閉じ込められていない狭間性界面活性剤ベースの剪断間粘弾性流体における球状粒子の沈降速度の実験的測定
Summary
本論文では、界面活性剤ベースの剪断間粘弾性流体中の球状粒子の末端沈降速度を測定する実験手順を示す。多様なレオロジー特性を超える流体が準備され、平行な壁の間の無限の流体および流体の粒径の範囲に対して、沈降速度が測定されます。
Abstract
実験研究は、界面活性剤ベースのせん断薄化粘弾性(VES)流体における球形粒子の末端沈降速度を測定するために行われる。測定は、境界のない流体に沈降するパーティクルと、平行な壁の間の流体に対して行われます。広範囲のレオロジー特性にわたるVES液は調製され、レオロジー的に特徴づけられる。レオロジー特性は、安定したせん断粘度と動的振動せん断測定を含み、粘性および弾性特性をそれぞれ定量化します。無制限の条件下での沈降速度は、粒子の直径の少なくとも25倍の直径を有するビーカーで測定される。平行壁間の沈降速度を測定するために、異なる壁間隔を持つ2つの実験細胞が構成される。様々なサイズの球状粒子は、静かに流体中にドロップされ、沈着させる。このプロセスは高解像度のビデオカメラで記録され、粒子の軌跡は画像解析ソフトウェアを使用して記録されます。端子のセトリング速度はデータから計算されます。
無限の流体における沈降速度に対する弾性の影響は、実験沈降速度を、ルノーらの非弾性抗力予測によって計算された沈降速度と比較することによって定量化される 。1結果は、流体の弾性が沈降速度を増加または減少させることができることを示しています。減少/増加の大きさは、流体のレオロジー特性と粒子の特性の関数です。閉じ込められた壁は沈降に対して遅滞効果を引き起こすのが観察され、遅滞は壁因子の観点から測定される。
Introduction
医薬品製造、廃水処理、宇宙推進剤再注入、半導体処理、液体洗剤製造などの用途で液体中の粒子の懸濁液が発生します。石油業界では、粘弾性破砕液は、油圧破断でプロパント(典型的には砂)を輸送するために使用されます。プロパンツのポンピングの停止時に、骨折を開いたままにして、炭化水素が戻って流れる導電経路を提供します。
粒子の沈降は、流体の流動学と密度、粒子の大きさ、形状および密度、および閉じ壁の効果によって支配される。クリーピング流動の中でニュートン流体に沈降する球形粒子の場合、沈降速度はストークス方程式によって与えられ、1851年にストークスによって導出される。より高いレイノルズ数での抗力を計算する式は、その後の研究者2-6によって提示されている。壁を閉じると、パーティクルに対して遅滞効果が出ることで、沈降速度が低下します。壁率 Fwは、境界のない条件下での閉じ壁の存在下での端子のセトリング速度の比率として定義されます。壁係数は、閉じ壁の遅位効果を定量化します。レイノルズ数の広い範囲にわたって異なる断面管内の異なる断面管内のニュートン流体に沈降する球体の壁因子を決定するための多くの理論的および実験的研究は、文献7-13で利用可能である。全体として、ニュートン流体の球体のドラッグを決定するために利用可能な情報の広範なボディがあります。
非ニュートン流体、特に粘弾性流体における粒子の沈降速度の決定に関する過去の研究は、あまり完全ではありません。様々な数値予測14-18 および実験研究19-24 は、非弾性力則流体における球体上の抗力を決定するために文献で利用可能である。トリパチらの理論予測 を用いて15 とトリパティとチャブラ17、ルノー ら1 は、非弾性力則流体における抗力係数(CD)を計算するために、次の式を開発した。
RePL<0.1(クリーピングフローレジーム)
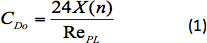
ここで、X(n) は、ドラッグ補正係数13です。RePLは、次のように定義された電力法則液体に含まれる球体のレイノルズ数です。
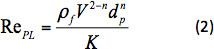
ここで ρfは液体の密度です。ドラッグ補正係数は、次の式1で合いました。
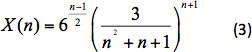
ドラッグ係数の定義を使用して、セトリング速度は次のように計算されます。
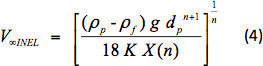
0.1<REPL<100の場合
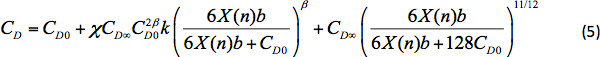
ここで Xは、パーティクルの投影された領域に対する表面積の比率で、球の場合は 4 に等しくなります。CD0は、ストークス領域の抵抗係数(RePL < 0.1)で、方程式 1、 CD∞はニュートン領域のドラッグ係数の値です (RePL > 5 x 102)は 0.44 です。β、b、kのパラメータは次のように表されます。
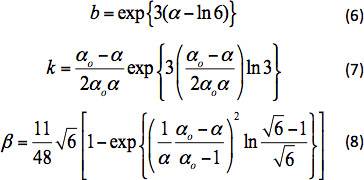
αo = 3 と α は 、X(n) に関連する平均せん断速度の補正です。
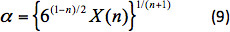
セトリング速度を計算するには、寸法なしグループNd 25が使用されます。
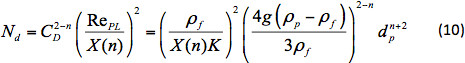
Nd は、セトリング速度とは無関係であり、明示的に計算できます。この値と 、方程式5のドラッグ係数式を使用して、RePL を反復的に解くことができます。次に、次の方法で定後速度を計算できます。
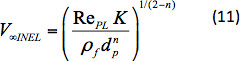
