마우스입니다 관류 신장 기법
Summary
마우스 절연 신장 관류 (MIPK)를 관류하고 1 시간 동안 기능성 생체 조건 마우스 신장을 유지하기위한 기술이다. 버퍼 수술 기법은 상세하게 설명된다.
Abstract
마우스 절연 신장 관류 (MIPK)를 관류하고 1 시간 동안 기능성 생체 조건 마우스 신장을 유지하기위한 기술이다. 이 분리 된 기관 및 관류 신장 생명 공학에 대한 탈세 포화 또는 항 거부 또는 소수 신장에 고용량의 게놈 편집 약물의 투여를 포함한 미래에 가능할 수있다 많은 혁신적인 애플리케이션에 대한 생리 연구를위한 전제 조건입니다 이식. 재관류 시간 동안 신장은 신장 기능이 평가 될 수 있고, 조작, 및 다양한 제약으로 투여 될 수있다. 절차 후 신장 이식 될 수있다 또는 분자 생물학, 생화학 분석, 또는 현미경에 대한 처리.
본 논문은 관류 및 마우스 신장의 생체 외 관류에 필요한 수술 기법에 대해 설명합니다. 관류 장치의 상세에 주어진 데이터는 V를 도시 제시신장의 제조 iability : 형태소 판독 및 분자 판독 상이한 네프론 세그먼트 수송 단백질의 웨스턴 블랏 상이한 네프론 세그먼트 기능, 투과 전자 현미경과 같은 신장 혈류, 혈관 저항 및 소변 데이터.
Introduction
기관의 고립 된 관류는 수십 년 1 생리 학자들 사이에서 지속적인 노력의 대상이되고있다. 기술은 혈압, 호르몬 또는 신경 조직 등의 영향없이, 기관의 기능을 가능하게 검토한다. 칼 에두아르 Loebell는 1849 2, 고립 된 신장의 성공적인 재관류을 설명했습니다 첫 번째로 간주됩니다. 그 이후로, 관류 장치에 상당한 정련을 실시하고있다. 프레이와 그루버는 지속적인 관류 2 산소와 타악기 펌프 용 인공 폐를 소개했다. 초기 연구는 주로 큰 포유 동물 – 즉, 돼지 2 개 3 쥐 신장의 사용 – 첫번째 보고서, 와이즈 등으로의 신장을 공부하는 동안. , 작은 포유 동물 기관 관류 (4)의 연구에서 획기적인 사건이었다. Schurek 등. 충분한 신 세뇨관 경우 관류에 포유류의 적혈구를 추가의 필요성을보고산소는 5를 달성 할 수 있었다. 장기간 실험 긴급 동일한 연구 그룹 (6)에 의해 버퍼의 연속 투석의 도입이었다. 2003 년 SCHWEDA 등. 나중에 Rahgozar 등에 의해 정제 기능 마우스 고립 관류 신장 (MIPK) 7을보고 처음이었다. 18 Lindell 등의 알. 14.
절연 신장 관류 래트보다 기술적으로 어려운 반면, MIPK의 사용은 유전자 변형 마우스의 다양한 배열의 사용을 가능하게하는 장점을 맺는다. 이 논문은 1 시간 동안 고립 된 마우스 신장 관류에 대한 저자의 방법의 세부 사항을 제공합니다. 상기 방법은 신장 유량 혈관 저항 호르몬 방출 혈액 가스 분석, 소변 분석, 약물의 애플리케이션의 지속적인 평가를 허용한다. 절차에 따라, 신장은, 분자 및 생화학 분석을 위해 처리 할 수있는 현미경에 대한 고정, 또는받는 사람 마우스에 이식 (그림 1).
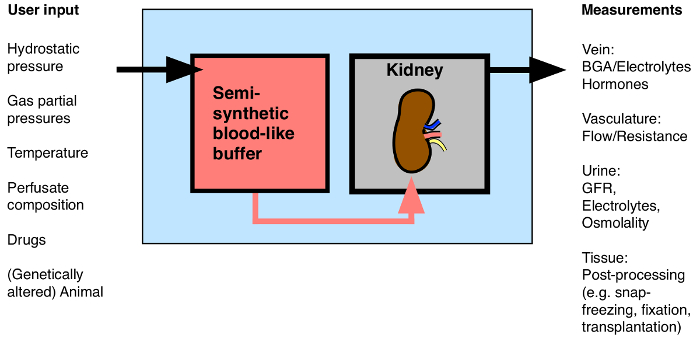
그림 1 : 절연 관류 신장에 가능한 입 / 출력의 개요. BGA : 혈액 가스 분석. 이 그림의 더 큰 버전을 보려면 여기를 클릭하십시오.
