كشف الجليكوجين في خلايا الدم المحيطي وحيدات النوى مع الدوري حمض شيف تلطيخ
Summary
Periodic acid Schiff staining is a technique that visualizes the polysaccharide content of tissues. This article demonstrates periodic acid Schiff staining protocol adapted for use on peripheral blood mononuclear cells purified from human venous blood. Such samples are enriched for lymphocytes and other white blood cells of the immune system.
Abstract
Periodic acid Schiff (PAS) staining is an immunohistochemical technique used on muscle biopsies and as a diagnostic tool for blood samples. Polysaccharides such as glycogen, glycoproteins, and glycolipids stain bright magenta making it easy to enumerate positive and negative cells within the tissue. In muscle cells PAS staining is used to determine the glycogen content in different types of muscle cells, while in blood cell samples PAS staining has been explored as a diagnostic tool for a variety of conditions. Blood contains a proportion of white blood cells that belong to the immune system. The notion that cells of the immune system possess glycogen and use it as an energy source has not been widely explored. Here, we describe an adapted version of the PAS staining protocol that can be applied on peripheral blood mononuclear immune cells from human venous blood. Small cells with PAS-positive granules and larger cells with diffuse PAS staining were observed. Treatment of samples with amylase abrogates these patterns confirming the specificity of the stain. An alternate technique based on enzymatic digestion confirmed the presence and amount of glycogen in the samples. This protocol is useful for hematologists or immunologists studying polysaccharide content in blood-derived lymphocytes.
Introduction
حمض الدوري شيف (PAS) تلطيخ هو أسلوب المناعى التي يتم استخدامها على نطاق واسع في مجال البحوث العضلات والتشخيص. ويستخدم أيضا كأداة تشخيصية على عينات الدم. هذه التقنية تعمل من خلال تطبيق محلول حمض الدوري للعينة، والذي يتأكسد وحدات داخل السكاريد إنشاء مجموعات ألدهيد التي تتفاعل مع كاشف وعديم اللون شيف وبالتالي إنتاج منتج أرجواني عميق. وتظهر الخطوات من هذا الإجراء في الشكل 1. وصمة عار تتحول أي شيء مع السكريات أرجواني، بما في ذلك الجليكوجين، البروتينات السكرية، السكرية، mucins، أو جزيئات أخرى مع الأنصاف السكاريد.
وكثيرا ما يستخدم تلطيخ PAS لقياس مستويات الجليكوجين في الألياف العضلية. أقسام الأنسجة العضلات هي مثالية للتقنية كما نعلق بحزم إلى الشريحة وتحمل متعددة الغسيل وتلطيخ الخطوات. الجليكوجين هو الأكثر حضورا في نشل سريع من النوع الثاني ألياف العضلات، والتي تعاني من ارتفاع الطلبلإنتاج ATP السريع تتطلب الجليكوجين لأقصى قدر من الأداء 1،2. الجليكوجين هو بوليمر أفرع الجلوكوز التي يمكن تقسيمها إلى الجلوكوز مجانا من خلال عمل انزيمات الجليكوجين فسفوريلاز. في أوقات الراحة والتغذية الاكتفاء، وتجديد الجليكوجين خلال عملية تكون الغليكوجين، بينما في أوقات التغذية قصور أو ذات الطاقة العالية الطلب. يتم تقسيم الجليكوجين إلى جلوكوز عن طريق تحلل الغليكوجين. في وقت مبكر من واستكشفت عام 1950 العلماء الطبيب تلطيخ PAS على عينات الدم لتحليل المحتوى الجليكوجين في الأمراض المختلفة 3-7. على سبيل المثال، في بومب مرض تخزين الجليكوجين المخلصين خلايا الدم البيضاء بأمراض تتراكم كميات كبيرة من الجليكوجين الذي يختلف كثيرا عن الاصحاء 8.