数式 1 ~ 9の式は、0.4 ≥ nの値に対して得られた理論上の予測≥基づいていました。Chhabra13は、上記の式からの予測をシャー26-27(nは0.281-0.762から変化した)およびFordらの実験結果と比較した。 28 (n は0.06 から 0.29 まで変化した)。この式は、ドラッグ係数を正確に予測するために示された。これらの解析に基づいて、上記の配合は、1≥n 0.06の非弾性パワーロー流体中の球状粒子の沈降速度≥計算するために使用することができる。この非弾性力則流体におけるこの予測された沈降速度は、パワーロー粘弾性流体の実験速度と比較され、沈降速度に対する流体弾性の影響を決定する。詳細な手順については、次のセクションで説明します。
粘弾性流体中の粒子の沈降速度の決定は、異なる研究者による様々な観測を用いた研究のトピックとなっています。(i)クリーピングフローレジームでは、せん断薄化効果が粘弾性効果に完全に影を落とし、沈降速度は純粋に粘性理論29-32と良好に一致しており、(ii)粒子は忍び寄る流れ体制の内外での抗力減少を経験し、弾力性のために沈降速度が増加する30,33,34、(iii)沈降速度は流弾性に起因する流動性を低下させる35.ウォルターズとタナー36 は、ボガー流体(一定粘性弾性流体)の弾性のために、低いヴァイセンバーグ数でのドラッグ低減を引き起こし、その後、より高いヴァイゼンベルグ数でドラッグエンハンスメントすることを要約した。マッキンリー37 は、球の後の延長効果がワイゼンベルクの数でより高い抗力増加を引き起こすことを強調した。Chhabra13 は、無限で閉じ込められた粘弾性流体中の粒子の沈降に関する以前の作業を包括的に見直した後、理論的な開発における流体弾性と共にせん断速度依存粘度の現実的な記述を取り入れるという課題を強調した。球状粒子の沈降に及ぼす壁の影響の研究は、過去数年間で研究の分野ともなっています38-42.しかし、すべての作業は、円筒形のチューブ内の球状粒子の沈降に行われています。平行壁間の粘弾性流体に沈降する球状の粒子にはデータがありません。
この研究は、剪断間粘弾性流体における球体の沈降を実験的に研究することを試みる。この実験研究の目的は、流体の弾力性、剪断間薄化および閉じ込め壁が、剪断薄化粘弾性流体における球状粒子の沈降速度に及ぼす影響を理解することである。本論文では、この研究に用いられる実験方法といくつかの代表的な結果に焦点を当てた。分析と共に詳細な結果は、以前の出版物43で見つけることができます。
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
実験研究は、閉じ込められていない限り閉じ込められた条件下での剪断間粘弾性流体における球状粒子の沈降速度の測定に焦点を当てています。沈降速度の反復可能な測定値を得るための詳細な実験手順が提示される。流体の弾性が沈降速度を増減できることを示す結果が示されます。壁は沈降に対して遅滞効果を発揮し、この効果は壁の係数の観点から測定されます。
<p class="jove_content"…Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
著者らは、財政支援とテキサス大学オースティン校の油圧破砕と砂の制御に関するJIPを後援する企業(エアリキード、エアプロダクツ、アナダルコ、アパッチ、ベイカーヒューズ、BHPビリトン、BPアメリカ、シェブロン、コノコフィリップス、エクソンモービル、フェルス、ハリバートン、ヘス、リンデグループ、プレンツ、パイオニア、ミデグループ、ミトン、ミトン、パイオニア、アンタチュアル・リニューアルに感謝しています。、プラクセア、サウジアラムコ、シュルンベルガー、シェル、サウスウェスタンエナジー、スタトイル、ウェザーフォード、YPF)。
Materials
| Name of the reagent / equipment | Company | Catalogue number | Comments |
| Glass Microspheres | Whitehouse Scientific | #GP1750 | Available in different sieve fractions. |
| Rheometer | TA Instruments | ARES | Any standard rheometer capable of taking dynamic and static measurements |
| Anionic Surfactant (Component A) | Proprietary fluid | Used in oil field services for hydraulic fracturing. Sodium Xylene Sulfonate can be used as a substitute. | |
| Cationic Surfactant (Component B) | Proprietary fluid | Used in oil field services for hydraulic fractuing. N,N,N-Trimethyl-1-Octadecamonium Chloride can be used as a substitute. |
References
- Renaud, M., Mauret, E., Chhabra, R. P. Power-law fluid flow over a sphere: average shear rate and drag. 82, 1066-1070 (2004).
