طريقة موحدة لقياس المساحة الداخلية الرئة السطحية عن طريق استئصال رئوي الماوس وزرع الاصطناعية
Summary
منطقة سطح الرئة الداخلية (عيسى) هو معيار حاسم لتقييم مورفولوجيا الرئة وعلم وظائف الأعضاء في أمراض الرئة والتجدد السنخي الناجم عن الاصابة. نحن تصف هنا طريقة موحدة التي يمكن أن تقلل من التحيز قياس عيسى في كل من استئصال رئوي الرئوي ونماذج الفئران زرع الاصطناعية.
Abstract
Pulmonary morphology, physiology, and respiratory functions change in both physiological and pathological conditions. Internal lung surface area (ISA), representing the gas-exchange capacity of the lung, is a critical criterion to assess respiratory function. However, observer bias can significantly influence measured values for lung morphological parameters. The protocol that we describe here minimizes variations during measurements of two morphological parameters used for ISA calculation: internal lung volume (ILV) and mean linear intercept (MLI). Using ISA as a morphometric and functional parameter to determine the outcome of alveolar regeneration in both pneumonectomy (PNX) and prosthesis implantation mouse models, we found that the increased ISA following PNX treatment was significantly blocked by implantation of a prosthesis into the thoracic cavity1. The ability to accurately quantify ISA is not only expected to improve the reliability and reproducibility of lung function studies in injured-induced alveolar regeneration models, but also to promote mechanistic discoveries of multiple pulmonary diseases.
Introduction
الوظيفة الأساسية للرئة هي تبادل الأكسجين وثاني أكسيد الكربون بين الأوعية الدموية والغلاف الجوي. أمراض الرئة مثل خلل التنسج القصبي الرئوي (بد)، مرض الانسداد الرئوي المزمن (كوبد)، والتهابات الجهاز التنفسي الحادة، ويؤدي إلى انخفاض عيسى 2 . وقد طور الباحثون الذين يدرسون أمراض الرئة العديد من الطرق الكمية لتقييم التغيرات المورفولوجية في الرئتين، بما في ذلك ملي، إلف، وعدد من وحدات تبادل الغاز، عيسى، والالتزام أنسجة الرئة 2 ، 3 . دراسات رائدة من قبل ويبل وآخرون. 4 و دوغويد إت آل. 5 معا أن المعیار الدولي للتدقیق یمکن استخدامھ کمقیاس مباشر لقدرة تبادل الغاز الرئوي في الرئتین البشریة ویمکن استخدامھ کمعیار لتحدید شدة انتفاخ الرئة. وقد استخدم عدد من الدراسات التي نشرت في السنوات الخمس الماضية المعلمات المورفولوجية الرئة (على سبيل المثال، </eم> عيسى و ملي) لتقييم التغيرات المورفولوجية والوظيفية في الرئتين من الفئران خلال التنمية 6 وخلال الانتعاش من إصابة ينكس 1 ، 7 . ويحسب عيسى باستخدام المعادلة 1 8 و 9 :
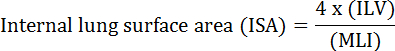
، حيث إلف هو حجم الرئة الداخلية و ملي هو وسيط المعلمة التي تمثل المجال الجوي الطرفية الرئوية حجم 10 .
ينكس، إزالة جراحية واحدة أو أكثر من فصوص الرئة، تم الإبلاغ على نطاق واسع للحث على تجديد السنخية في العديد من الأنواع، بما في ذلك البشر 11 ، الفئران 1 ، الكلاب 12 ، الفئران 13 ، والأرانب 14 ، 15 . مسمارذ من الرئتين الفئران في أربعة عشر يوما بعد بنكس أظهرت أن كلا من التوسع في الحويصلات الهوائية الموجودة مسبقا وتشكيل دي نوفو من الحويصلات الهوائية تسهم في استعادة عيسى، إلف، وعدد من الحويصلات الهوائية في أنسجة الرئة المتبقية 1 . لقد أظهرنا نحن وآخرون أن إدخال مواد مثل الإسفنج أو الشمع أو بدلة على شكل مخصص في التجويف الصدري الفارغ بعد بنكس ( أي زرع الأطراف الاصطناعية) يضعف تجديد السنخية. ومن الثابت الآن أن القوة الميكانيكية تعمل باعتبارها واحدة من أهم العوامل لبدء تجديد السنخية 1 ، 16 ، 17 . وقد سلطت هذه الدراسات الضوء على فعالية استخدام قيم عيسى من بنكس المعالجة والرئة الاصطناعية مزروع كمعيار لتقييم كميا تجديد السنخية.
