27678 | |
| Brain Heart infusion (BHI) broth | Himedia | M2101 | After autoclaving, Both BHI broth and agar were introduced into the anaerobic chamber, supplemented with Menadione (1 µg/L), hematin (1.2 µg/L), and L-Cysteine Hydrochloride (0.05%). They were then incubated for at least 24 h under anaerobic conditions before inoculation with the anaerobic bacterial strains. |
| C-300 microfluidics cartridge | Spectradyne | ||
| Chloramphenicol | MP Biomedicals | ICN19032105 | |
| Escherichia coli HST08 (Steller competent cells) | Takara | 636763 | |
| Escherichia coli MP1 | Dr. Mark Goulian (gift) | commensal bacteria derived from mouse gut | |
| Fiberlite 500 mL to 250 mL adapter | ThermoFisher | 010-0151-05 | used with Fiberlite rotor to enable 250 mL bottles to be used for smaller size of starting bacterial culture |
| Fiberlite fixed-angle centrifuge rotor | ThermoFisher | F12-6×500-LEX | fits 6 x 500 mL bottles |
| Formvar Carbon Film 400 Mesh, Copper | Electron microscopy sciences | FCF-400-CU | |
| Glutaraldehyde (EM-grade, 10% aqeous solution) | Electron microscopy sciences | 16100 | |
| Hematin | ChemCruz | 207729B | Stock solution was made in 0.2 M L-histidine solution as 1.2 mg/mL |
| Infinite M Nano+ Microplate reader | Tecan | This equibment was used to measure the mCherry fluorescence | |
| In-Fusion HD Cloning Plus | Takara | 638909 | For cloning of the PCR fragements into the PCR-lineraized vectors |
| JS-5.3 AllSpin Swinging-Bucket Rotor | Beckman Coulter | 368690 | |
| Lauria Bertani (LB) broth, Miller | Difco | 244620 | |
| L-Cysteine Hydrochloride | J.T. Baker | 2071-05 | It should be weighed and added directly to the autoclaved BHI media inside the anaerobic chamber |
| Masterflex Fitting, Polypropylene, Straight, Female Luer to Hose Barb Adapter, 1/8" ID; 25/PK | cole-parmer – special | HV-30800-08 | connection adapters for filtration tubing circuit |
| Masterflex Fitting, Polypropylene, Straight, Male Luer to Hose Barb Adapter, 1/8" ID; 25/PK | cole-parmer – special | HV-30800-24 | connection adapters for filtration tubing circuit |
| Masterflex L/S Analog Variable-Speed Console Drive, 20 to 600 rpm | Masterflex | HV-07555-00 | |
| Masterflex L/S Easy-Load Head for Precision Tubing, 4-Roller, PARA Housing, SS Rotor | Masterflex | EW-07514-10 | |
| Masterflex L/S Precision Pump Tubing, PharmaPure, L/S 16; 25 ft | Cole Palmer | EW-06435-16 | low-binding/low-leaching tubing |
| Menadione (Vitamin K3) | MP | 102259 | Stock solution was made in ethanol as 1 mg/mL |
| MIDIKROS 41.5CM 100K MPES 0.5MM FLL X FLL 1/PK | Repligen | D04-E100-05-N | TFF device we have used to filter up to 2 L of E. coli culture supernatant |
| Nano-Glo Luciferase Assay System | Promega | N1110 | This assay kit was used to measure the luminescence of the nluc reporter protein |
| NanoLuc (Nluc) Luciferase Antibody, clone 965808 | R&D Systems | MAB10026 | |
| nCS1 microfluidics resistive pulse sensing instrument | Spectradyne | ||
| nCS1 Viewer | Spectradyne | Analysis software for particle size distribution | |
| OneTaq 2x Master Mix with Standard Buffer | NEB | M0482 | DNA polymerase master mix used to perform the routine PCR reactions for colony checking |
| Protein LoBind, 2.0 mL, PCR clean tubes | Eppendorf | 30108450 | |
| Q5 High-Fidelity 2x Master Mix | NEB | M0492 | DNA polymerase master mix used to perform the PCR reactions needed for cloning |
| qEV original, 35 nm | Izon | maximal loading volume of 0.5 mL | |
| qEV rack | Izon | for use with the qEV-original SEC columns | |
| qEV-2, 35 nm | Izon | maximal loading volume of 2 mL | |
| Qubit fluorometer | ThermoFisher | Item no longer available. Closest available product is Qubit 4.0 Fluorometer (cat. No. Q33238) | |