많은 혁신적인 응용 프로그램 (또는 항 거부 또는 게놈 편집 약물의 응용 프로그램없이) 8, 9, 이전 이식에 장기간 정상 체온 신장 관류의 새벽 논의되는 바와 같이이 기술은 가능성, 10, 향후 몇 년에 걸쳐 관심을 증가 받게됩니다 11, decellularized 발판 (12)의 전체 신장의 생명 공학 및 광자 이미징 13 형광 염료의 고용량의 적용 </sup>. 또한 급성 신부전 (14) 중 특정 유전자의 역할을 연구와 이상적인 모델이다.
단계별 프로토콜은 다른 실험실에서 성공적으로 격리 된 마우스 신장 재관류를 수행 할 수 있도록 설명한다. 첫째, 조성물 및 완충액의 제조 지정된다. 그리고, 수술 상세히 설명되며 중요한 단계가 도시되어있다. 셋째, 데이터가 성공적으로 제조 나타내는 것을 제시되어 신장 혈류, 혈관 저항, 사구체 여과율 및 분수 전해질 배설 모두 관류 신장 다른 네프론 세그먼트 형태의 생존 및 투과형 전자 현미경의 기능적 측정 관류의 1 시간 후 고정.
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
관류 신장 절연 마우스 수많은 전신 요인의 영향에 의해 결함이 될 수있다 손상 동물 생체 실험 간의 격차를 1 시간 동안 제어 된 환경 생체 신장 기능을 연구하기위한 도구이고, 시험 관내 실험에서 격리 된 네프론 세그먼트 또는 반드시 기능에 손상 장기 구조의 영향을 무시 배양 된 세포. , 저자의 지식과 대안 기술이 특정 작업을이 수행하지 않는 것입니다. 신장 조직의 생?…
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Hans-Joachim Schurek for invaluable scientific advice. The authors would like to thank Monique Carrel and Michèle Heidemeyer for excellent technical assistance, David Penton Ribas and Nourdine Faresse for a critical reading of the manuscript and Carsten Wagner and Jürg Biber for the NaPi-2a antibody. This work was supported by the Swiss National Centre for Competence in Research “Kidney.CH” and by a project grant (310030_143929/1) from the Swiss National Science Foundation.
Materials
| Perfusion Circuit: | |||
| Moist chamber 834/8 | Harvard Apparatus/Hugo Sachs Elektronik GmbH | 73-2901 | |
| Cannular with basket and side port | Harvard Apparatus/Hugo Sachs Elektronik GmbH | 73-2947 | |
| Thermostat TC120-ST5 | Harvard Apparatus/Hugo Sachs Elektronik GmbH | 73-4544 | |
| ISM 827/230V Roller Pump Reglo Analogue | Harvard Apparatus/Hugo Sachs Elektronik GmbH | 73-0114 | |
| Reservoir jacketed for buffer solution 1L | Harvard Apparatus/Hugo Sachs Elektronik GmbH | 73-3438 | |
| Reservoir jacketed for buffer solution 0.5L | Harvard Apparatus/Hugo Sachs Elektronik GmbH | 73-3436 | |
| Pressure Transducer APT300 | Harvard Apparatus/Hugo Sachs Elektronik GmbH | 73-3862 | |
| TAM-D Plugsys Transducer | Harvard Apparatus/Hugo Sachs Elektronik GmbH | 73-1793 | |
| SCP Plugsys servo controller | Harvard Apparatus/Hugo Sachs Elektronik GmbH | 73-2806 | |
| Windkessel | Harvard Apparatus/Hugo Sachs Elektronik GmbH | 73-3717 | |
| HSE-USB data acquisition | Harvard Apparatus/Hugo Sachs Elektronik GmbH | 73-3330 | |
| Low-Flux Dialysator Diacap Polysulfone | B.Braun | 7203525 | |
| PE-Tubing for aorta cannulation 1.19mm I.D. x 1.70mm O.D. | Scientific Commodities Inc. | BB31695-PE/8 | |
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Buffer reagents: | |||
| Aminoplasmal 10% | B.Braun | 134518064 | |
| Sodium pyruvate | Sigma-Aldrich | P2256-25G | |
| L-Glutamic acid monosodium salt hydrate | Sigma-Aldrich | G1626-100G | |
| L-(-)-Malic acid sodium salt | Sigma-Aldrich | M1125-25G | |
| Sodium-L-Lactate | Sigma-Aldrich | L7022-10G | |
| alpha-Ketoglutaric acid sodium salt | Sigma-Aldrich | K1875-25G | |
| NaCl | Sigma-Aldrich | 31434-1KG-R | |
| NaHCO3 | Sigma-Aldrich | S5761-5KG | |
| KCl | Sigma-Aldrich | 60130-1KG | |
| Urea | Sigma-Aldrich | U5378-500G | |
| Creatinine | Sigma-Aldrich | C4255-10G | |
| Ampicillin | Roche | 10835242001 | |
| MgCl2 * 6H2O | Sigma-Aldrich | M2393-500G | |
| D-Glucose | Sigma-Aldrich | G8270-1KG | |
| CaCl2 * 6H2O | Riedel-de-Haën | 12074 | |
| NaH2PO4 | Sigma-Aldrich | S9638-500G | |
| Na2HPO4 | Sigma-Aldrich | S0876-500G | |
| Antidiuretic Hormone dDAVP | Sigma-Aldrich | V2013-1MG | |
| FITC-Inulin | Sigma-Aldrich | ||
| Filter used for erythrocyte filtration | Macherey-Nagel | MN 615 | |
| BGA Analysis: | |||
| ABL 80 flex | Radiometer Medical ApS | ||
| Electron Microscope: | |||
| Philips CM100 TEM | FEI |
References
- Carrel, A., Lindbergh, C. A. The culture of whole organs. Science (New York, N.Y.). 81 (2112), 621-623 (1935).