ومن المعروف أن التحيز المراقب تؤثر تأثيرا كبيرا فازهري لمعلمات المورفولوجية الرئة (على سبيل المثال، MIL وILV). ويمكن استخدام بروتوكولات موحدة لتفادي هذا التحيز في تحديد كل من إلف و ملي، وهما البارامترات المستخدمة في حساب عيسى. هنا، ونحن نقدم بروتوكولات مفصلة للغاية، موحدة لقياس هذه المعلمات الرئة. الأهم من ذلك، القدرة على تحديد بدقة عيسى وعد بتحسين موثوقية واستنساخ الدراسات من وظائف الرئة في نماذج تجديد السنخية الناجم عن إصابة وينبغي أن تسهل الاكتشافات الميكانيكية في أمراض رئوية متعددة.
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
في هذا البروتوكول، ونحن نقدم أوصاف مفصلة عن قياس المعلمات الرئوية بعد الماوس اليسار الرئة ينكس وزرع الاصطناعية. ويعتبر عيسى الآن مقياسا رئيسيا لتقييم وظيفة الجهاز التنفسي في العديد من الأمراض الرئوية وفي تجديد السنخية الناجم عن الإصابة. ومع ذلك، على الرغم من أن مجت?…
Declarações
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
ويود المؤلفون أن يعترفوا بالمعهد الوطني للعلوم البيولوجية، بيجين، على المساعدة. وأيد هذا العمل من قبل مؤسسة العلوم الطبيعية لبلدية بكين (رقم Z17110200040000).
Materials
| Low cost cautery kit | Fine Science Tools | 18010-00 | |
| Noyes scissors | Fine Science Tools | 15012-12 | |
| Standard pattern forceps | Fine Science Tools | 11000-12 | |
| Castroviejo Micro Needle Holders | Fine Science Tools | 12060-01 | |
| Vessel clips | Fine Science Tools | 18374-44 | |
| I. V. Cannula-20 gauge | Jinhuan Medical Product Co., LTD. | 29P0601 | |
| Surgical suture | Jinhuan Medical Product Co., LTD. | F602 | |
| Mouse intubation platform | Penn-Century, Inc | Model MIP | |
| Small Animal Laryngoscope | Penn-Century, Inc | Model LS-2-M | |
| TOPO Small Animal Ventilator | Kent Scientific | RSP1006-05L | |
| Thermal pad | Stuart equipment | SBH130D | |
| Pentobarbital sodium salt | Sigma | P3761 | |
| Heparin sodium salt | Sigma | H3393 | |
| Hematoxylin Solution | Sigma | GHS132 | |
| Eosin Y solution, alcoholic | Sigma | HT110116 | |
| 10 ml Pipette | Thermo Scientific | 170356 | |
| Paraformaldehyde | Sigma | P6148 | |
| O.C.T Compound | Tissue-Tek | 4583 | |
| cryosection machine | Leica | CM1950 | |
| Disposable Base Molds | Fisher HealthCare | 22-363-553 | |
| 18 gauge needle | Becton Dickinson | 305199 | |
| Povidone iodine | Fisher Scientific | 19-027132 | |
| 70% ethanol | Fisher Scientific | BP82011 | |
| Infusion sets for single use | Weigao | SFDA 2012 3661704 | |
| Phosphate buffered saline | Gibco | 10010023 | |
| Tapes | 3M Scotch | 8915 | |
| Cotton pad | Vinda | Dr.P | |
| Silicone prosthesis | Custom made | ||
| Brightfield microscope | Olympus | VS120 | |
| Ruler tool | Adobe Photoshop |
Referências
- Liu, Z., et al. MAPK-Mediated YAP Activation Controls Mechanical-Tension-Induced Pulmonary Alveolar Regeneration. Cell Rep. 16 (7), 1810-1819 (2016).