- Clift, R., Grace, J. R., Weber, M. E. . Bubbles, Drops and Particles. , (1978).
- Khan, A. R., Richardson, J. F. The resistance to motion of a solid sphere in a fluid. Chem. Eng. Sci. 62, 135-150 (1987).
- Zapryanov, Z., Tabakova, S. . Dynamics of Bubbles, Drops and Rigid Particles. , (1999).
- Michaelides, E. E., DeKee, D., Chhabra, R. P. Chapter 2. Analytical expressions for the motion of particles. Transport Processes in Bubbles Drops and Particles. , (2002).
- Michaelides, E. E. Hydrodynamic force and heat/mass transfer from particles, bubbles and drops – the Freeman Scholar Lecture. Journal of Fluids Engineering (AMSE. 125, 209-238 (2003).
- Der Faxen, H. Widerstand gegen die Bewegung einer starren Kugel in einer zähen Flüssigkeit, die zwischen zwei parallelen ebenen Wänden eingeschlossen ist). Annalen der Physics. 68, 89-119 (1922).
- Bohlin, T. On the drag on a sphere moving in a viscous fluid inside a cylindrical tube. Trans Royal Insitute of Technology Stockholm. 155, (1960).
- Miyamura, A., Iwasaki, S., Ishii, T. Experimental wall correction factors of single solid spheres in triangular and square cylinders, and parallel plates. International Journal of Multiphase Flow. 7, 41-46 (1981).
- Tullock, D. L., Phan-Thien, N., Graham, A. L. Boundary element simulations of spheres settling in circular, square and triangular ducts. Rheol. Acta. 31, 139-150 (1992).
- Chhabra, R. P. Wall effects on terminal velocity of non-spherical particles in non-Newtonian polymer solutions. Powder Technology. 88, 39-44 (1996).
- Chhabra, R. P., Dekes, D., Chhabra, R. P. Chapter 2. Wall effects on spheres falling axially in cylindrical tubes. Transport Processes in Bubbles Drops and Particles. , (2002).
- Chhabra, R. P., Francis, S. e. c. o. n. d. e. d. .. ,. T. a. y. l. o. r. &. a. m. p. ;. . Bubbles, Drops, and Particles in Non-Newtonian Fluids. , (2007).
- Dazhi, G., Tanner, R. I. The drag on a sphere in a power law fluid. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics. 17, 1-12 (1984).
- Tripathi, A., Chhabra, R. P., Sundararajan, T. Power-law fluid over spheroidal particles. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research. 33, 403-410 (1994).
- Graham, D. I., Jones, T. E. R. Settling and transport of spherical particles in power-law fluids at finite Reynolds number. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics. 54, 465-488 (1994).
- Tripathi, A., Chhabra, R. P. Drag on spheroidal particles in dilatant fluids. AIChE. 41 (3), 728-731 (1995).
- Missirlis, K. A., Assimacopoulos, D., Mitsoulis, E., Chhabra, R. P. Wall effects for motion of spheres in power-law fluids. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics. 96 (3), 459-471 (2001).
- Dallon, D. S. . A drag coefficient correlation for spheres settling in Ellis fluids [Ph.D. Dissertation]. , (1967).
- Uhlherr, P. H. T., Le, T. N., Tiu, C. Characterization of inelastic power-law fluids using falling sphere data. Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering. 54, 497-502 (1976).
- Machac, I., Lecjaks, Z. Wall Effect for a Sphere Falling Through a Non-Newtonian Fluid in a Rectangular Duct. Chemical Engineering Science. 50 (1), 143-148 (1995).
