免疫组化检测异常朊蛋白
Summary
使用免疫组织化学方案对异常朊蛋白进行免疫标记需要特定的样品和抗PrP抗体制备方法。本协议描述了表位去掩膜的关键步骤,以确保适当的PrP免疫标记并最大限度地减少非特异性背景染色。此外,这种方法在对朊病毒感染的组织进行免疫组织化学研究时考虑了生物安全措施。
Abstract
异常朊蛋白 (PrPSc) 是细胞朊蛋白的疾病相关亚型,也是传染性海绵状脑病 (TSE) 的诊断标志物。这些神经退行性疾病影响人类和几种动物物种,包括搔痒症、人畜共患牛海绵状脑病 (BSE)、宫颈慢性消耗性疾病 (CWD) 和新发现的骆驼朊病毒病 (CPD)。TSE的诊断依赖于通过对脑组织(即脑干)应用免疫组织化学(IHC)和西方免疫印迹法(WB)对PrPSc 进行免疫检测。IHC是一种广泛使用的方法,它使用一抗(单克隆或多克隆)来对抗组织切片细胞中的目标抗原。抗体-抗原结合可以通过颜色反应来可视化,该颜色反应仍局限于抗体靶向的组织或细胞区域。因此,在朊病毒疾病中,与其他研究领域一样,免疫组织化学技术不仅用于诊断目的,还用于发病机制研究。此类研究涉及从先前描述的模式和类型中检测PrPSc 模式和类型,以鉴定新的朊病毒菌株。由于疯牛病可以感染人类,建议使用生物安全实验室3级(BSL-3)设施和/或实践来处理TSE监测中包含的牛,小反刍动物和宫颈样本。此外,建议尽可能使用密闭和朊病毒专用设备,以限制污染。PrPSc IHC程序包括甲酸表位去掩蔽步骤,也作为朊病毒灭活措施,因为该技术中使用的福尔马林固定和石蜡包埋组织仍然具有传染性。在解释结果时,必须注意区分非特异性免疫标记和靶标标记。为此,重要的是要识别在已知的TSE阴性对照动物中获得的免疫标记伪影,以区分这些伪影与特定的PrPSc 免疫标记类型,其可以在TSE菌株,宿主物种和 prnp 基因型之间变化,本文进一步描述。
Introduction
根据朊病毒假说,异常亚型(PrPSc)是传染性海绵状脑病(TSE)中感染因子的主要或唯一成分。TSE 的诊断确认依赖于通过应用脑组织的免疫组织化学 (IHC) 方案和/或蛋白质免疫印迹法 (WB) 对 PrPSc 进行免疫检测1。
IHC是一种采用单克隆抗体或在某些情况下使用多克隆抗体(作为一抗)作为对位于组织切片细胞中的特定目标抗原进行免疫染色的第一步的方法。然后使用针对一抗的二抗观察任何有效的一抗-抗原结合。这些二抗与辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)或碱性磷酸酶(AP))偶联。然后通过向这些酶添加底物来实现可视化,产生位于一抗与靶抗原结合的区域的不溶性颜色产物。改进的可视化可以通过复染来实现,其中染料用于在免疫标记和非免疫标记的组织之间产生对比2。
对于使用福尔马林固定石蜡包埋组织 (FFPE) 的 IHC,福尔马林固定可能会由于甲醛交联以及石蜡包埋过程中的加热和脱水而使一抗的有效性失效。这些改变蛋白质的构象,破坏、变性或掩盖表位,从而减少或取消其检测3。因此,这需要抗原修复(AR)。AR技术破坏抗原分子中与甲醛相关的化学基团交联,从而恢复或揭示原始的抗原 – 蛋白质构象。这导致恢复抗体-抗原(表位)亲和力以进行免疫标记。AR的最终疗效取决于靶向抗原和/或一抗的质量2。
热诱导抗原(表位)修复(HIER)是AR3 的一个程序,常规用于PrPScIHC 检测,如本文所述。IHC 对于诊断至关重要,在研究实验室中用于确定病理相关抗原的组织分布。它广泛用于诊断和研究癌症、神经科学和传染病4 等。对于TSEs,IHC在诊断和研究中起着重要作用,以确认和研究PrPSc 在自然宿主和实验模型中的分布。IHC有助于朊病毒发病机制研究和PrPSc 沉积类型和模式的分析,即在神经组织中5中,以检测与常规描述的感染的偏差并识别推定的新朊病毒株。
由于牛海绵状脑病(BSE)的朊病毒可以感染人类,因此涉及BSE工作的某些实验室方案可能需要使用BSL-3设施和实践6。这些措施包括使用密封的二级容器在研究所和实验室内运输潜在的BSE感染组织样本。它还包括尽可能为疯牛病研究和分析指定遏制区域和朊病毒专用设备。这样做是为了防止工作区域以外的污染,并提供一个密闭的空间,因为净化程序变得必要。
因此,INIAV 病理学实验室遵循推荐的生物安全 3 级 (BSL-3) 设施和实践6 ,以管理与 TSE 监测相关的牛、小反刍动物和子宫颈的潜在朊病毒感染组织样本。
TSE诊断或研究程序中包含的福尔马林固定和石蜡包埋组织,特别是在中枢神经系统中,可能具有潜在的传染性。因此,在组织处理之前,必须用甲酸处理这些固定组织,以降低朊病毒(如果存在)的感染性。这是通过将固定的,修剪的组织(约2-4毫米厚)放置在处理盒中来完成的。然后将盒浸入98%甲酸中(1小时)。浸泡后,将带有组织的盒在流动的自来水中洗涤30分钟,并在进一步处理之前返回固定剂。如果在处理前未处理组织切片,则在组织学染色之前,必须将切片后的切片浸入未稀释的甲酸中至少5分钟7。PrPSc 的IHC方案包括常规的甲酸表位去掩蔽步骤,也用于灭活朊病毒7。在这些朊病毒灭活步骤之后,可以使用标准的BSL-2实践在BSL-2下处理所得的固定组织。
TSE监测中包含的任何动物TSE诊断的最低组织采样要求是收集脑干(在obex水平)。此外,为了检测非典型疯牛病和搔痒症,建议还应收集部分小脑1,8。对于CWD诊断,应检测脑干(obex)和咽后淋巴结,因为PrPSc可以在淋巴组织中检测到,而在obex9中没有检测到PrPSc,由Machado等人审查10。
脑干的obex部分包括诊断性TSE靶位点,即迷走神经背侧核(DVN)、孤立束核(STN)和三叉神经的脊髓束核(V)。这些区域始终呈现双侧PrPSc 积累,即使在疯牛病和经典搔痒症的早期阶段也是如此。在晚期 TSE 的临床病例中,脑干内的所有灰质区域都显示出广泛的 PrPSc 分布11。
在切片和处理之前,对脑样本进行评估(图1),以确定自溶水平和是否存在任何可能损害样本适用于基于IHC的确认性诊断的组织损伤8。为了验证制备方案和分析结果的完整性,将TSE阳性和阴性组织样品作为对照包括在内,并在每次测定中从测试用例制备组织。
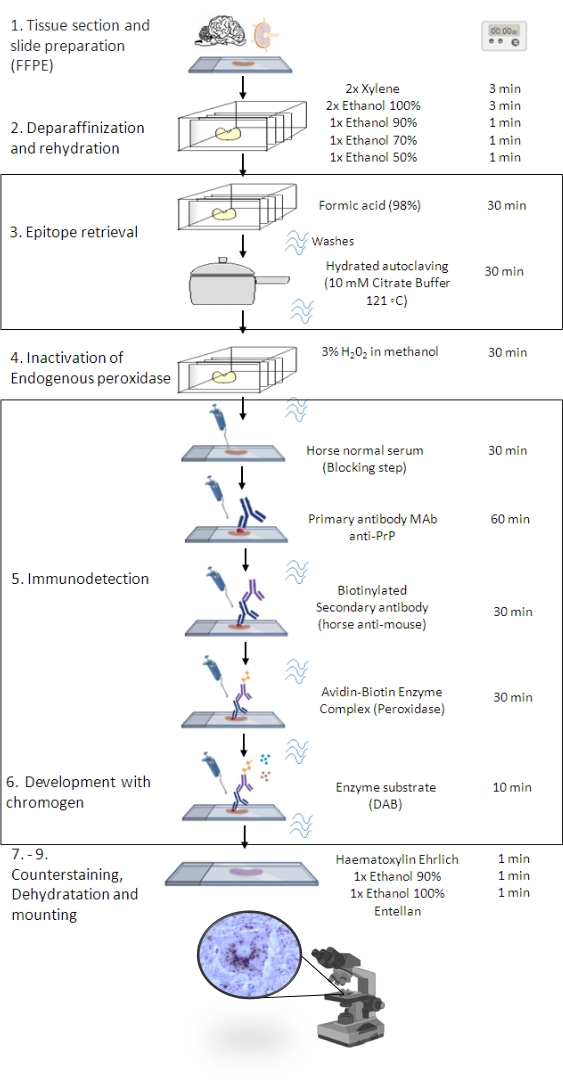