- Thurlbeck, W. M. Internal surface area and other measurements in emphysema. Thorax. 22 (6), 483-496 (1967).
- Knudsen, L., Weibel, E. R., Gundersen, H. J. G., Weinstein, F. V., Ochs, M. Assessment of air space size characteristics by intercept (chord) measurement: an accurate and efficient stereological approach. J Appl Physiol. 108 (2), 412-421 (2010).
- Weibel, E. R. . Morphometry of the Human Lung. , (1963).
- Duguid, J. B., Young, A., Cauna, D., Lambert, M. W. The internal surface area of the lung in emphysema. J Pathol Bacteriol. 88, 405-421 (1964).
- Branchfield, K., et al. Pulmonary neuroendocrine cells function as airway sensors to control lung immune response. Science. 351 (6274), 707-710 (2016).
- Ding, B. -. S., et al. Endothelial-derived angiocrine signals induce and sustain regenerative lung alveolarization. Cell. 147 (3), 539-553 (2011).
- Dunnill, M. S. Quantitative methods in the study of pulmonary pathology. Thorax. 17 (4), 320-328 (1962).
- Weibel, E. R., Gomez, M. Architecture of the human lung. Use of quantitative methods establishes fundamental relations between size and number of lung structures. Science. 137 (3530), 577-585 (1962).
- Thurlbeck, W. M. The internal surface area of nonemphysematous lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 95 (5), 765-773 (1967).
- Butler, J. P., et al. Evidence for adult lung growth in humans. N Engl J Med. 367 (16), 244-247 (2012).
- Hsia, C. C. W., Herazo, L. F., Fryder-Doffey, F., Weibel, E. R. Compensatory lung growth occurs in adult dogs after right pneumonectomy. J Clin Invest. 94 (1), 405-412 (1994).
- Thurlbeck, S. W. M. Pneumonectomy in Rats at Various Ages. Am Rev Respir Dis. 120 (5), 1125-1136 (1979).
- Cagle, P. T., Langston, C., Thurlbeck, W. M. The Effect of Age on Postpneumonectomy Growth in Rabbits. Pediatr Pulmonol. 5 (2), 92-95 (1988).
- Langston, C., et al. Alveolar multiplication in the contralateral lung after unilateral pneumonectomy in the rabbit. Am Rev Respir Dis. 115 (1), 7-13 (1977).
- Cohn, R. Factors Affecting The Postnatal Growth of The Lung. Anatomical Record. 75 (2), 195-205 (1939).
- Hsia, C. C., Wu, E. Y., Wagner, E., Weibel, E. R. Preventing mediastinal shift after pneumonectomy impairs regenerative alveolar tissue growth. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 281 (5), L1279-L1287 (2001).
- Das, S., MacDonald, K., Chang, H. -. Y. S., Mitzner, W. A simple method of mouse lung intubation. J Vis Exp. (73), e50318 (2013).
- Liu, S., Cimprich, J., Varisco, B. M. Mouse pneumonectomy model of compensatory lung growth. J Vis Exp. (94), (2014).
- Silva, M. F. R., Zin, W. A., Saldiva, P. H. N. Airspace configuration at different transpulmonary pressures in normal and paraquat-induced lung injury in rats. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 158 (4), 1230-1234 (1998).
- Yilmaz, C., et al. Noninvasive quantification of heterogeneous lung growth following extensive lung resection by high-resolution computed tomography. J Appl Physiol. 107 (5), 1569-1578 (2009).
- Voswinckel, R., et al. Characterisation of post-pneumonectomy lung growth in adult mice. Eur Respir J. 24 (4), 524-532 (2004).
- Ravikumar, P., et al. Regional Lung Growth and Repair Regional lung growth following pneumonectomy assessed by computed tomography. J Appl Physiol. 97, 1567-1574 (2004).
- Gibney, B. C., et al. Detection of murine post-pneumonectomy lung regeneration by 18FDG PET imaging. EJNMMI Res. 2 (1), (2012).
- Muñoz-Barrutia, A., Ceresa, M., Artaechevarria, X., Montuenga, L. M., Ortiz-De-Solorzano, C. Quantification of lung damage in an elastase-induced mouse model of emphysema. Int J Biomed Imaging. 2012, (2012).