- Kelessidis, V. C., Mpandelis, G. Measurements and prediction of terminal velocity of solid particles falling through stagnant pseudoplastic liquids. Powder Technology. 147, 117-125 (2004).
- Shah, S. N., Fadili, Y. E., Chhabra, R. P. New model for single spherical particle settling velocity in power law (visco-inelastic) fluids. International Journal of Multiphase Flow. 33, 51-66 (2007).
- Rodrigue, D., DeKee, D., Chan Man Fong, C. F. The slow motion of a spherical particle in a Carreau fluid. Chemical Engineering Communications. 154, 203-215 (1996).
- Darby, R. . Chemical Engineering Fluid Mechanics. , (2001).
- Shah, S. N. Proppant settling correlations for non-Newtonian fluids. Society of Petroleum Engineers Journal. 22 (2), 164-170 (1982).
- Shah, S. N. Proppant-settling correlations for non-Newtonian Fluids. Society of Petroleum Engineers Production Engineering Journal. 1 (6), 446-448 (1986).
- Ford, J. T., Oyeneyin, M. B., et al. The formulation of milling fluids for efficient hole cleaning: an experimental investigation. Paper SPE 38819. , (1994).
- Acharya, A., Mashelkar, R. A., Ulbrecht, J. Flow of inelastic and viscoelastic fluids past a sphere, Part II: Anomalous separation in the viscoelastic fluid flow. Rheological Acta. 15, 471-478 (1976).
- Acharya, A. R. Viscoelasticity of crosslinked fracturing fluids and proppant transport. SPE Production Engineering. 3, 483-488 (1988).
- Chhabra, R. P., Uhlherr, P. H. T. Creeping motion of spheres through shear-thinning elastic fluids described by the Carreau viscosity equation. Rheological Acta. 19 (2), 187-195 (1980).
- Bush, M. B., Phan-Thien, N. Drag force on a sphere in creeping motion through a Carreau model fluid. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics. 16 (3), 303-313 (1984).
- Broadbent, J. M., Mena, B. Slow flow of an elastico-viscous fluid past cylinders and spheres. Chemical Engineering Journal. 8, 11-19 (1974).
- Sigli, D., Coutanceau, M. Effect of finite boundaries on the slow laminar isothermal flow of a viscoelastic fluid around a spherical obstacle. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics. 2, 1-21 (1977).
- Brule, B. H. A. A. V. D., Gheissary, G. Effects of fluid elasticity on the static and dynamic settling of a spherical particle. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics. 49, 123-132 (1993).
- Walters, K., Tanner, R. I., Chhabra, R. P. . D. e. K. e. e. ,. D. .. ,., DeKee, D. Chapter 3. The Motion of a Sphere through an Elastic Fluid.. Transport Processes in Bubbles, Drops and Particles. , (1992).
- McKinley, G. H., DeKee, D., Chhabra, R. P. Chapter 14. Steady and transient motion of spherical particles in viscoelastic liquids. Transport Processes in Bubbles, Drops and Particles. , (2002).
- Chhabra, R. P., Tiu, C., Uhlherr, P. H. T. A study of wall effects on the motion of a sphere in viscoelastic fluids. Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering. 59, 771-775 (1981).
- Jones, W. M., Price, A. H., Walters, K. The motion of a sphere falling under gravity in a constant viscosity elastic liquid. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics. 53, 175-196 (1994).
- Navez, V., Walters, K. A note on settling in shear-thinning polymer solutions. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics. 67, 325-334 (1996).
- Huang, P. Y., Wall Feng, J. effects on the flow of viscoelastic fluids around a circular cylinder. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics. 60, 179-198 (1995).
- Sugeng, F., Tanner, R. I. The drag on spheres in viscoelastic fluids with significant wall effects. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics. 20, 281-292 (1986).
- Malhotra, S., Sharma, M. M. Settling of Spherical Particles in Unbounded and Confined Surfactant-Based Shear Thinning Viscoelastic Fluids: An Experimental Study. Chemical Engineering Science. 84, 646-655 (2012).
- Zhang, K. Fluids for Fracturing Subterranean Formations.U.S. US patent. , (2002).
- Gupta, D. V. S., Leshchyshyn, T. T., Hlidek, B. T. Surfactant gel foam/emulsions: History and field application in the western Canadian sedimentary basin. , (2005).
- Ferry, J. D. . Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers. , (1970).
- Yesilata, B., Clasen, C., McKinley, G. H. Nonlinear shear and extensional Flow dynamics of wormlike surfactant solutions. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics. 133, 73-90 (2006).