图1:PrPSc免疫 接种程序。 表示显示从组织切片脱蜡到最终免疫染色和检测的 PrPSc IHC 程序的分步顺序(FFPE – 福尔马林固定石蜡包埋;Mab – 单克隆抗体;DAB – 3,3′ 二氨基联苯胺)。这个数字是在 BioRender.com 年创建的。 请点击此处查看此图的大图。
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
TSE是潜在的人畜共患疾病。1986年英国出现疯牛病后,葡萄牙成为该病发病率较高的欧盟成员国之一14,15。为了控制这种疾病,已经出现的其他TSE(经典和非典型搔痒症,疯牛病变体,以及目前对宫颈慢性消耗性疾病的监测),食品和兽医总局(DGAV)和国家农业和兽医研究所(IP)开发了监测机制,该研究所作为TSE国家兽医实验室进行TSE诊断。该实验室…
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
本文由FCT(科学和技术基金会)支持的POCI-01-0145-FEDER-029947项目“葡萄牙的慢性消耗性疾病风险评估”资助 – FEDER-Balcão2020。此外,研究单位CECAV的作者在UIDB / CVT / 0772 / 2020项目下获得了FCT的资助.我们感谢美国农业部西部区域研究中心研究主任(退休)Bruce C. Campbell的帮助。
Materials
| Absolute ethanol | Labchem | LB0507-9010 | Undituled |
| Diluted 90%, 70% and 50% in distilled water | |||
| Avidin-biotin complex and peroxidase Vectastain Elite ABC kit Peroxidase |
Vector Laboratories | PK-6100 | Prepare and gently mix 30 min before use according to kit instructions. Do not mix after standing. |
| Biotinylated secondary antibody (Horse anti-mouse IgG H+L) | Vector Laboratories | BA-2000-1.5 | Dilute at 1/200 in TBS with 10% horse normal serum. Prepare the volume required depending on the number of sections. |
| Chromogen Diaminobenzidine- DAB, substrate kit, Peroxidase | Vector Laboratories | SK-4100 | Prepare before use according to kit instructions. Use 400 µL of solution per section. |
| DakoCytomation Pascal pressure chamber | DAKO | S2800 | |
| Ehrlich’s Hematoxylin: | |||
| Hematoxylin | Merck | 115938 | Dissolve 2 g of hematoxylin in 100 mL of absolute ethanol. Add 100 mL of distilled water, 10 mL of glacial acetic acid and 15 g of potassium alum with constant stirring. Add 100 mL of glycerin. The natural oxidation process takes 2 months, before use. |
| Absolute ethanol | Labchem | LB0507-9010 | |
| Glacial acetic acid | Merck | 101830 | |
| Potassium alum | Merck | 1.01047.1000 | |
| Glycerin | Merck | 1.04091.1000 | |
| Endogenous Peroxidase Block solution (3% concentration H2O2): | 40 mL Hydrogen peroxide (30% w/w) in 360 mL Methanol. Prepare before use |
||
| Hydrogen peroxide (30% w/w) | Scharlau | HI0136 | |
| Methanol | Sigma Aldrich | 322415-2L | |
| Formic acid 98% | Merck | 1.00264.1000 | Undiluted |
| Microtome | Shandon-AS325 | Microtome | Shandon-AS325 |
| Mounting medium Entellan | Merck | 107960 | Ready- to- use. |
| Normal serum (20% ) block solution in TBS: Horse normal serum |
Gibco |
16050-122 |
Prepare final volume according to the number of sections in the assay (200 µL of solution per section). |
