Unchelated Gadolinium için bir Aptamer tabanlı Sensörü (III)
Summary
The use of polydeoxynucleotide (44-mer aptamer) molecules for sensing unchelated gadolinium(III) ion in an aqueous solution is described. The presence of the ion is detected via an increase in the fluorescence emission of the sensor.
Abstract
A method for determining the presence of unchelated trivalent gadolinium ion (Gd3+) in aqueous solution is demonstrated. Gd3+ is often present in samples of gadolinium-based contrast agents as a result of incomplete reactions between the ligand and the ion, or as a dissociation product. Since the ion is toxic, its detection is of critical importance. Herein, the design and usage of an aptamer-based sensor (Gd-sensor) for Gd3+ are described. The sensor produces a fluorescence change in response to increasing concentrations of the ion, and has a limit of detection in the nanomolar range (~100 nM with a signal-to-noise ratio of 3). The assay may be run in an aqueous buffer at ambient pH (~7 – 7.4) in a 384-well microplate. The sensor is relatively unreactive toward other physiologically relevant metal ions such as sodium, potassium, and calcium ions, although it is not specific for Gd3+ over other trivalent lanthanides such as europium(III) and terbium(III). Nevertheless, the lanthanides are not commonly found in contrast agents or the biological systems, and the sensor may therefore be used to selectively determine unchelated Gd3+ in aqueous conditions.
Introduction
Tekniğin doğal duyarlılığı ile sınırlıdır klinik tanı, manyetik rezonans görüntüleme (MRG) artan önemi, yeni gadolinyum bazlı kontrast maddeler (GBKM'lerin) 1 geliştirilmesine yönelik araştırma hızlı büyüme sonuçlandı. GBKM'lerin görüntü kalitesini artırmak için tatbik edilmektedir moleküllerdir ve bunlar genellikle çok dişli bir ligand ile koordine bir üç değerli gadolinyum iyonu (Gd 3+) kimyasal yapıya sahiptir. Bu kompleksleşme toksik 3+ unchelated Gd gibi kritik öneme sahiptir; böbrek hastalığı veya yetmezliği 2 olan bazı hastalarda nefrojenik sistemik fibrozis gelişiminde rolü olduğu bilinmektedir. Sonuç olarak, sulu serbest iyon tespit GBKM'lerin güvenliğini sağlamada etkili olduğunu. GBCA Çözeltilerin unchelated Gd 3+ varlığı genellikle ligand ve iyon kompleksinin ayrışma veya displacemen arasında bir tam olmayan reaksiyon sonucudiğer biyolojik metal katyonları 3 ile t.
Şu Gd 3+, çok yönlülük ve uygulanabilirliği 4 açısından kromatografi ve / veya spektrometre en yüksek değerli dayalı olanlar varlığını tespit etmek için kullanılan çeşitli teknikler arasında. Onların güçlü yanları arasında yüksek hassasiyet ve doğruluk, (bir liste ve çoklu Gd 3+ komplekslerin eşzamanlı ölçümü (insan serumu 5, idrar ve saç 6, atıksu 7 ve kontrast ajan formülasyonları 8 dahil) çeşitli numune matrisleri analiz yeteneği olan çalışmaların 2013 öncesinde Telgmann ve diğ.) 4 kapsamlı bir inceleme açıklanmaktadır. Tek dezavantajı bu yöntemlerden birkaç bazı laboratuvarlar erişimi olmayabilir (örneğin indüktif eşleşmiş plazma-kütle spektrometresi gibi) instrumentations 4 gerektirir olmasıdır. araştırma ve kanıt-of-concept seviyelerinde, ar de roman GBCA keşif kapsamındaelatively daha rahat, hızlı ve uygun maliyetli spektroskopik tabanlı bir yöntem (örneğin UV-Vis absorpsiyon veya floresan gibi) değerli bir alternatif olarak hizmet verebilir. Akılda bu uygulamalar sayesinde, sulu Gd 3+ için bir floresan aptamer tabanlı sensör 9 geliştirilmiştir.