| Qubit protein assay kit | ThermoFisher | Q33211 | Store kit at room temperature. Standards are stored at 4 °C. |
| Sorvall Lynx 4000 centrifuge | ThermoFisher | 75006580 | |
| SpectraMax i3x Microplate reader | Molecular Devices | This equipment was used to measure the nanoluciferase bioluminescence | |
| Stericup Quick-release-GP Sterile Vacuum Filtration system (150, 250, or 500 mL) | MilliporeSigma | S2GPU01RE S2GPU02RE S2GPU05RE |
One or multiple filters can be used to accommodate working volumes. In our experience, you can filter twice the volume listed on the product size. |
| Uranyl acetate | Electron microscopy sciences | 22400 | |
| Vinyl anaerobic chamber | Coy Lab | ||
| Vivacell 100, 100,000 MWCO PES | Sartorius | VC1042 | |
| Whatman Anotop 10 Plus syringe filters (0.02 micron) | MilliporeSigma | WHA68093002 | to filter MRPS diluent |
References
- Yanez-Mo, M., et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. 4, 27066 (2015).
- Chatterjee, S. N., Das, J. Electron microscopic observations on the excretion of cell-wall material by Vibrio cholerae. Journal of General Microbiology. 49 (1), 1-11 (1967).
- Ciofu, O., Beveridge, T. J., Kadurugamuwa, J., Walther-Rasmussen, J., Hoiby, N. Chromosomal beta-lactamase is packaged into membrane vesicles and secreted from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 45 (1), 9-13 (2000).
- Yonezawa, H., et al. Outer membrane vesicles of Helicobacter pylori TK1402 are involved in biofilm formation. BMC Microbiology. 9, 197 (2009).
- Mashburn, L. M., Whiteley, M. Membrane vesicles traffic signals and facilitate group activities in a prokaryote. Nature. 437 (7057), 422-425 (2005).
- Kato, S., Kowashi, Y., Demuth, D. R. Outer membrane-like vesicles secreted by Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans are enriched in leukotoxin. Microbial Pathogenesis. 32 (1), 1-13 (2002).
- Petousis-Harris, H., et al. Effectiveness of a group B outer membrane vesicle meningococcal vaccine against gonorrhoea in New Zealand: a retrospective case-control study. Lancet. 390 (10102), 1603-1610 (2017).
- Kim, O. Y., et al. Bacterial outer membrane vesicles suppress tumor by interferon-gamma-mediated antitumor response. Nature Communications. 8 (1), 626 (2017).
- Thery, C., et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. 7 (1), 1535750 (2018).
- Consortium, E. -. T., et al. EV-TRACK: transparent reporting and centralizing knowledge in extracellular vesicle research. Nature Methods. 14 (3), 228-232 (2017).
- Watson, D. C., et al. Efficient production and enhanced tumor delivery of engineered extracellular vesicles. Biomaterials. 105, 195-205 (2016).
- Watson, D. C., et al. Scalable, cGMP-compatible purification of extracellular vesicles carrying bioactive human heterodimeric IL-15/lactadherin complexes. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. 7 (1), 1442088 (2018).
- Lasaro, M., et al. Escherichia coli isolate for studying colonization of the mouse intestine and its application to two-component signaling knockouts. Journal of Bacteriology. 196 (9), 1723-1732 (2014).
- Kim, J. Y., et al. Engineered bacterial outer membrane vesicles with enhanced functionality. Journal of Molecular Biology. 380 (1), 51-66 (2008).
- Beveridge, T. J. Structures of gram-negative cell walls and their derived membrane vesicles. Journal of Bacteriology. 181 (16), 4725-4733 (1999).
- Reimer, S. L., et al. Comparative analysis of outer membrane vesicle isolation methods with an Escherichia coli tolA mutant reveals a hypervesiculating phenotype with outer-inner membrane vesicle content. Frontiers in Microbiology. 12, 628801 (2021).