| Primary antibody anti-PrP Mouse MAb 2G11 | BIORAD | MCA2460 | PrP 146-R154R171182 Ovine including atypical scrapie, cervine, feline. Not suitable for bovine. According to the number of sections in the assay (200 µL of solution per section) and antibody dilution, prepare final volume in TBS supplemented with 10% of normal serum from the species the secondary antibody was raised in (horse normal serum) Usual antibody dilution: MAb 2G11 1/100 but working dilution should be established in every new batch to get the concentration to give the strongest labelling with lowest background. For storage, freeze aliquot volumes of a minimum of 10 μL into sterile microtubes. Defrost and use one aliquot at a time. |
| Primary antibody anti-PrP Mouse MAb 12F10 | Cayman Chemical Company | 189710 | PrP142-160 Bovine, not suitable for ovine Usual antibody dilution: 1/200 but working dilution should also be established. Prepare as MAb 2G11 |
| Shandon CoverplateTM chamber | Thermo Scientific | 72110017 | |
| Shandon Sequenza® Immunstaining center | Thermo Scientific | 73300001 | |
| Shandon Sequenza® Immunstaining slide rack | Thermo Scientific | 73310017 | |
| Solution Citrate Buffer (10 mM pH 6.1): | 2.55 g Tri-sodium citrate dihydrate and 0.255 g Citric acid in one litre purified water. Adjust pH of working solution to 6.1 using 10 mM citric acid solution (1.05 g citric acid in 500 mL purified water) Prepare on assay day. |
||
| Tri-sodium citrate dihydrate | Sigma-aldrich | S4641-500G | |
| Citric acid | Sigma Aldrich | C0759 | |
| Staining jar and basket | Deltalab | 19360 | |
| 19361 | |||
| Superfrost Plus microscope slides | VWR | 631-0108 | |
| Tris-Buffered Saline solution (TBS) (50 mM TRIZMA BASE; 0.8% NaCI; pH 7.6): | 10xTBS (stock solution 0.5 M TRIZMA BASE; 8% NaCI; pH 7.6): TRIZMA BASE 60,57 g and NaCl 80 g in 800 mL purified water. Adjust pH of stock solution using Hydrochloric acid 37% and final volume to one litre with purified water (keep 5± 3 °C until 2 months) Dilute TBS stock solution 1/10 on assay day. |
||
| TRIZMA BASE | Sigma Aldrich | T6066-1KG | |
| Sodium Chloride (NaCl) | Merck | 106404 | |
| Xylene | Panreac Applied Chem ITW reagents | 251769 | Undiluted |
References
- . WOAH, Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals Online Access. Chapter 3.4.5.-Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (Version May 2021) and Chapter 3.8.11. – Scrapie (Version May 2022) Available from: https://www.woah.org/en/what-we-do/standards/codes-and-manuals/terrestrial-manual-online-access/ (2022)
- Ramos-Vara, J. A. Principles and methods of immunohistochemistry. Methods in Molecular Biology. 1641, 115-128 (2017).
- Krenacs, L., Krenacs, T., Stelkovics, E., Raffeld, M., Oliver, C., Jamur, M. Heat-Induced antigen retrieval for immunohistochemical reactions in routinely processed paraffin sections. Immunocytochemical Methods and Protocols. Methods in Molecular Biology. 588, 103-119 (2010).