Aptamer (Gd-aptamerin) üstel zenginleştirme (SELEX) 9 tarafından ligandların sistematik evrim süreci boyunca izole edildi bazların spesifik dizisi ile bir 44 baz uzunluğunda tek iplikli bir DNA molekülüdür. Floresan sensör içine aptamer uyarlamak için, bir flüorofor, sonra 13 tamamlayıcı bazlar (Şekil 1) aracılığı ile su verme telinin (QS) ile hibridize olan telin, 5 'ucuna eklenir. QS 3 'ucunda bir karanlık söndürücü molekülü ile etiketlenir. 1 oluşan Gd 3+, sensör (Gd-sensör) yokluğunda, sırasıyla: Gd-aptamer ve QS 2 mol oranı, en az floresans emisyon nedeniyle t olacaktırquencher için fluorofordan o enerji transferi. Sulu Gd 3+ eklenmesi floresan emisyonunda bir artışa neden, Gd-aptamer gelen QS ettirilir.
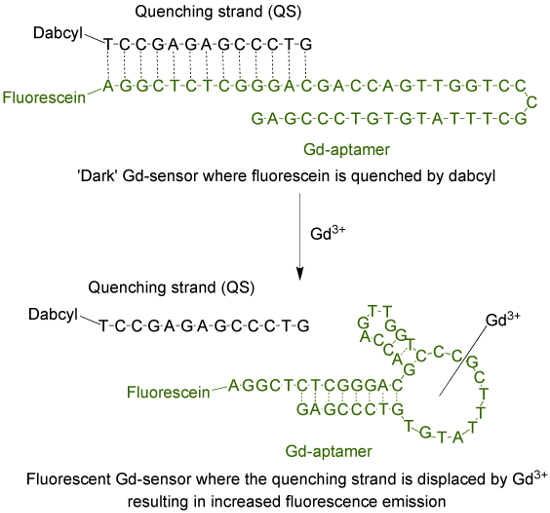
Floresein (bir fluorofor) ve DABCYL ile etiketlenmiş 13 baz uzunluğunda söndürme iplikçik (QS) ile etiketlenmiş 44 baz uzunluğunda aptamer (Gd-aptamer) (koyu söndürücü) oluşur Şekil 1. sensörü (Gd-sensör) . Unchelated Gd 3+ yokluğunda, algılayıcının flüoresan az. Gd 3+ eklenmesiyle, QS yerinden oluşur ve floresan emisyonunda bir artış gözlenmektedir. Bu rakamın büyük halini görmek için lütfen buraya tıklayınız.
Günümüzde vardır, yaygın bir şekilde kullanılan spektroskopik bazlı yöntem algılama içinSulu Gd 3+ ing. Bu tahlil iyonunun 10 şelasyon üzerine 433 nm 573 ila maksimum absorpsiyon dalga boyu bir kayma uğrar molekül ksilenol turuncu kullanır. Bu iki emilimi maksimum oranı unchelated Gd 3+ miktarını belirlemek için kullanılabilir. iki yöntem, hedef seçicilik, miktarının doğrusal aralıkları ve algılama yöntemlerinin (örneğin pH ve kullanılan tampon çözeltilerin bileşiminde gibi) farklı reaksiyon koşullarına sahip olarak aptamer sensörü, ksilenol turuncu tahlil alternatif (aynı zamanda tamamlayıcı olabilir) 'dir 9.
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
Aptamer göre Gd-sensörü, gözlenen unchelated Gd 3+ konsantrasyonu ile orantılıdır flüoresan emisyonunda bir artışa kullanılması. Kullanılan örnek miktarı en aza indirmek için, deney, göz başına 45 uL toplam numune hacmi olan bir 384-çukurlu bir mikrolevhadaki çalıştırılabilir. Bu tasarımda, floresein (FAM) ve DABCYL (Dab) seçimi öncelikle reaktiflerin maliyeti dayanmaktadır; emisyon dalga boyu, floroforun farklı eşleştirme değiştirme ve söndürücü 11 kullanılab…
Divulgazioni
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
We would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr. Milan N Stojanovic from Columbia University, New York, NY for valuable scientific input. This work is supported by funding from the California State University East Bay (CSUEB) and the CSUEB Faculty Support Grant-Individual Researcher. O.E., T.C., and A.L. were supported by the CSUEB Center for Student Research (CSR) Fellowship.