توضح هذه المقالة الفيديو-نسخة معدلة من PAS تلطيخ للاستخدام على خلايا الدم وحيدات النوى المحيطية (PBMC) عينات من الدم الوريدي من الموضوعات البشرية السليمة. PBMCS احتواء معظمها الخلايا الليمفاوية من الخلايا اللمفاوية T و B الأسر الخلايا اللمفاوية، وكذلك الخلايا المناعية الأخرى مثل الخلايا القاتلة الطبيعية وحيدات. الخطوة الأولى تنقية يزيل الكريات الحمراء، العدلات، والمحببة الأخرى. توفر هذه التقنية البيانات على نسبة مركزة من الخلايا الليمفاوية مما يسمح للتعداد أكثر قوة من خلايا PAS إيجابي مقارنة باستخدام مسحات الدم الكامل.
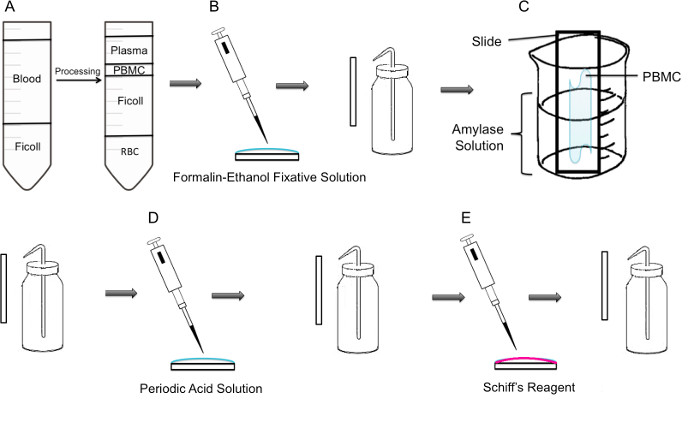
الشكل 1: خطوة منهجية خطوة من PAS تلطيخ على PBMC (A) أولا، ويتحقق عزل PBMC من خلال ficoll الانحدار، وتظهر اللوحة اليسرى إعداد قبل الطرد المركزي، وتظهر اللوحة اليمنى بعد الطرد المركزي حيث معطف الشهباء التي تحتوي على PBMC لوحظ في وسط الأنبوب. ثابتة (B) PBMCs المعزولة على الشريحة باستخدام الفورمالين الإيثانول المحاليل تثبيتينشوئها. يتم شطف الشريحة بلطف بالماء المقطر من زجاجة غسل البلاستيكية. ثم يتم وضع (C) الشريحة في 100 مل دورق منتصف الطريق مليئة حل الأميليز، والتي سوف تذوب الجليكوجين. وتشطف الشريحة بلطف. يتم التعامل مع (D) الشريحة بمحلول حامض الدوري، حيث أكسدة ساتشاريديس تأخذ مكان. يتم شطف بلطف الشرائح. هذا سوف إزالة حمض الدوري الزائد ووقف الخطوة الأكسدة. (E) عند إضافة كاشف شيف على الشرائح، وسوف تتفاعل مع الألدهيدات إنشاؤها أثناء الخطوة الأكسدة. وهذا كاشف عديم اللون ثم يؤدي إلى منتج أرجواني أحمر عميق. وتشطف الشرائح برفق لإزالة شيف كاشف الزائد.
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
كانت الخطوات الحاسمة من هذه المقالة الفيديو أثناء الغسيل والأميليز علاج الخلايا. في حين غسل الشرائح، وخطوة رئيسية كانت تستخدم زجاجة غسل للعصر البلاستيكية والسماح الماء تشغيل بلطف من خلال العينة على الشريحة ولا تستهدف مباشرة على العينات. سيكون حتى أدنى ضغط المياه ال…
Declarações
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a grant from the NSERC Discovery program grant number RGPIN 418522-2013. We thank R. Kilgour for helpful discussions, and Katelin Gresty and Dr. A. Berghdal for providing the mouse muscle sections.