- Duraiyan, J., Govindarajan, R., Kaliyappan, K., Palanisamy, M. Applications of immunohistochemistry). Journal Pharmacy Bioallied Sciences. 4, 307-309 (2012).
- Orge, L., et al. Neuropathology of Animal Prion Diseases. Biomolecules. 11 (3), 466 (2021).
- . Biosafety in Microbiological and Biomedical Laboratories. 6th Edition Revised June 2020 Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/labs/pdf/SF_19_308133-A_BMBL6_00-BOOK-WEB-final-3.pdf (2022)
- APHA. Fixation, tissue processing, histology and immunohistochemistry procedures for diagnosis of animal TSE (BSE, scrapie, atypical scrapie, CWD). Histo & IHC protocols for TSE diagnosis_Rev_Jan2019.pdf. TSEglobalNet – International Reference Laboratory for TSE. , (2022).
- Sample requirements for TSE testing and confirmation. Version 1.0. TSE EURL Available from: https://www.izsplv.it/it/istituto/212-centri-eccellenza/laboratori-internazionali-riferimento/422-eurl_tses.html (2019)
- TSE EU Reference Laboratory Guidelines for the detection of Chronic Wasting Disease in cervids. Version 1.0. TSE EURL Available from: https://www.izsplv.it/it/istituto/212-centri-eccellenza/laboratori-internazionali-riferimento/422-eurl_tses.html (2019)
- Machado, C. N., et al. TSE Monitoring in Wildlife Epidemiology, Transmission, Diagnosis, Genetics and Control. Wildlife Population Monitoring. IntechOpen. , (2019).
- APHA. Neuropathology: Confirmatory diagnosis of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) in cattle and small ruminants. Confirmatory (Histo & IHC) diagnostic criteria Rev_Jan2019.pdf. TSEglobalNet – International Reference Laboratory for TSE. , (2019).
- Ryder, S. J., Spencer, Y. I., Bellerby, P. J., March, S. A. Immunohistochemical detection of PrP in the medulla oblongata of sheep: The spectrum of staining in normal and scrapie-affected sheep. The Veterinary Record. 148 (1), 7-13 (2001).
- Simmons, M. M., et al. Experimental classical bovine spongiform encephalopathy: definition and progression of neural PrP immunolabeling in relation to diagnosis and disease controls. Veterinary Pathology. 48 (5), 948-963 (2011).
- Orge, L., et al. Identification of H-type BSE in Portugal. Prion. 9 (1), 22-28 (2015).
- Orge, L., Simas, J. P., Fernandes, A. C., Ramos, M., Galo, A. Similarity of the lesion profile of BSE in Portuguese cattle to that described in British cattle. Veterinary Record. 147 (17), 486-488 (2000).
- Pires, M. A., Travassos, F. S., Gärtner, F. Atlas of veterinary pathology. Biopathology. Lidel VII. 195 (6), 179-180 (2004).
- Pires, M. A., et al. Immunology protocols, didactic series. Applied Sciences. , 357 (2010).