Materials
| Gd-aptamer | IDTDNA | Input sequence and fluorophore modification in the order form | A fluorophore with a different emission wavelength may be used. The aptamer may also be ordered from another company. |
| Quenching strand | IDTDNA | Input sequence and quencher modification in the order form | A different quencher for optimal energy transfer from the fluorophore may be used. The aptamer may also be ordered from another company. |
| Molecular biology grade water | No specific manufacturer, both DEPC or non-DEPC treated work equally well | ||
| Gadolinium(III) chloride anhydrous | Strem | 936416 | Toxic |
| HEPES | Fisher Scientific | BP310-500 | |
| Magnesium chloride anhydrous | MP Biomedicals | 0520984480 – 100 g | |
| Sodium Chloride | Acros Organics | 327300025 | |
| Potassium chloride | Fisher Scientific | P333-500 | |
| Sodium hydroxide, pellets | Fisher Scientific | BP359 | Corrosive |
| Hydrochloric acid | Fisher Scientific | SA49 | Toxic and corrosive |
| 384-well low flange black flat bottom polystyrene NBS plates | Corning | 3575 | Plates which are suitable for fluorescence reading are required. |
| Nalgene Rapid-Flow sterile disposable bottle top filter | Thermo Scientific | 5680020 | The bottle top is fitted with 0.2 micron PES membrane |
| Disposable sterile bottles 250 mL | Corning | 430281 | A larger or smaller bottle may be used |
| 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tubes | No specific manufacturer, as long as they are DNAse and RNAse-free | ||
| 0.2 mL PCR tubes | No specific manufacturer, as long as they are DNAse and RNAse-free | ||
| Micropipets | No specific manufacturer | ||
| Pipet tips (non filter) of appropriate sizes | No specific manufacturer, as long as they are DNAse and RNAse-free | ||
| Name of Equipment | |||
| Plate reader | Biotek Synergy H1 | Plate readers from other manufacturers would work equally well |
Riferimenti
- Shen, C., New, E. J. Promising strategies for Gd-based responsive magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 17 (2), 158-166 (2013).
- Cheong, B. Y. C., Muthupillai, R. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: a concise review for cardiologists. Tex. Heart Inst. J. 37 (5), 508-515 (2010).
- Hao, D., Ai, T., Goerner, F., Hu, X., Runge, V. M., Tweedle, M. MRI contrast agents: basic chemistry and safety. J Magn. Reson. Imaging. 36 (5), 1060-1071 (2012).
- Telgmann, L., Sperling, M., Karst, U. Determination of gadolinium-based MRI contrast agents in biological and environmental samples: a review. Anal. Chim. Acta. 764, 1-16 (2013).
- Frenzel, T., Lengsfeld, P., Schirmer, H., Hütter, J., Weinmann, H. -. J. Stability of gadolinium-based magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents in human serum at 37 degrees C. Invest. Radiol. 43 (12), 817-828 (2008).
- Loreti, V., Bettmer, J. Determination of the MRI contrast agent Gd-DTPA by SEC-ICP-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 379 (7), 1050-1054 (2004).
- Telgmann, L., et al. Speciation and isotope dilution analysis of gadolinium-based contrast agents in wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 46 (21), 11929-11936 (2012).
- Cleveland, D., et al. Chromatographic methods for the quantification of free and chelated gadolinium species in MRI contrast agent formulations. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 398 (7), 2987-2995 (2010).
- Edogun, O., Nguyen, N. H., Halim, M. Fluorescent single-stranded DNA-based assay for detecting unchelated gadolinium(III) ions in aqueous solution. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 408 (15), 4121-4131 (2016).
- Barge, A., Cravotto, G., Gianolio, E., Fedeli, F. How to determine free Gd and free ligand in solution of Gd chelates. A technical note. Contrast Med. Mol. Imaging. 1 (5), 184-188 (2006).
- Johansson, M. K. Choosing reporter-quencher pairs for efficient quenching through formation of intramolecular dimers. Methods Mol. Biol. 335, 17-29 (2006).
- Sherry, A. D., Caravan, P., Lenkinski, R. E. A primer on gadolinium chemistry. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 30 (6), 1240-1248 (2009).
- Shakhverdov, T. A. A cross-relaxation mechanism of fluorescence quenching in complexes of lanthanide ions with organic ligands. Opt. Spectrosc. 95 (4), 571-580 (2003).
- Brittain, H. G. Submicrogram determination of lanthanides through quenching of calcein blue fluorescence. Anal. Chem. 59 (8), 1122-1125 (1987).