Materials
| Periodic Acid Shiff Kit | Sigma-Aldrich | 395B | Bring to room temperature prior to use. Materials in this kit are toxic and harmful. Use caution http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/sigma/395b?lang=en®ion=CA |
| α-Amylase from porcine pancreas | Sigma-Aldrich | A3176 | http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/sigma/a3176?lang=en®ion=CA |
| Binocular Microscope | Carl Zeiss Microscopy | Axio Lab A0 | |
| Glycogen Assay Kit | Sigma-Aldrich | MAK016 | http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/sigma/mak016?lang=en®ion=CA |
| Ficoll-Paque PLUS | VWR, GE Healthcare | 17-1440-02 | Nonionic synthetic polymer of sucrose https://us.vwr.com/store/catalog/product.jsp?product_id=4779441 |
| Centrifuge | For PBMC isolation, swing buckets were used |
Referências
- Rich, P. R. The molecular machinery of keilin’s respiratory chain. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 31 (Pt 6), 1095-1105 (2003).
- Peter, J. B., Barnard, R. J., Edgerton, V. R., Gillespie, C. A., Stempel, K. E. Metabolic profiles of three fiber types of skeletal muscle in guinea pigs and rabbits). Bioquímica. 11 (14), 2627-2633 (1972).
- Jones, R. V., Goffi, G. P., Hutt, M. S. R. Lymphocyte glycogen content in various disease. J. Clin. Pathol. 15 (1), 36-39 (1962).
- Scott, R. B. Glycogen in human peripheral blood leukocytes. I. characteristics of the synthesis and turnover of glycogen in vitro. J. Clin. Invest. 47 (2), 344-352 (1968).
- Fedele, D., et al. positive index of lymphocytes and metabolic control in insulin-treated and type II diabetes mellitus. Diabete Metab. 9 (3), 188-192 (1983).
- Brelińska-Peczalska, R., Mackiewicz, S. Cytochemical studies of peripheral blood granulocytes and lymphocytes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Pol.Med.Sci.Hist.Bull. 15 (2), 231-234 (1976).
- Yunis, A. A., Arimura, G. K. Enzymes of glycogen metabolism in white blood cells. I. glycogen phosphorylase in normal and leukemic human leukocytes. Cancer, Res. 24, 489-492 (1964).
- Hagemans, M. L., et al. PAS-positive lymphocyte vacuoles can be used as diagnostic screening test for pompe disease. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 33 (2), 133-139 (2010).
- Totsuka, Y., et al. Physical performance and soleus muscle fiber composition in wild-derived and laboratory inbred mouse strains. 95 (2), 720-727 (2003).
- Murat, J. C., Serfaty, A. Simple enzymatic determination of polysaccharide (glycogen) content of animal tissues. Clin. Chem. 20 (12), 1576-1577 (1974).
- Arrizabalaga, O., Lacerda, H. M., Zubiaga, A. M., Zugaza, J. L. Rac1 protein regulates glycogen phosphorylase activation and controls interleukin (IL)-2-dependent T cell proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 287 (15), 11878-11890 (2012).
- Pelletier, J., G, J., Mazure, N. M. Biochemical titration of glycogen in vitro. J.Vis.Exp. (81), (2013).
- Roach, P. J., Depaoli-Roach, A. A., Hurley, T. D. Tagliabracci V.S. Glycogen and its metabolism: Some new developments and old themes. Biochem.J. 441 (3), 763-787 (2012).
- Salmoral, E. M., Tolmasky, D. S., Krisman, C. R. Evidence for the presence of glycogen in rat thymus. Cell Mol.Biol. 36 (2), 163-174 (1990).
- Darlington, P. J., et al. Diminished Th17 (not Th1) responses underlie multiple sclerosis disease abrogation after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Ann.Neurol. 73 (3), 341-354 (2013).