- Skutul, K. . Über Durchströmungsapparate Pflüger’s Archiv. 123 (4-6), 249-273 (1908).
- Nizet, A. The isolated perfused kidney: possibilities, limitations and results. Kidney Int. 7 (1), 1-11 (1975).
- Weiss, C., Passow, H., Rothstein, A. Autoregulation of flow in isolated rat kidney in the absence of red cells. Am J Physiol. 196 (5), 1115-1118 (1959).
- Schurek, H. J., Kriz, W. Morphologic and functional evidence for oxygen deficiency in the isolated perfused rat kidney. Lab Invest. 53 (2), 145-155 (1985).
- Stolte, H., Schurek, H. J., Alt, J. M. Glomerular albumin filtration: a comparison of micropuncture studies in the isolated perfused rat kidney with in vivo experimental conditions. Kidney Int. 16 (3), 377-384 (1979).
- Schweda, F., Wagner, C., Krämer, B. K., Schnermann, J., Kurtz, A. Preserved macula densa-dependent renin secretion in A1 adenosine receptor knockout mice. AJP Renal Physiol. 284 (4), F770-F777 (2003).
- Moers, C., Smits, J. M., et al. Machine perfusion or cold storage in deceased-donor kidney transplantation. N Engl J Med. 360 (1), 7-19 (2009).
- Nicholson, M. L., Hosgood, S. A. Renal transplantation after ex vivo normothermic perfusion: the first clinical study. Am J Transplant. 13 (5), 1246-1252 (2013).
- Worner, M., Poore, S., Tilkorn, D., Lokmic, Z., Penington, A. J. A low-cost, small volume circuit for autologous blood normothermic perfusion of rabbit organs. Art Org. 38 (4), 352-361 (2014).
- Kaths, J. M., Spetzler, V. N., et al. Normothermic Ex Vivo Kidney Perfusion for the Preservation of Kidney Grafts prior to Transplantation. J Vis Exp. (101), e52909 (2015).
- Song, J. J., Guyette, J. P., Gilpin, S. E., Gonzalez, G., Vacanti, J. P., Ott, H. C. Regeneration and experimental orthotopic transplantation of a bioengineered kidney. Nature Med. 19 (5), 646-651 (2013).
- Hall, A. M., Crawford, C., Unwin, R. J., Duchen, M. R., Peppiatt-Wildman, C. M. Multiphoton imaging of the functioning kidney. JASN. 22 (7), 1297-1304 (2011).
- Lindell, S. L., Williams, N., Brusilovsky, I., Mangino, M. J. Mouse IPK: A Powerful Tool to Partially Characterize Renal Reperfusion and Preservation Injury. Open Transplant J. 5, 15-22 (2011).
- Wagner, C., De Wit, C., Kurtz, L., Grünberger, C., Kurtz, A., Schweda, F. Connexin40 is essential for the pressure control of renin synthesis and secretion. Circ Res. 100 (4), 556-563 (2007).
- Czogalla, J., Vohra, T., Penton, D., Kirschmann, M., Craigie, E., Loffing, J. The mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) regulates ENaC but not NCC in mice with random MR deletion. Pflüger’s Archiv. , (2016).
- Poosti, F., et al. Precision-cut kidney slices (PCKS) to study development of renal fibrosis and efficacy of drug targeting ex vivo. Dis Model Mech. 8 (10), 1227-1236 (2015).
- Rahgozar, M., Guan, Z., Matthias, A., Gobé, G. C., Endre, Z. H. Angiotensin II facilitates autoregulation in the perfused mouse kidney: An optimized in vitro model for assessment of renal vascular and tubular function. Nephrology. 9 (5), 288-296 (2004).

